Nithya Shikarpur
Exploratory Study Of Human-AI Interaction For Hindustani Music
Nov 21, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a study of participants interacting with and using GaMaDHaNi, a novel hierarchical generative model for Hindustani vocal contours. To explore possible use cases in human-AI interaction, we conducted a user study with three participants, each engaging with the model through three predefined interaction modes. Although this study was conducted "in the wild"- with the model unadapted for the shift from the training data to real-world interaction - we use it as a pilot to better understand the expectations, reactions, and preferences of practicing musicians when engaging with such a model. We note their challenges as (1) the lack of restrictions in model output, and (2) the incoherence of model output. We situate these challenges in the context of Hindustani music and aim to suggest future directions for the model design to address these gaps.
Hierarchical Generative Modeling of Melodic Vocal Contours in Hindustani Classical Music
Aug 26, 2024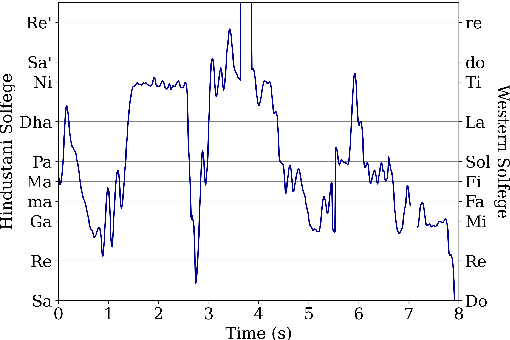
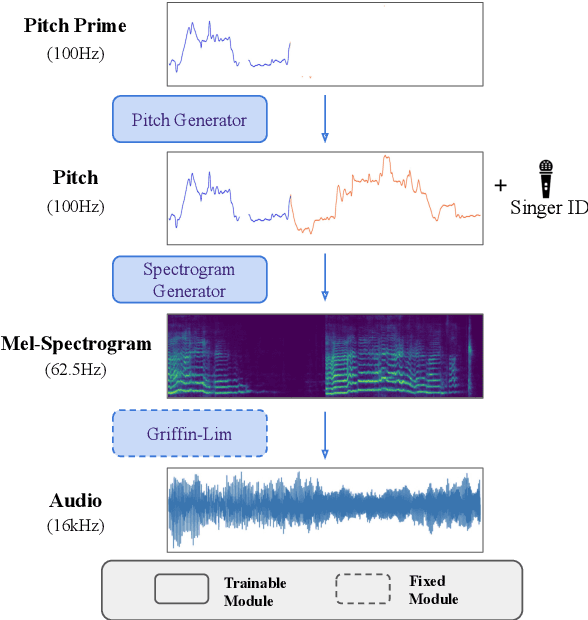
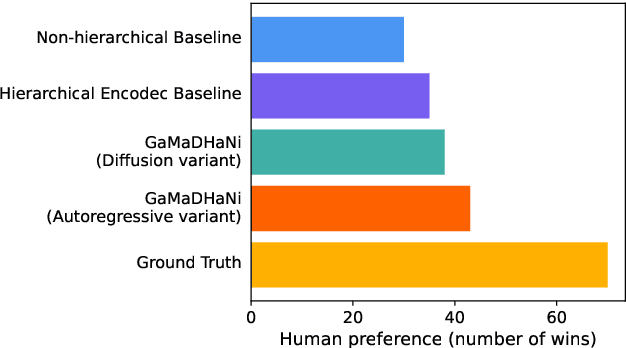
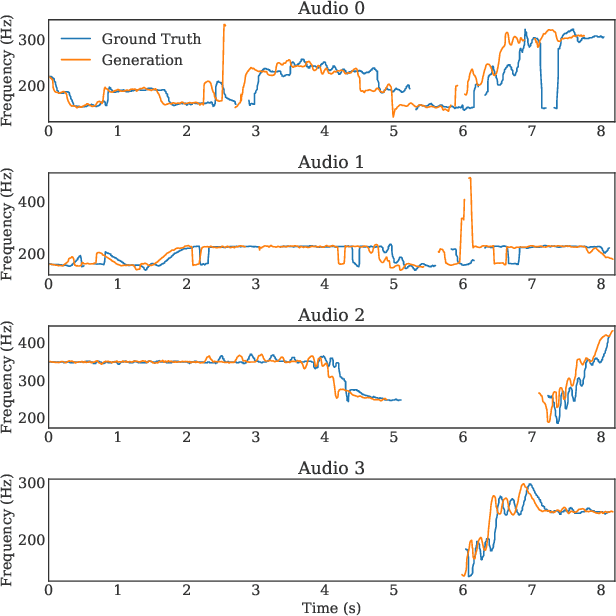
Abstract:Hindustani music is a performance-driven oral tradition that exhibits the rendition of rich melodic patterns. In this paper, we focus on generative modeling of singers' vocal melodies extracted from audio recordings, as the voice is musically prominent within the tradition. Prior generative work in Hindustani music models melodies as coarse discrete symbols which fails to capture the rich expressive melodic intricacies of singing. Thus, we propose to use a finely quantized pitch contour, as an intermediate representation for hierarchical audio modeling. We propose GaMaDHaNi, a modular two-level hierarchy, consisting of a generative model on pitch contours, and a pitch contour to audio synthesis model. We compare our approach to non-hierarchical audio models and hierarchical models that use a self-supervised intermediate representation, through a listening test and qualitative analysis. We also evaluate audio model's ability to faithfully represent the pitch contour input using Pearson correlation coefficient. By using pitch contours as an intermediate representation, we show that our model may be better equipped to listen and respond to musicians in a human-AI collaborative setting by highlighting two potential interaction use cases (1) primed generation, and (2) coarse pitch conditioning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge