Olivier Elshocht
GAD-NR: Graph Anomaly Detection via Neighborhood Reconstruction
Jun 07, 2023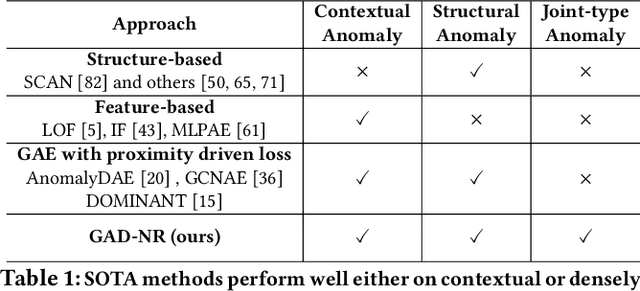


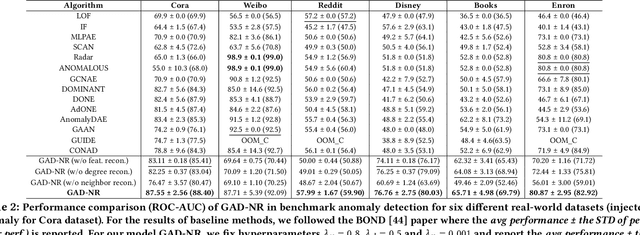
Abstract:Graph Anomaly Detection (GAD) is a technique used to identify abnormal nodes within graphs, finding applications in network security, fraud detection, social media spam detection, and various other domains. A common method for GAD is Graph Auto-Encoders (GAEs), which encode graph data into node representations and identify anomalies by assessing the reconstruction quality of the graphs based on these representations. However, existing GAE models are primarily optimized for direct link reconstruction, resulting in nodes connected in the graph being clustered in the latent space. As a result, they excel at detecting cluster-type structural anomalies but struggle with more complex structural anomalies that do not conform to clusters. To address this limitation, we propose a novel solution called GAD-NR, a new variant of GAE that incorporates neighborhood reconstruction for graph anomaly detection. GAD-NR aims to reconstruct the entire neighborhood of a node, encompassing the local structure, self-attributes, and neighbor attributes, based on the corresponding node representation. By comparing the neighborhood reconstruction loss between anomalous nodes and normal nodes, GAD-NR can effectively detect any anomalies. Extensive experimentation conducted on six real-world datasets validates the effectiveness of GAD-NR, showcasing significant improvements (by up to 30% in AUC) over state-of-the-art competitors. The source code for GAD-NR is openly available. Importantly, the comparative analysis reveals that the existing methods perform well only in detecting one or two types of anomalies out of the three types studied. In contrast, GAD-NR excels at detecting all three types of anomalies across the datasets, demonstrating its comprehensive anomaly detection capabilities.
Adversarial Attacks for Tabular Data: Application to Fraud Detection and Imbalanced Data
Jan 20, 2021



Abstract:Guaranteeing the security of transactional systems is a crucial priority of all institutions that process transactions, in order to protect their businesses against cyberattacks and fraudulent attempts. Adversarial attacks are novel techniques that, other than being proven to be effective to fool image classification models, can also be applied to tabular data. Adversarial attacks aim at producing adversarial examples, in other words, slightly modified inputs that induce the Artificial Intelligence (AI) system to return incorrect outputs that are advantageous for the attacker. In this paper we illustrate a novel approach to modify and adapt state-of-the-art algorithms to imbalanced tabular data, in the context of fraud detection. Experimental results show that the proposed modifications lead to a perfect attack success rate, obtaining adversarial examples that are also less perceptible when analyzed by humans. Moreover, when applied to a real-world production system, the proposed techniques shows the possibility of posing a serious threat to the robustness of advanced AI-based fraud detection procedures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge