Oluwaseyi Onasami
Underwater Acoustic Communication Channel Modeling using Reservoir Computing
May 30, 2022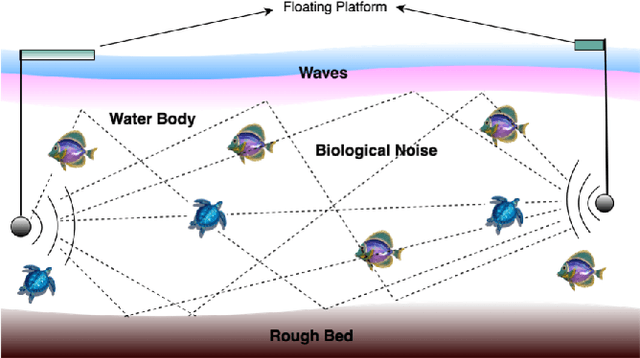
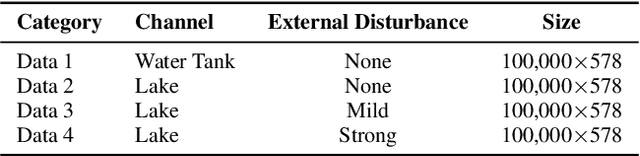
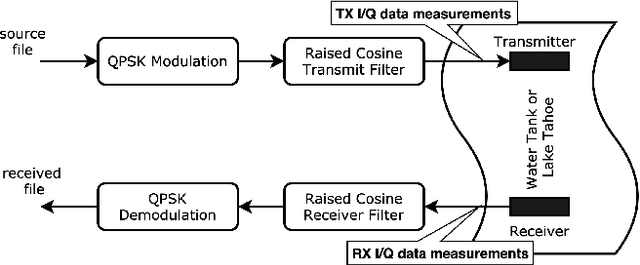
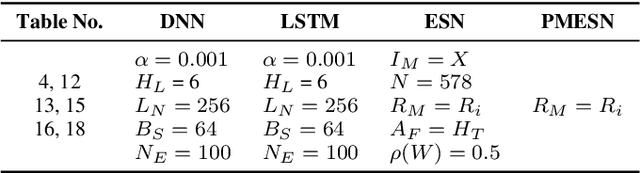
Abstract:Underwater acoustic (UWA) communications have been widely used but greatly impaired due to the complicated nature of the underwater environment. In order to improve UWA communications, modeling and understanding the UWA channel is indispensable. However, there exist many challenges due to the high uncertainties of the underwater environment and the lack of real-world measurement data. In this work, the capability of reservoir computing and deep learning has been explored for modeling the UWA communication channel accurately using real underwater data collected from a water tank with disturbance and from Lake Tahoe. We leverage the capability of reservoir computing for modeling dynamical systems and provided a data-driven approach to modeling the UWA channel using Echo State Network (ESN). In addition, the potential application of transfer learning to reservoir computing has been examined. Experimental results show that ESN is able to model chaotic UWA channels with better performance compared to popular deep learning models in terms of mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), specifically, ESN has outperformed deep neural network by 2% and as much as 40% in benign and chaotic UWA respectively.
Underwater Acoustic Communication Channel Modeling using Deep Learning
Jan 25, 2022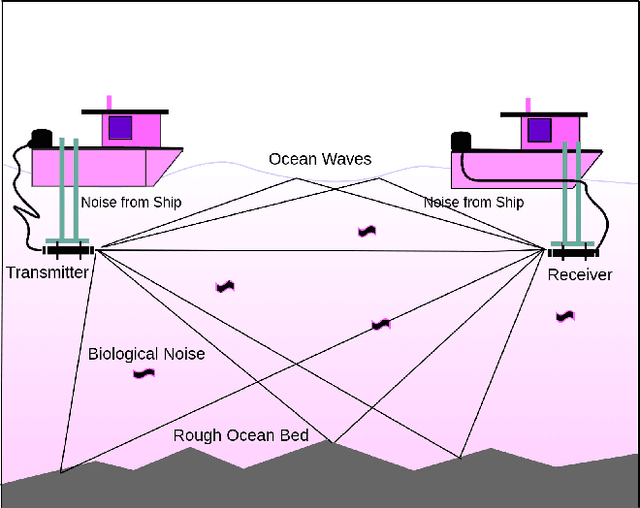
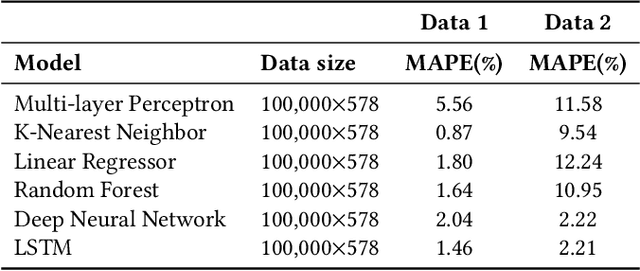

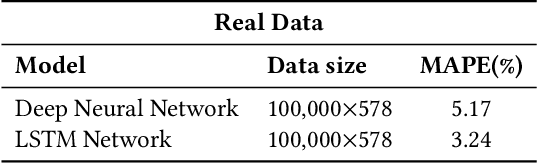
Abstract:With the recent increase in the number of underwater activities, having effective underwater communication systems has become increasingly important. Underwater acoustic communication has been widely used but greatly impaired due to the complicated nature of the underwater environment. In a bid to better understand the underwater acoustic channel so as to help in the design and improvement of underwater communication systems, attempts have been made to model the underwater acoustic channel using mathematical equations and approximations under some assumptions. In this paper, we explore the capability of machine learning and deep learning methods to learn and accurately model the underwater acoustic channel using real underwater data collected from a water tank with disturbance and from lake Tahoe. Specifically, Deep Neural Network (DNN) and Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) are applied to model the underwater acoustic channel. Experimental results show that these models are able to model the underwater acoustic communication channel well and that deep learning models, especially LSTM are better models in terms of mean absolute percentage error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge