Pablo Ortiz
SiamTST: A Novel Representation Learning Framework for Enhanced Multivariate Time Series Forecasting applied to Telco Networks
Jul 02, 2024



Abstract:We introduce SiamTST, a novel representation learning framework for multivariate time series. SiamTST integrates a Siamese network with attention, channel-independent patching, and normalization techniques to achieve superior performance. Evaluated on a real-world industrial telecommunication dataset, SiamTST demonstrates significant improvements in forecasting accuracy over existing methods. Notably, a simple linear network also shows competitive performance, achieving the second-best results, just behind SiamTST. The code is available at https://github.com/simenkristoff/SiamTST.
The Norwegian Parliamentary Speech Corpus
Jan 26, 2022
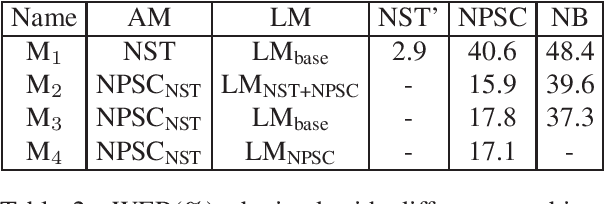
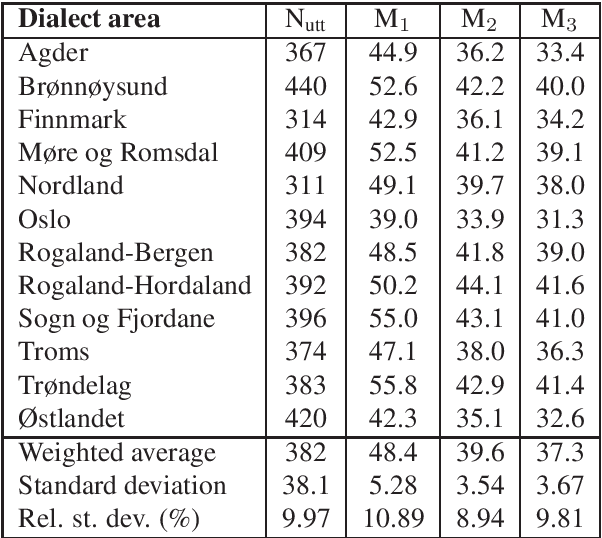
Abstract:The Norwegian Parliamentary Speech Corpus (NPSC) is a speech dataset with recordings of meetings from Stortinget, the Norwegian parliament. It is the first, publicly available dataset containing unscripted, Norwegian speech designed for training of automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. The recordings are manually transcribed and annotated with language codes and speakers, and there are detailed metadata about the speakers. The transcriptions exist in both normalized and non-normalized form, and non-standardized words are explicitly marked and annotated with standardized equivalents. To test the usefulness of this dataset, we have compared an ASR system trained on the NPSC with a baseline system trained on only manuscript-read speech. These systems were tested on an independent dataset containing spontaneous, dialectal speech. The NPSC-trained system performed significantly better, with a 22.9% relative improvement in word error rate (WER). Moreover, training on the NPSC is shown to have a "democratizing" effect in terms of dialects, as improvements are generally larger for dialects with higher WER from the baseline system.
Disambiguation-BERT for N-best Rescoring in Low-Resource Conversational ASR
Oct 05, 2021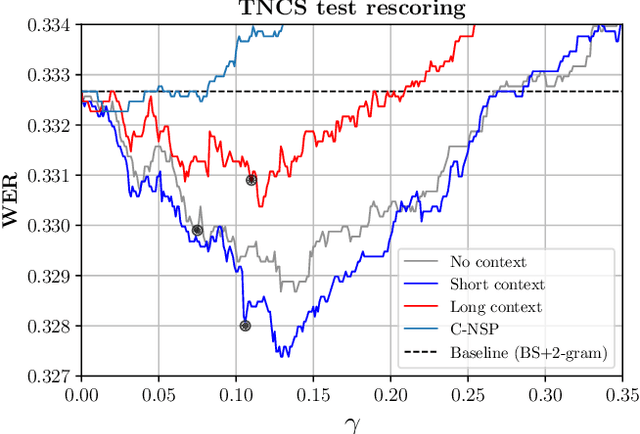
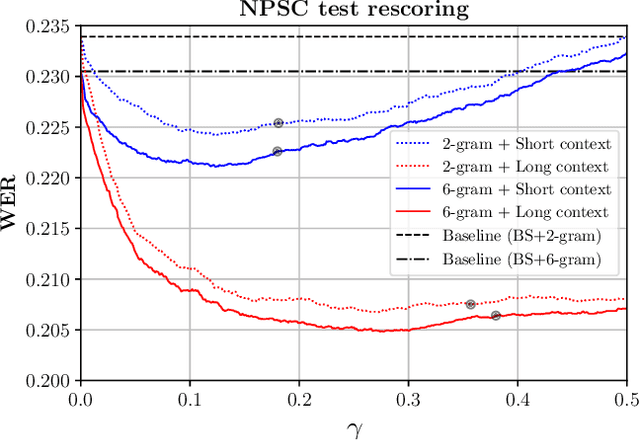
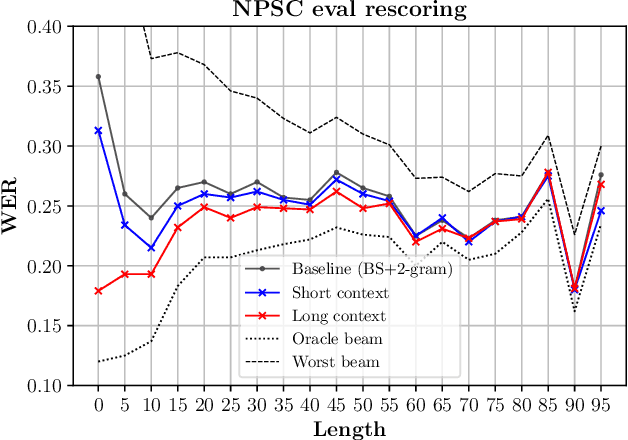
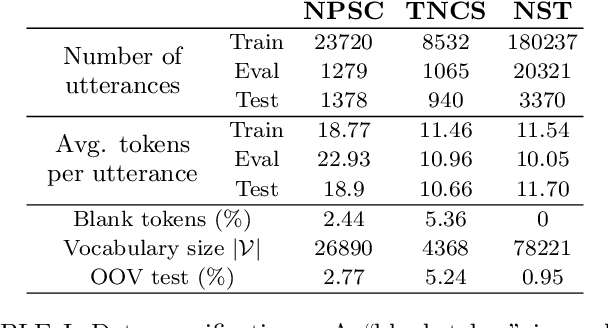
Abstract:We study the inclusion of past conversational context through BERT language models into a CTC-based Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system via N-best rescoring. We introduce a data-efficient strategy to fine-tune BERT on transcript disambiguation without external data. Our results show word error rate recoveries up to 37.2% with context-augmented BERT rescoring. We do this in low-resource data domains, both in language (Norwegian), tone (spontaneous, conversational), and topics (parliament proceedings and customer service phone calls). We show how the nature of the data greatly affects the performance of context-augmented N-best rescoring.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge