Olga Kellert
Evaluating Compositional Approaches for Focus and Sentiment Analysis
Aug 11, 2025

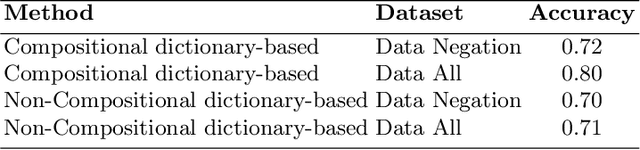

Abstract:This paper summarizes the results of evaluating a compositional approach for Focus Analysis (FA) in Linguistics and Sentiment Analysis (SA) in Natural Language Processing (NLP). While quantitative evaluations of compositional and non-compositional approaches in SA exist in NLP, similar quantitative evaluations are very rare in FA in Linguistics that deal with linguistic expressions representing focus or emphasis such as "it was John who left". We fill this gap in research by arguing that compositional rules in SA also apply to FA because FA and SA are closely related meaning that SA is part of FA. Our compositional approach in SA exploits basic syntactic rules such as rules of modification, coordination, and negation represented in the formalism of Universal Dependencies (UDs) in English and applied to words representing sentiments from sentiment dictionaries. Some of the advantages of our compositional analysis method for SA in contrast to non-compositional analysis methods are interpretability and explainability. We test the accuracy of our compositional approach and compare it with a non-compositional approach VADER that uses simple heuristic rules to deal with negation, coordination and modification. In contrast to previous related work that evaluates compositionality in SA on long reviews, this study uses more appropriate datasets to evaluate compositionality. In addition, we generalize the results of compositional approaches in SA to compositional approaches in FA.
Parsing the Switch: LLM-Based UD Annotation for Complex Code-Switched and Low-Resource Languages
Jun 08, 2025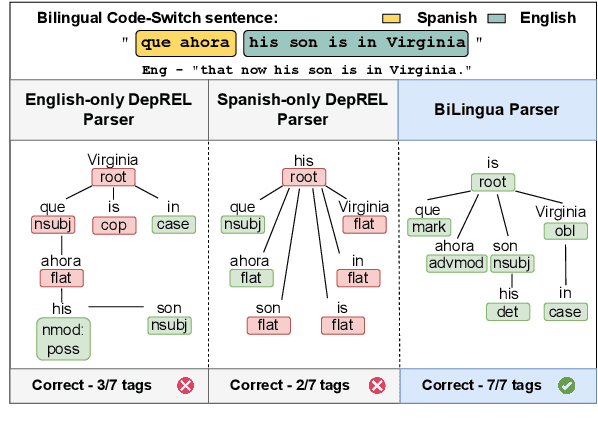
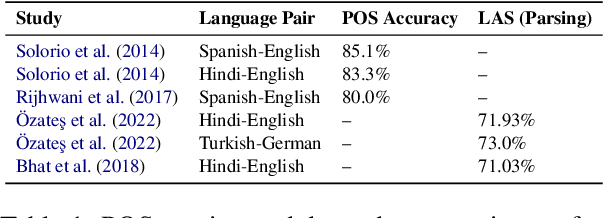
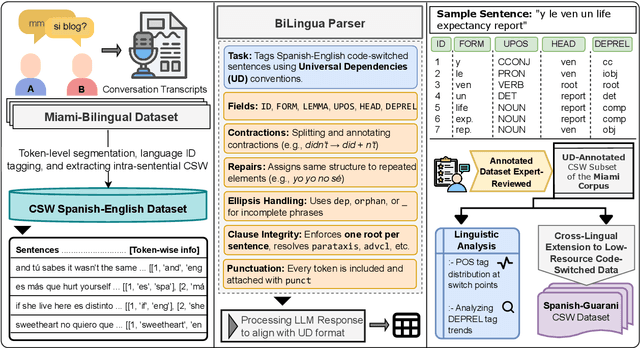
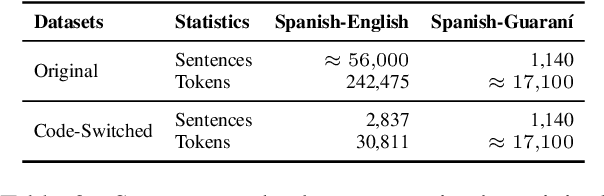
Abstract:Code-switching presents a complex challenge for syntactic analysis, especially in low-resource language settings where annotated data is scarce. While recent work has explored the use of large language models (LLMs) for sequence-level tagging, few approaches systematically investigate how well these models capture syntactic structure in code-switched contexts. Moreover, existing parsers trained on monolingual treebanks often fail to generalize to multilingual and mixed-language input. To address this gap, we introduce the BiLingua Parser, an LLM-based annotation pipeline designed to produce Universal Dependencies (UD) annotations for code-switched text. First, we develop a prompt-based framework for Spanish-English and Spanish-Guaran\'i data, combining few-shot LLM prompting with expert review. Second, we release two annotated datasets, including the first Spanish-Guaran\'i UD-parsed corpus. Third, we conduct a detailed syntactic analysis of switch points across language pairs and communicative contexts. Experimental results show that BiLingua Parser achieves up to 95.29% LAS after expert revision, significantly outperforming prior baselines and multilingual parsers. These results show that LLMs, when carefully guided, can serve as practical tools for bootstrapping syntactic resources in under-resourced, code-switched environments. Data and source code are available at https://github.com/N3mika/ParsingProject
Dancing in the syntax forest: fast, accurate and explainable sentiment analysis with SALSA
Jun 23, 2024Abstract:Sentiment analysis is a key technology for companies and institutions to gauge public opinion on products, services or events. However, for large-scale sentiment analysis to be accessible to entities with modest computational resources, it needs to be performed in a resource-efficient way. While some efficient sentiment analysis systems exist, they tend to apply shallow heuristics, which do not take into account syntactic phenomena that can radically change sentiment. Conversely, alternatives that take syntax into account are computationally expensive. The SALSA project, funded by the European Research Council under a Proof-of-Concept Grant, aims to leverage recently-developed fast syntactic parsing techniques to build sentiment analysis systems that are lightweight and efficient, while still providing accuracy and explainability through the explicit use of syntax. We intend our approaches to be the backbone of a working product of interest for SMEs to use in production.
A Syntax-Injected Approach for Faster and More Accurate Sentiment Analysis
Jun 21, 2024



Abstract:Sentiment Analysis (SA) is a crucial aspect of Natural Language Processing (NLP), addressing subjective assessments in textual content. Syntactic parsing is useful in SA because explicit syntactic information can improve accuracy while providing explainability, but it tends to be a computational bottleneck in practice due to the slowness of parsing algorithms. This paper addresses said bottleneck by using a SEquence Labeling Syntactic Parser (SELSP) to inject syntax into SA. By treating dependency parsing as a sequence labeling problem, we greatly enhance the speed of syntax-based SA. SELSP is trained and evaluated on a ternary polarity classification task, demonstrating its faster performance and better accuracy in polarity prediction tasks compared to conventional parsers like Stanza and to heuristic approaches that use shallow syntactic rules for SA like VADER. This increased speed and improved accuracy make SELSP particularly appealing to SA practitioners in both research and industry. In addition, we test several sentiment dictionaries on our SELSP to see which one improves the performance in polarity prediction tasks. Moreover, we compare the SELSP with Transformer-based models trained on a 5-label classification task. The results show that dictionaries that capture polarity judgment variation provide better results than dictionaries that ignore polarity judgment variation. Moreover, we show that SELSP is considerably faster than Transformer-based models in polarity prediction tasks.
Unveiling factors influencing judgment variation in Sentiment Analysis with Natural Language Processing and Statistics
May 20, 2024Abstract:TripAdvisor reviews and comparable data sources play an important role in many tasks in Natural Language Processing (NLP), providing a data basis for the identification and classification of subjective judgments, such as hotel or restaurant reviews, into positive or negative polarities. This study explores three important factors influencing variation in crowdsourced polarity judgments, focusing on TripAdvisor reviews in Spanish. Three hypotheses are tested: the role of Part Of Speech (POS), the impact of sentiment words such as "tasty", and the influence of neutral words like "ok" on judgment variation. The study's methodology employs one-word titles, demonstrating their efficacy in studying polarity variation of words. Statistical tests on mean equality are performed on word groups of our interest. The results of this study reveal that adjectives in one-word titles tend to result in lower judgment variation compared to other word types or POS. Sentiment words contribute to lower judgment variation as well, emphasizing the significance of sentiment words in research on polarity judgments, and neutral words are associated with higher judgment variation as expected. However, these effects cannot be always reproduced in longer titles, which suggests that longer titles do not represent the best data source for testing the ambiguity of single words due to the influence on word polarity by other words like negation in longer titles. This empirical investigation contributes valuable insights into the factors influencing polarity variation of words, providing a foundation for NLP practitioners that aim to capture and predict polarity judgments in Spanish and for researchers that aim to understand factors influencing judgment variation.
Experimenting with UD Adaptation of an Unsupervised Rule-based Approach for Sentiment Analysis of Mexican Tourist Texts
Sep 11, 2023Abstract:This paper summarizes the results of experimenting with Universal Dependencies (UD) adaptation of an Unsupervised, Compositional and Recursive (UCR) rule-based approach for Sentiment Analysis (SA) submitted to the Shared Task at Rest-Mex 2023 (Team Olga/LyS-SALSA) (within the IberLEF 2023 conference). By using basic syntactic rules such as rules of modification and negation applied on words from sentiment dictionaries, our approach exploits some advantages of an unsupervised method for SA: (1) interpretability and explainability of SA, (2) robustness across datasets, languages and domains and (3) usability by non-experts in NLP. We compare our approach with other unsupervised approaches of SA that in contrast to our UCR rule-based approach use simple heuristic rules to deal with negation and modification. Our results show a considerable improvement over these approaches. We discuss future improvements of our results by using modality features as another shifting rule of polarity and word disambiguation techniques to identify the right sentiment words.
Geolocation differences of language use in urban areas
Aug 01, 2021



Abstract:The explosion in the availability of natural language data in the era of social media has given rise to a host of applications such as sentiment analysis and opinion mining. Simultaneously, the growing availability of precise geolocation information is enabling visualization of global phenomena such as environmental changes and disease propagation. Opportunities for tracking spatial variations in language use, however, have largely been overlooked, especially on small spatial scales. Here we explore the use of Twitter data with precise geolocation information to resolve spatial variations in language use on an urban scale down to single city blocks. We identify several categories of language tokens likely to show distinctive patterns of use and develop quantitative methods to visualize the spatial distributions associated with these patterns. Our analysis concentrates on comparison of contrasting pairs of Tweet distributions from the same category, each defined by a set of tokens. Our work shows that analysis of small-scale variations can provide unique information on correlations between language use and social context which are highly valuable to a wide range of fields from linguistic science and commercial advertising to social services.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge