Paheding Sidike
Trends in deep learning for medical hyperspectral image analysis
Nov 27, 2020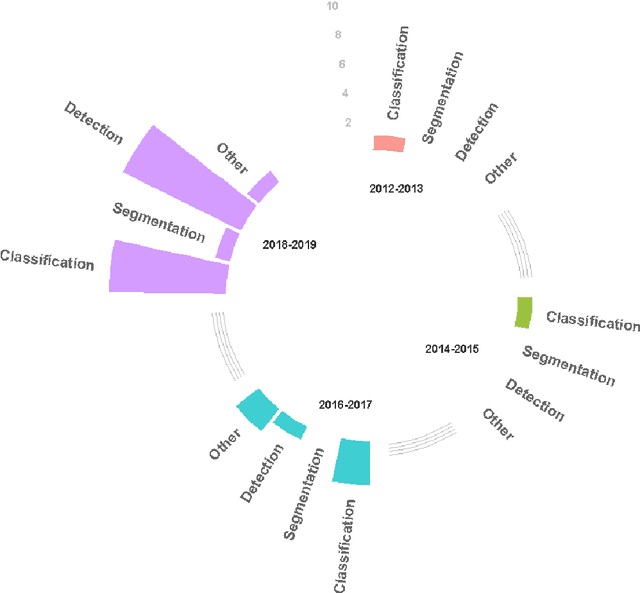
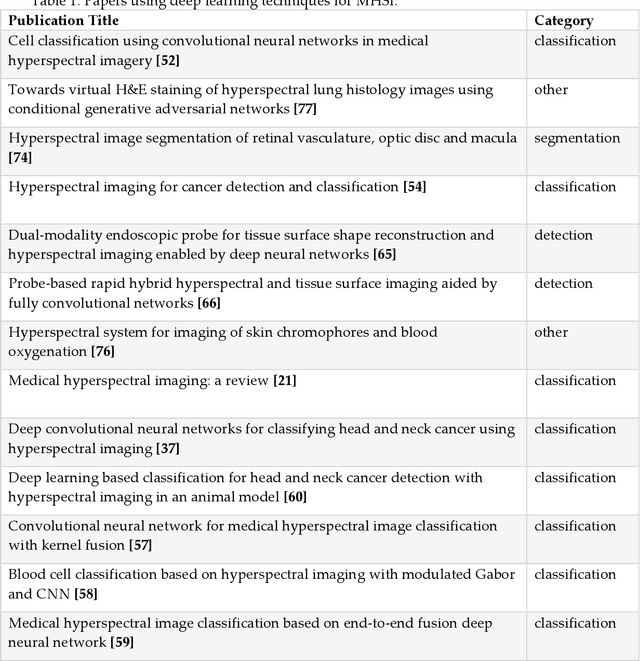
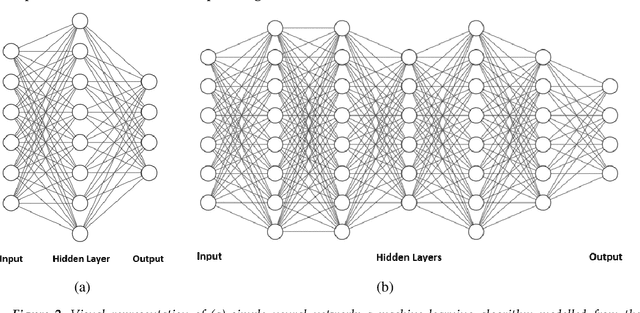
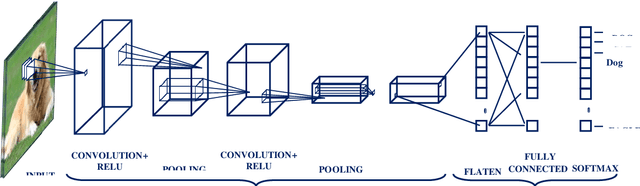
Abstract:Deep learning algorithms have seen acute growth of interest in their applications throughout several fields of interest in the last decade, with medical hyperspectral imaging being a particularly promising domain. So far, to the best of our knowledge, there is no review paper that discusses the implementation of deep learning for medical hyperspectral imaging, which is what this review paper aims to accomplish by examining publications that currently utilize deep learning to perform effective analysis of medical hyperspectral imagery. This paper discusses deep learning concepts that are relevant and applicable to medical hyperspectral imaging analysis, several of which have been implemented since the boom in deep learning. This will comprise of reviewing the use of deep learning for classification, segmentation, and detection in order to investigate the analysis of medical hyperspectral imaging. Lastly, we discuss the current and future challenges pertaining to this discipline and the possible efforts to overcome such trials.
U-Net and its variants for medical image segmentation: theory and applications
Nov 02, 2020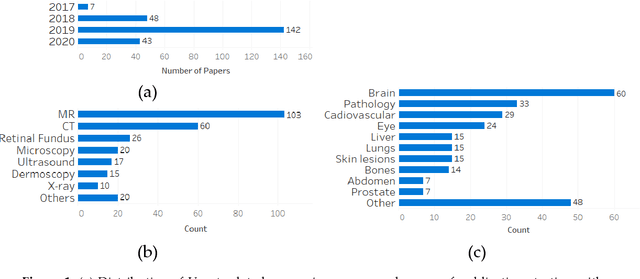

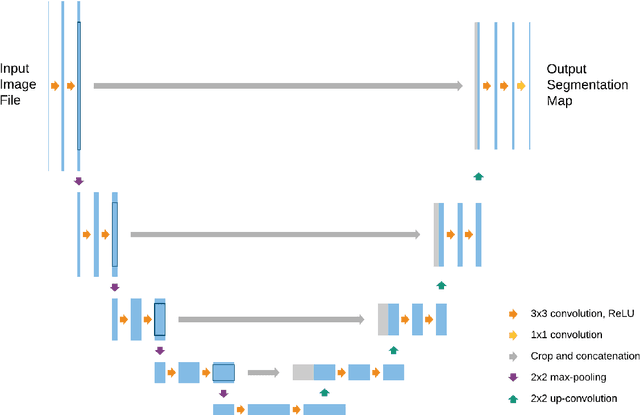
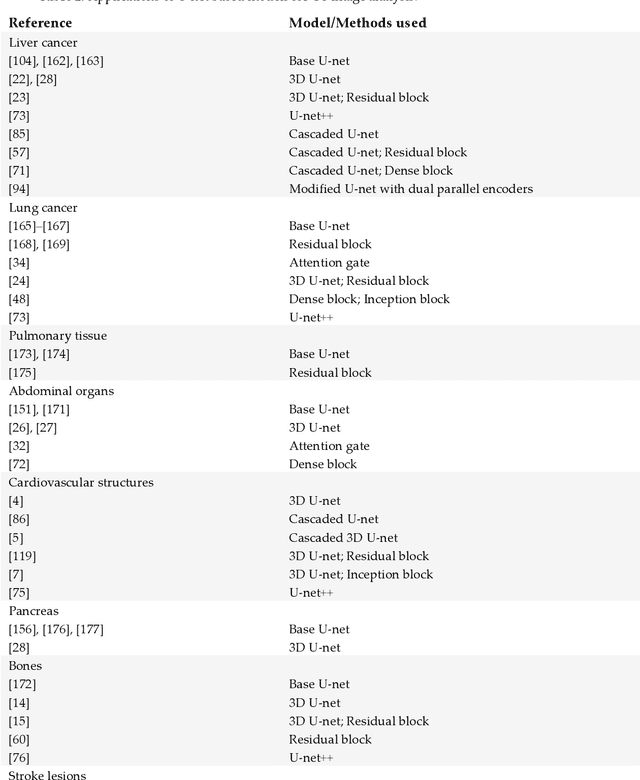
Abstract:U-net is an image segmentation technique developed primarily for medical image analysis that can precisely segment images using a scarce amount of training data. These traits provide U-net with a very high utility within the medical imaging community and have resulted in extensive adoption of U-net as the primary tool for segmentation tasks in medical imaging. The success of U-net is evident in its widespread use in all major image modalities from CT scans and MRI to X-rays and microscopy. Furthermore, while U-net is largely a segmentation tool, there have been instances of the use of U-net in other applications. As the potential of U-net is still increasing, in this review we look at the various developments that have been made in the U-net architecture and provide observations on recent trends. We examine the various innovations that have been made in deep learning and discuss how these tools facilitate U-net. Furthermore, we look at image modalities and application areas where U-net has been applied.
The History Began from AlexNet: A Comprehensive Survey on Deep Learning Approaches
Sep 12, 2018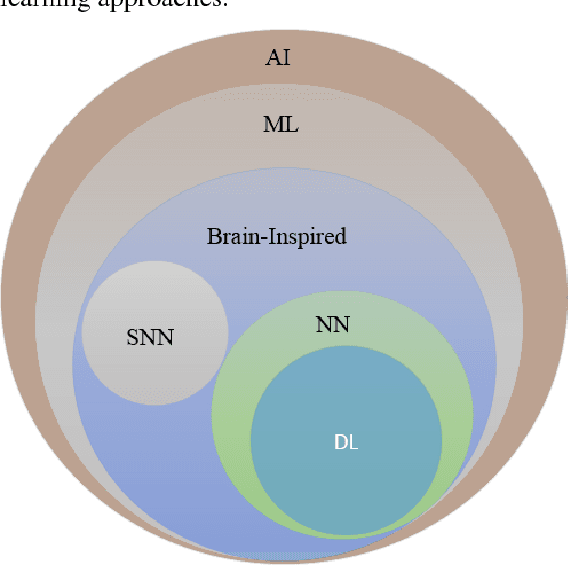
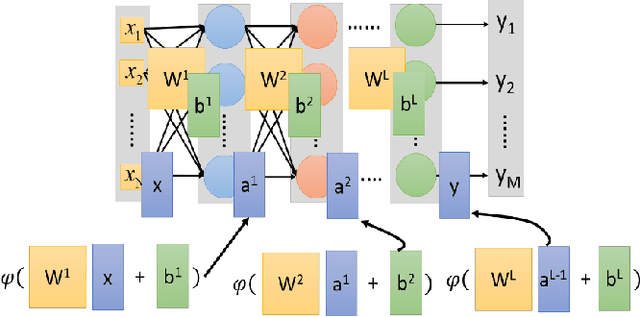
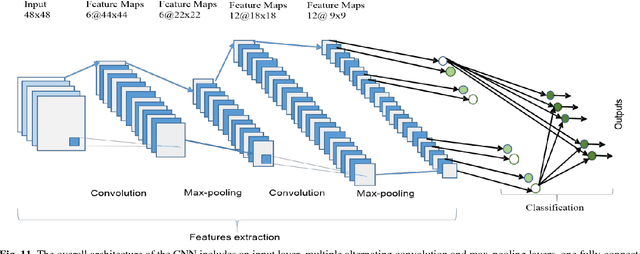
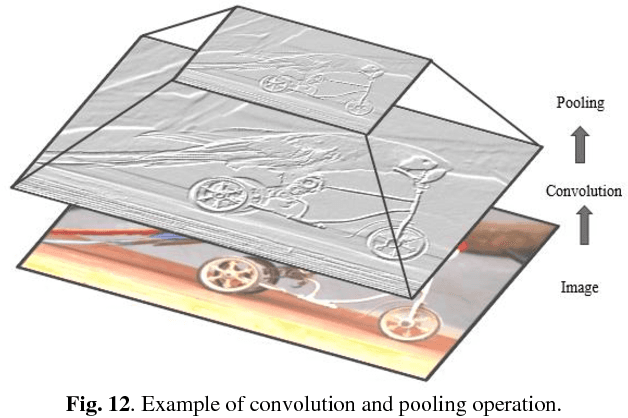
Abstract:Deep learning has demonstrated tremendous success in variety of application domains in the past few years. This new field of machine learning has been growing rapidly and applied in most of the application domains with some new modalities of applications, which helps to open new opportunity. There are different methods have been proposed on different category of learning approaches, which includes supervised, semi-supervised and un-supervised learning. The experimental results show state-of-the-art performance of deep learning over traditional machine learning approaches in the field of Image Processing, Computer Vision, Speech Recognition, Machine Translation, Art, Medical imaging, Medical information processing, Robotics and control, Bio-informatics, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Cyber security, and many more. This report presents a brief survey on development of DL approaches, including Deep Neural Network (DNN), Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) including Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Units (GRU), Auto-Encoder (AE), Deep Belief Network (DBN), Generative Adversarial Network (GAN), and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL). In addition, we have included recent development of proposed advanced variant DL techniques based on the mentioned DL approaches. Furthermore, DL approaches have explored and evaluated in different application domains are also included in this survey. We have also comprised recently developed frameworks, SDKs, and benchmark datasets that are used for implementing and evaluating deep learning approaches. There are some surveys have published on Deep Learning in Neural Networks [1, 38] and a survey on RL [234]. However, those papers have not discussed the individual advanced techniques for training large scale deep learning models and the recently developed method of generative models [1].
Handwritten Bangla Digit Recognition Using Deep Learning
May 07, 2017

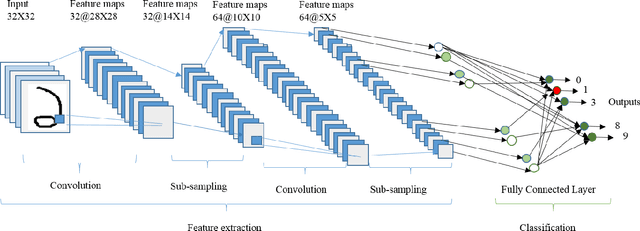

Abstract:In spite of the advances in pattern recognition technology, Handwritten Bangla Character Recognition (HBCR) (such as alpha-numeric and special characters) remains largely unsolved due to the presence of many perplexing characters and excessive cursive in Bangla handwriting. Even the best existing recognizers do not lead to satisfactory performance for practical applications. To improve the performance of Handwritten Bangla Digit Recognition (HBDR), we herein present a new approach based on deep neural networks which have recently shown excellent performance in many pattern recognition and machine learning applications, but has not been throughly attempted for HBDR. We introduce Bangla digit recognition techniques based on Deep Belief Network (DBN), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), CNN with dropout, CNN with dropout and Gaussian filters, and CNN with dropout and Gabor filters. These networks have the advantage of extracting and using feature information, improving the recognition of two dimensional shapes with a high degree of invariance to translation, scaling and other pattern distortions. We systematically evaluated the performance of our method on publicly available Bangla numeral image database named CMATERdb 3.1.1. From experiments, we achieved 98.78% recognition rate using the proposed method: CNN with Gabor features and dropout, which outperforms the state-of-the-art algorithms for HDBR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge