Nontawat Tritrong
LUSD: Localized Update Score Distillation for Text-Guided Image Editing
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:While diffusion models show promising results in image editing given a target prompt, achieving both prompt fidelity and background preservation remains difficult. Recent works have introduced score distillation techniques that leverage the rich generative prior of text-to-image diffusion models to solve this task without additional fine-tuning. However, these methods often struggle with tasks such as object insertion. Our investigation of these failures reveals significant variations in gradient magnitude and spatial distribution, making hyperparameter tuning highly input-specific or unsuccessful. To address this, we propose two simple yet effective modifications: attention-based spatial regularization and gradient filtering-normalization, both aimed at reducing these variations during gradient updates. Experimental results show our method outperforms state-of-the-art score distillation techniques in prompt fidelity, improving successful edits while preserving the background. Users also preferred our method over state-of-the-art techniques across three metrics, and by 58-64% overall.
DiFaReli: Diffusion Face Relighting
Apr 21, 2023



Abstract:We present a novel approach to single-view face relighting in the wild. Handling non-diffuse effects, such as global illumination or cast shadows, has long been a challenge in face relighting. Prior work often assumes Lambertian surfaces, simplified lighting models or involves estimating 3D shape, albedo, or a shadow map. This estimation, however, is error-prone and requires many training examples with lighting ground truth to generalize well. Our work bypasses the need for accurate estimation of intrinsic components and can be trained solely on 2D images without any light stage data, multi-view images, or lighting ground truth. Our key idea is to leverage a conditional diffusion implicit model (DDIM) for decoding a disentangled light encoding along with other encodings related to 3D shape and facial identity inferred from off-the-shelf estimators. We also propose a novel conditioning technique that eases the modeling of the complex interaction between light and geometry by using a rendered shading reference to spatially modulate the DDIM. We achieve state-of-the-art performance on standard benchmark Multi-PIE and can photorealistically relight in-the-wild images. Please visit our page: https://diffusion-face-relighting.github.io
Repurposing GANs for One-shot Semantic Part Segmentation
Mar 24, 2021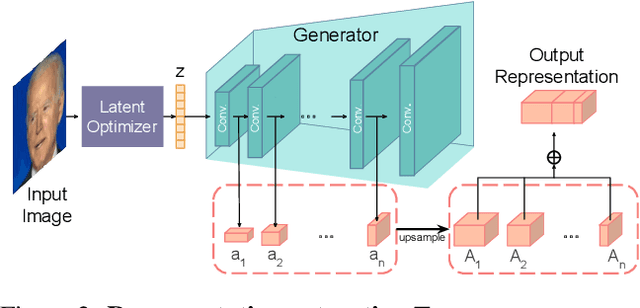
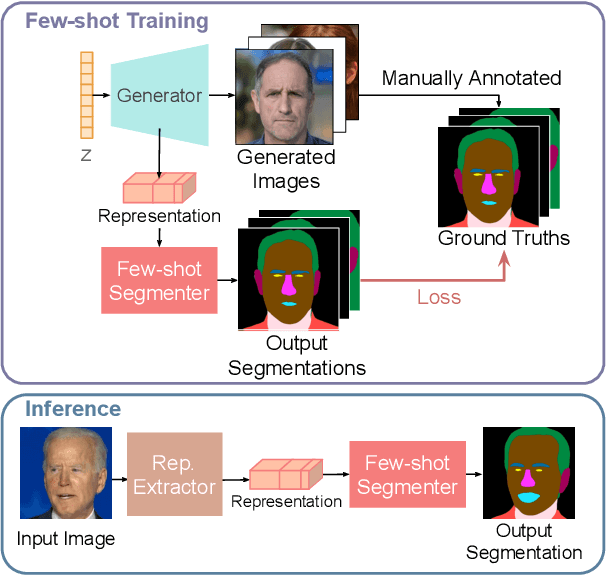

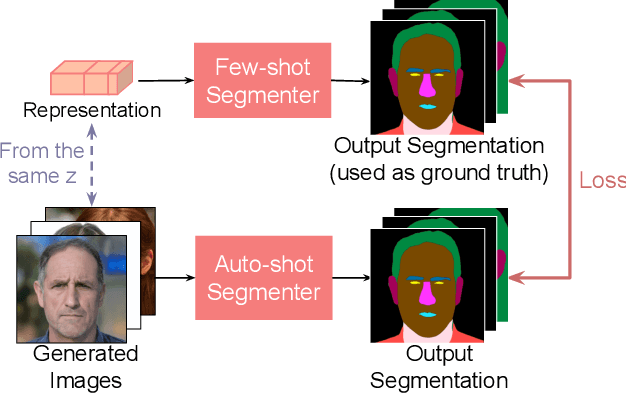
Abstract:While GANs have shown success in realistic image generation, the idea of using GANs for other tasks unrelated to synthesis is underexplored. Do GANs learn meaningful structural parts of objects during their attempt to reproduce those objects? In this work, we test this hypothesis and propose a simple and effective approach based on GANs for semantic part segmentation that requires as few as one label example along with an unlabeled dataset. Our key idea is to leverage a trained GAN to extract pixel-wise representation from the input image and use it as feature vectors for a segmentation network. Our experiments demonstrate that GANs representation is "readily discriminative" and produces surprisingly good results that are comparable to those from supervised baselines trained with significantly more labels. We believe this novel repurposing of GANs underlies a new class of unsupervised representation learning that is applicable to many other tasks. More results are available at https://repurposegans.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge