Oliver Daniels-Koch
CoinRun: Solving Goal Misgeneralisation
Sep 28, 2023Abstract:Goal misgeneralisation is a key challenge in AI alignment -- the task of getting powerful Artificial Intelligences to align their goals with human intentions and human morality. In this paper, we show how the ACE (Algorithm for Concept Extrapolation) agent can solve one of the key standard challenges in goal misgeneralisation: the CoinRun challenge. It uses no new reward information in the new environment. This points to how autonomous agents could be trusted to act in human interests, even in novel and critical situations.
The Expertise Problem: Learning from Specialized Feedback
Nov 12, 2022Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) is a powerful technique for training agents to perform difficult-to-specify tasks. However, human feedback can be noisy, particularly when human teachers lack relevant knowledge or experience. Levels of expertise vary across teachers, and a given teacher may have differing levels of expertise for different components of a task. RLHF algorithms that learn from multiple teachers therefore face an expertise problem: the reliability of a given piece of feedback depends both on the teacher that it comes from and how specialized that teacher is on relevant components of the task. Existing state-of-the-art RLHF algorithms assume that all evaluations come from the same distribution, obscuring this inter- and intra-human variance, and preventing them from accounting for or taking advantage of variations in expertise. We formalize this problem, implement it as an extension of an existing RLHF benchmark, evaluate the performance of a state-of-the-art RLHF algorithm, and explore techniques to improve query and teacher selection. Our key contribution is to demonstrate and characterize the expertise problem, and to provide an open-source implementation for testing future solutions.
CULT: Continual Unsupervised Learning with Typicality-Based Environment Detection
Jul 17, 2022
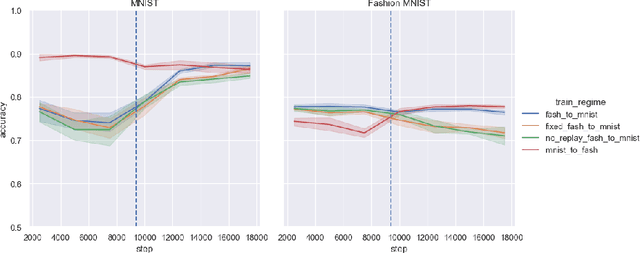

Abstract:We introduce CULT (Continual Unsupervised Representation Learning with Typicality-Based Environment Detection), a new algorithm for continual unsupervised learning with variational auto-encoders. CULT uses a simple typicality metric in the latent space of a VAE to detect distributional shifts in the environment, which is used in conjunction with generative replay and an auxiliary environmental classifier to limit catastrophic forgetting in unsupervised representation learning. In our experiments, CULT significantly outperforms baseline continual unsupervised learning approaches. Code for this paper can be found here: https://github.com/oliveradk/cult
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge