Nikolaos Nomikos
A Survey on UAV-Aided Maritime Communications: Deployment Considerations, Applications, and Future Challenges
Sep 20, 2022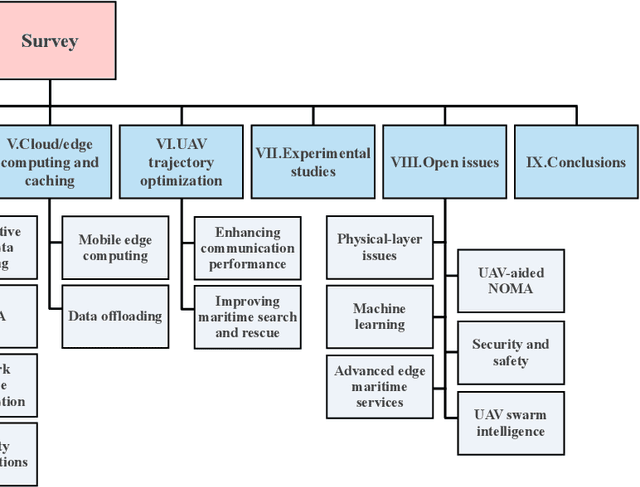
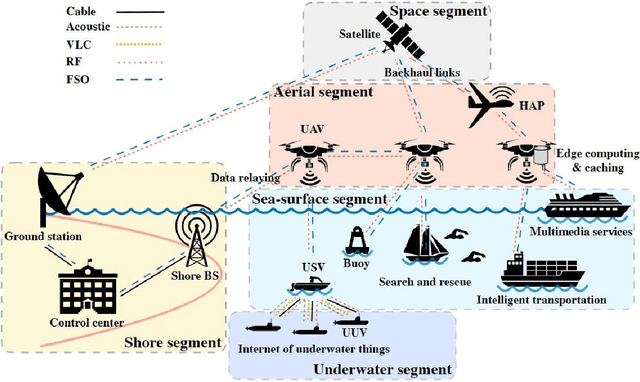
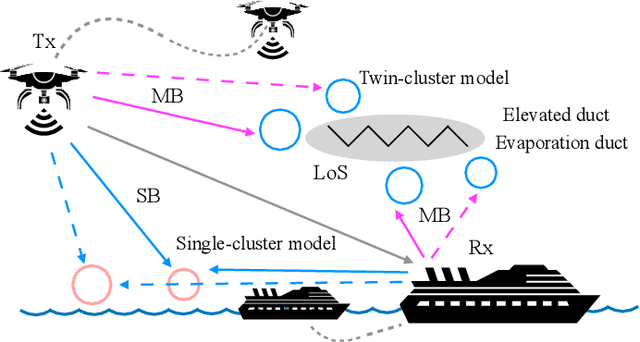
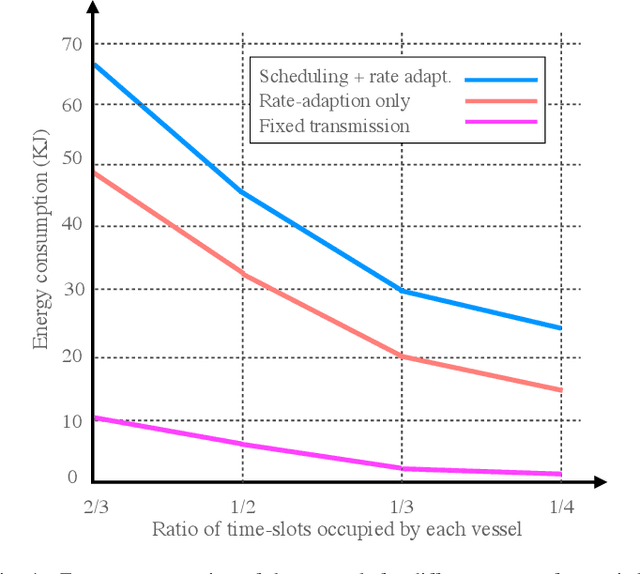
Abstract:Maritime activities represent a major domain of economic growth with several emerging maritime Internet of Things use cases, such as smart ports, autonomous navigation, and ocean monitoring systems. The major enabler for this exciting ecosystem is the provision of broadband, low-delay, and reliable wireless coverage to the ever-increasing number of vessels, buoys, platforms, sensors, and actuators. Towards this end, the integration of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in maritime communications introduces an aerial dimension to wireless connectivity going above and beyond current deployments, which are mainly relying on shore-based base stations with limited coverage and satellite links with high latency. Considering the potential of UAV-aided wireless communications, this survey presents the state-of-the-art in UAV-aided maritime communications, which, in general, are based on both conventional optimization and machine-learning-aided approaches. More specifically, relevant UAV-based network architectures are discussed together with the role of their building blocks. Then, physical-layer, resource management, and cloud/edge computing and caching UAV-aided solutions in maritime environments are discussed and grouped based on their performance targets. Moreover, as UAVs are characterized by flexible deployment with high re-positioning capabilities, studies on UAV trajectory optimization for maritime applications are thoroughly discussed. In addition, aiming at shedding light on the current status of real-world deployments, experimental studies on UAV-aided maritime communications are presented and implementation details are given. Finally, several important open issues in the area of UAV-aided maritime communications are given, related to the integration of sixth generation (6G) advancements.
A Survey on Reinforcement Learning-Aided Caching in Mobile Edge Networks
May 14, 2021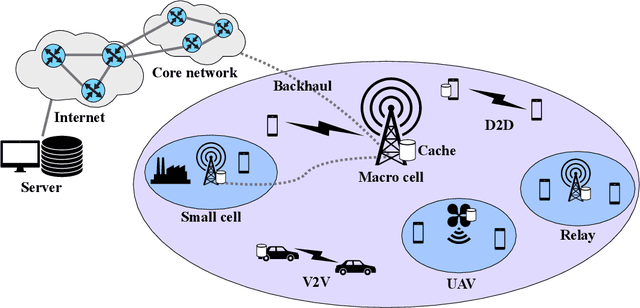
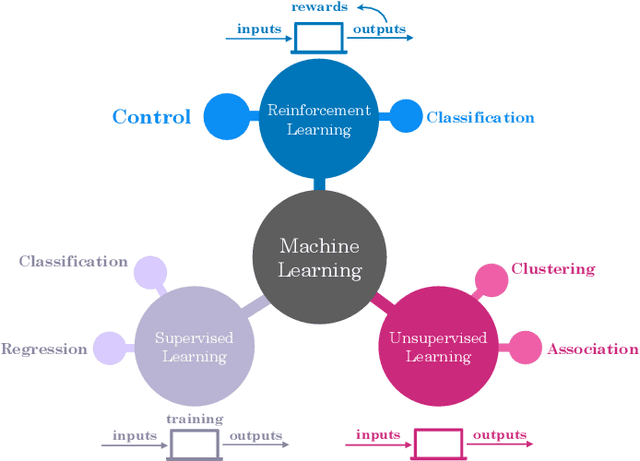
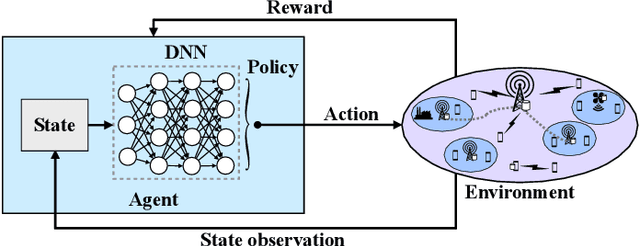
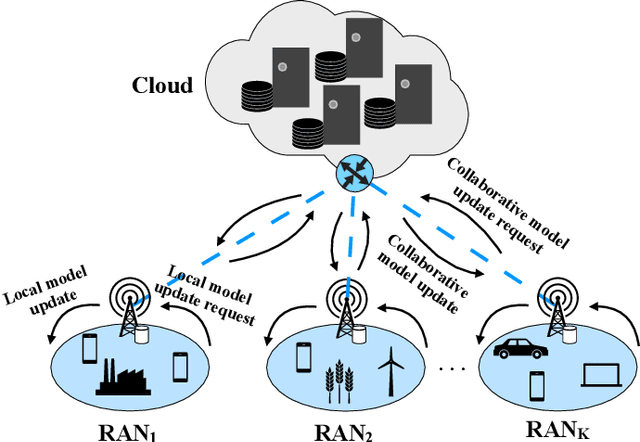
Abstract:Mobile networks are experiencing tremendous increase in data volume and user density. An efficient technique to alleviate this issue is to bring the data closer to the users by exploiting the caches of edge network nodes, such as fixed or mobile access points and even user devices. Meanwhile, the fusion of machine learning and wireless networks offers a viable way for network optimization as opposed to traditional optimization approaches which incur high complexity, or fail to provide optimal solutions. Among the various machine learning categories, reinforcement learning operates in an online and autonomous manner without relying on large sets of historical data for training. In this survey, reinforcement learning-aided mobile edge caching is presented, aiming at highlighting the achieved network gains over conventional caching approaches. Taking into account the heterogeneity of sixth generation (6G) networks in various wireless settings, such as fixed, vehicular and flying networks, learning-aided edge caching is presented, departing from traditional architectures. Furthermore, a categorization according to the desirable performance metric, such as spectral, energy and caching efficiency, average delay, and backhaul and fronthaul offloading is provided. Finally, several open issues are discussed, targeting to stimulate further interest in this important research field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge