Niklas Penzel
FastCAV: Efficient Computation of Concept Activation Vectors for Explaining Deep Neural Networks
May 23, 2025Abstract:Concepts such as objects, patterns, and shapes are how humans understand the world. Building on this intuition, concept-based explainability methods aim to study representations learned by deep neural networks in relation to human-understandable concepts. Here, Concept Activation Vectors (CAVs) are an important tool and can identify whether a model learned a concept or not. However, the computational cost and time requirements of existing CAV computation pose a significant challenge, particularly in large-scale, high-dimensional architectures. To address this limitation, we introduce FastCAV, a novel approach that accelerates the extraction of CAVs by up to 63.6x (on average 46.4x). We provide a theoretical foundation for our approach and give concrete assumptions under which it is equivalent to established SVM-based methods. Our empirical results demonstrate that CAVs calculated with FastCAV maintain similar performance while being more efficient and stable. In downstream applications, i.e., concept-based explanation methods, we show that FastCAV can act as a replacement leading to equivalent insights. Hence, our approach enables previously infeasible investigations of deep models, which we demonstrate by tracking the evolution of concepts during model training.
Towards Locally Explaining Prediction Behavior via Gradual Interventions and Measuring Property Gradients
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:Deep learning models achieve high predictive performance but lack intrinsic interpretability, hindering our understanding of the learned prediction behavior. Existing local explainability methods focus on associations, neglecting the causal drivers of model predictions. Other approaches adopt a causal perspective but primarily provide more general global explanations. However, for specific inputs, it's unclear whether globally identified factors apply locally. To address this limitation, we introduce a novel framework for local interventional explanations by leveraging recent advances in image-to-image editing models. Our approach performs gradual interventions on semantic properties to quantify the corresponding impact on a model's predictions using a novel score, the expected property gradient magnitude. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach through an extensive empirical evaluation on a wide range of architectures and tasks. First, we validate it in a synthetic scenario and demonstrate its ability to locally identify biases. Afterward, we apply our approach to analyze network training dynamics, investigate medical skin lesion classifiers, and study a pre-trained CLIP model with real-life interventional data. Our results highlight the potential of interventional explanations on the property level to reveal new insights into the behavior of deep models.
Facing Asymmetry -- Uncovering the Causal Link between Facial Symmetry and Expression Classifiers using Synthetic Interventions
Sep 24, 2024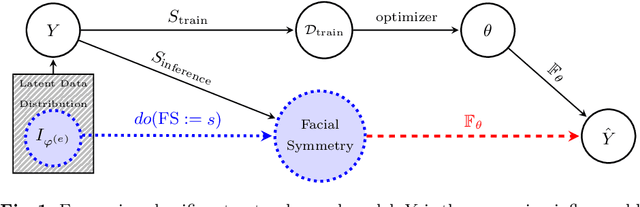
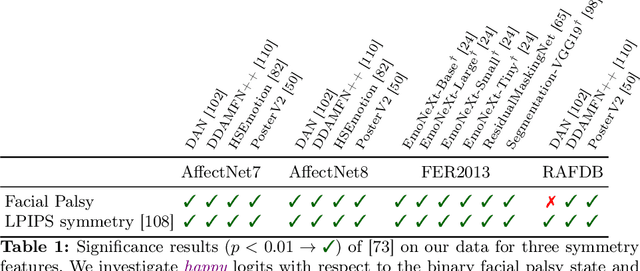
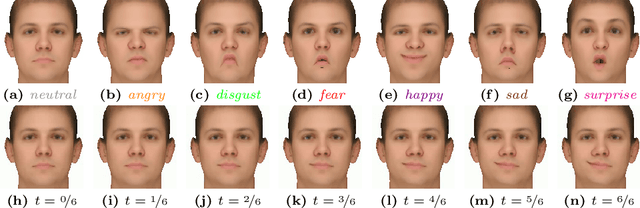
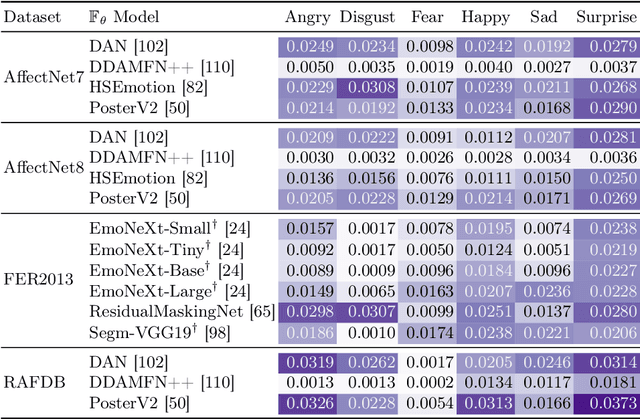
Abstract:Understanding expressions is vital for deciphering human behavior, and nowadays, end-to-end trained black box models achieve high performance. Due to the black-box nature of these models, it is unclear how they behave when applied out-of-distribution. Specifically, these models show decreased performance for unilateral facial palsy patients. We hypothesize that one crucial factor guiding the internal decision rules is facial symmetry. In this work, we use insights from causal reasoning to investigate the hypothesis. After deriving a structural causal model, we develop a synthetic interventional framework. This approach allows us to analyze how facial symmetry impacts a network's output behavior while keeping other factors fixed. All 17 investigated expression classifiers significantly lower their output activations for reduced symmetry. This result is congruent with observed behavior on real-world data from healthy subjects and facial palsy patients. As such, our investigation serves as a case study for identifying causal factors that influence the behavior of black-box models.
When Medical Imaging Met Self-Attention: A Love Story That Didn't Quite Work Out
Apr 18, 2024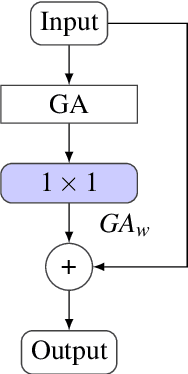
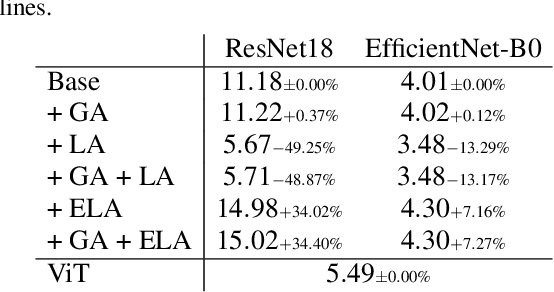
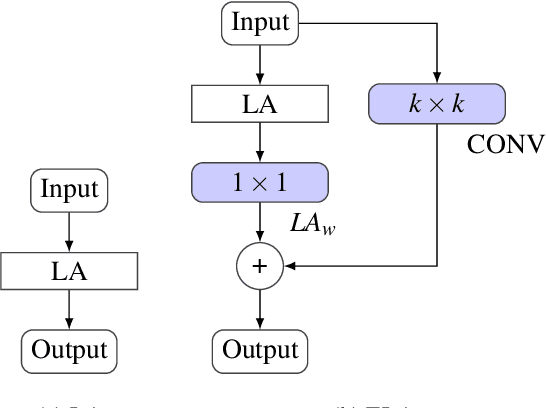
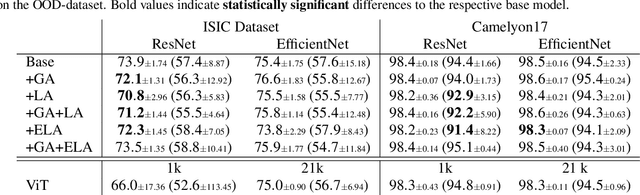
Abstract:A substantial body of research has focused on developing systems that assist medical professionals during labor-intensive early screening processes, many based on convolutional deep-learning architectures. Recently, multiple studies explored the application of so-called self-attention mechanisms in the vision domain. These studies often report empirical improvements over fully convolutional approaches on various datasets and tasks. To evaluate this trend for medical imaging, we extend two widely adopted convolutional architectures with different self-attention variants on two different medical datasets. With this, we aim to specifically evaluate the possible advantages of additional self-attention. We compare our models with similarly sized convolutional and attention-based baselines and evaluate performance gains statistically. Additionally, we investigate how including such layers changes the features learned by these models during the training. Following a hyperparameter search, and contrary to our expectations, we observe no significant improvement in balanced accuracy over fully convolutional models. We also find that important features, such as dermoscopic structures in skin lesion images, are still not learned by employing self-attention. Finally, analyzing local explanations, we confirm biased feature usage. We conclude that merely incorporating attention is insufficient to surpass the performance of existing fully convolutional methods.
* 10 pages, 2 figures, 5 tables, presented at VISAPP 2024
Reducing Bias in Pre-trained Models by Tuning while Penalizing Change
Apr 18, 2024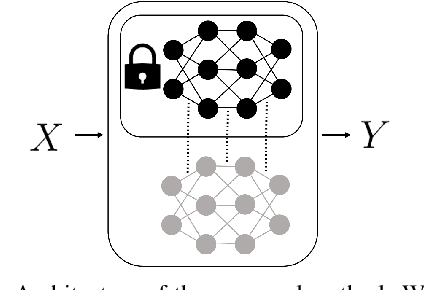
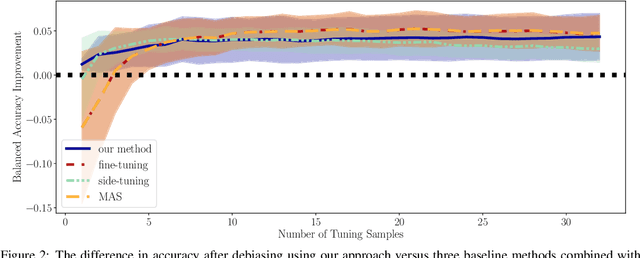
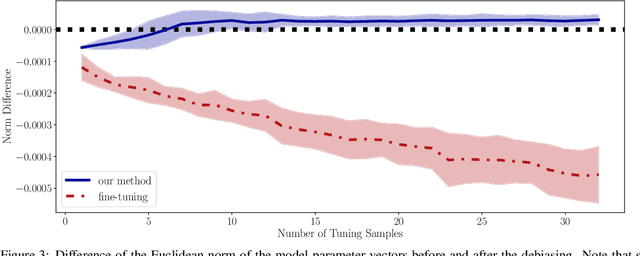
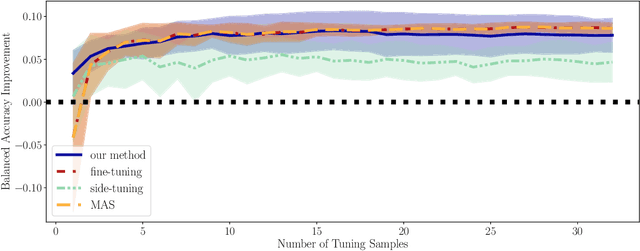
Abstract:Deep models trained on large amounts of data often incorporate implicit biases present during training time. If later such a bias is discovered during inference or deployment, it is often necessary to acquire new data and retrain the model. This behavior is especially problematic in critical areas such as autonomous driving or medical decision-making. In these scenarios, new data is often expensive and hard to come by. In this work, we present a method based on change penalization that takes a pre-trained model and adapts the weights to mitigate a previously detected bias. We achieve this by tuning a zero-initialized copy of a frozen pre-trained network. Our method needs very few, in extreme cases only a single, examples that contradict the bias to increase performance. Additionally, we propose an early stopping criterion to modify baselines and reduce overfitting. We evaluate our approach on a well-known bias in skin lesion classification and three other datasets from the domain shift literature. We find that our approach works especially well with very few images. Simple fine-tuning combined with our early stopping also leads to performance benefits for a larger number of tuning samples.
* 12 pages, 12 figures, presented at VISAPP 2024
The Power of Properties: Uncovering the Influential Factors in Emotion Classification
Apr 11, 2024



Abstract:Facial expression-based human emotion recognition is a critical research area in psychology and medicine. State-of-the-art classification performance is only reached by end-to-end trained neural networks. Nevertheless, such black-box models lack transparency in their decision-making processes, prompting efforts to ascertain the rules that underlie classifiers' decisions. Analyzing single inputs alone fails to expose systematic learned biases. These biases can be characterized as facial properties summarizing abstract information like age or medical conditions. Therefore, understanding a model's prediction behavior requires an analysis rooted in causality along such selected properties. We demonstrate that up to 91.25% of classifier output behavior changes are statistically significant concerning basic properties. Among those are age, gender, and facial symmetry. Furthermore, the medical usage of surface electromyography significantly influences emotion prediction. We introduce a workflow to evaluate explicit properties and their impact. These insights might help medical professionals select and apply classifiers regarding their specialized data and properties.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge