Nikitas Theodoropoulos
BERTtime Stories: Investigating the Role of Synthetic Story Data in Language pre-training
Oct 20, 2024

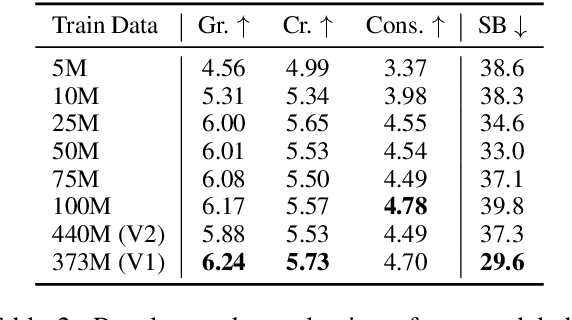

Abstract:We describe our contribution to the Strict and Strict-Small tracks of the 2nd iteration of the BabyLM Challenge. The shared task is centered around efficient pre-training given data constraints motivated by human development. In response, we study the effect of synthetic story data in language pre-training using TinyStories: a recently introduced dataset of short stories. Initially, we train GPT-Neo models on subsets of TinyStories, while varying the amount of available data. We find that, even with access to less than 100M words, the models are able to generate high-quality, original completions to a given story, and acquire substantial linguistic knowledge. To measure the effect of synthetic story data, we train LTG-BERT encoder models on a combined dataset of: a subset of TinyStories, story completions generated by GPT-Neo, and a subset of the BabyLM dataset. Our experimentation reveals that synthetic data can occasionally offer modest gains, but overall have a negative influence on linguistic understanding. Our work offers an initial study on synthesizing story data in low resource settings and underscores their potential for augmentation in data-constrained language modeling. We publicly release our models and implementation on our GitHub.
From {Solution Synthesis} to {Student Attempt Synthesis} for Block-Based Visual Programming Tasks
May 03, 2022
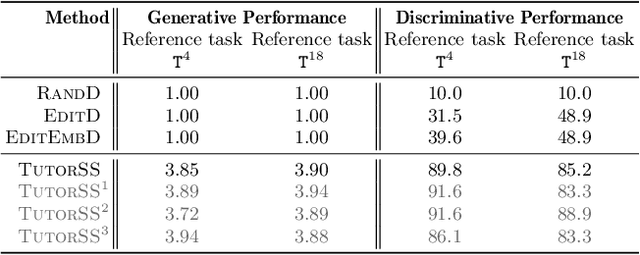

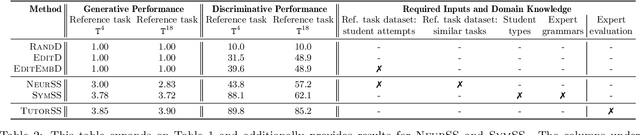
Abstract:Block-based visual programming environments are increasingly used to introduce computing concepts to beginners. Given that programming tasks are open-ended and conceptual, novice students often struggle when learning in these environments. AI-driven programming tutors hold great promise in automatically assisting struggling students, and need several components to realize this potential. We investigate the crucial component of student modeling, in particular, the ability to automatically infer students' misconceptions for predicting (synthesizing) their behavior. We introduce a novel benchmark, StudentSyn, centered around the following challenge: For a given student, synthesize the student's attempt on a new target task after observing the student's attempt on a fixed reference task. This challenge is akin to that of program synthesis; however, instead of synthesizing a {solution} (i.e., program an expert would write), the goal here is to synthesize a {student attempt} (i.e., program that a given student would write). We first show that human experts (TutorSS) can achieve high performance on the benchmark, whereas simple baselines perform poorly. Then, we develop two neuro/symbolic techniques (NeurSS and SymSS) in a quest to close this gap with TutorSS. We will publicly release the benchmark to facilitate future research in this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge