Oren Shrout
Concept Retrieval -- What and How?
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:A concept may reflect either a concrete or abstract idea. Given an input image, this paper seeks to retrieve other images that share its central concepts, capturing aspects of the underlying narrative. This goes beyond conventional retrieval or clustering methods, which emphasize visual or semantic similarity. We formally define the problem, outline key requirements, and introduce appropriate evaluation metrics. We propose a novel approach grounded in two key observations: (1) While each neighbor in the embedding space typically shares at least one concept with the query, not all neighbors necessarily share the same concept with one another. (2) Modeling this neighborhood with a bimodal Gaussian distribution uncovers meaningful structure that facilitates concept identification. Qualitative, quantitative, and human evaluations confirm the effectiveness of our approach. See the package on PyPI: https://pypi.org/project/coret/
SFMNet: Sparse Focal Modulation for 3D Object Detection
Mar 15, 2025



Abstract:We propose SFMNet, a novel 3D sparse detector that combines the efficiency of sparse convolutions with the ability to model long-range dependencies. While traditional sparse convolution techniques efficiently capture local structures, they struggle with modeling long-range relationships. However, capturing long-range dependencies is fundamental for 3D object detection. In contrast, transformers are designed to capture these long-range dependencies through attention mechanisms. But, they come with high computational costs, due to their quadratic query-key-value interactions. Furthermore, directly applying attention to non-empty voxels is inefficient due to the sparse nature of 3D scenes. Our SFMNet is built on a novel Sparse Focal Modulation (SFM) module, which integrates short- and long-range contexts with linear complexity by leveraging a new hierarchical sparse convolution design. This approach enables SFMNet to achieve high detection performance with improved efficiency, making it well-suited for large-scale LiDAR scenes. We show that our detector achieves state-of-the-art performance on autonomous driving datasets.
PatchContrast: Self-Supervised Pre-training for 3D Object Detection
Aug 14, 2023



Abstract:Accurately detecting objects in the environment is a key challenge for autonomous vehicles. However, obtaining annotated data for detection is expensive and time-consuming. We introduce PatchContrast, a novel self-supervised point cloud pre-training framework for 3D object detection. We propose to utilize two levels of abstraction to learn discriminative representation from unlabeled data: proposal-level and patch-level. The proposal-level aims at localizing objects in relation to their surroundings, whereas the patch-level adds information about the internal connections between the object's components, hence distinguishing between different objects based on their individual components. We demonstrate how these levels can be integrated into self-supervised pre-training for various backbones to enhance the downstream 3D detection task. We show that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art models on three commonly-used 3D detection datasets.
3DInAction: Understanding Human Actions in 3D Point Clouds
Mar 11, 2023Abstract:We propose a novel method for 3D point cloud action recognition. Understanding human actions in RGB videos has been widely studied in recent years, however, its 3D point cloud counterpart remains under-explored. This is mostly due to the inherent limitation of the point cloud data modality -- lack of structure, permutation invariance, and varying number of points -- which makes it difficult to learn a spatio-temporal representation. To address this limitation, we propose the 3DinAction pipeline that first estimates patches moving in time (t-patches) as a key building block, alongside a hierarchical architecture that learns an informative spatio-temporal representation. We show that our method achieves improved performance on existing datasets, including DFAUST and IKEA ASM.
GraVoS: Gradient based Voxel Selection for 3D Detection
Aug 18, 2022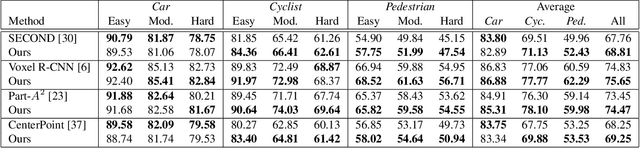
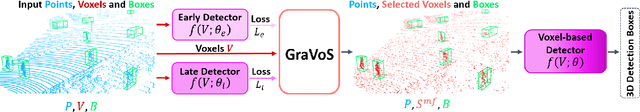
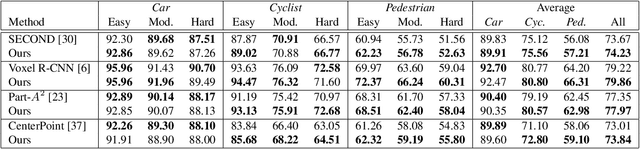
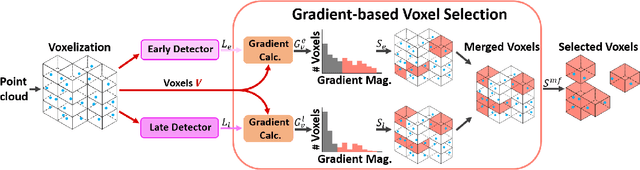
Abstract:3D object detection within large 3D scenes is challenging not only due to the sparse and irregular 3D point clouds, but also due to the extreme foreground-background imbalance in the scene and class imbalance. A common approach is to add ground-truth objects from other scenes. Differently, we propose to modify the scenes by removing elements (voxels), rather than adding ones. Our approach selects the "meaningful" voxels, in a manner that addresses both types dataset imbalance. The approach is general and can be applied to any voxel-based detector, yet the meaningfulness of a voxel is network-dependent. Our voxel selection is shown to improve the performance of several prominent 3D detection methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge