Nicolas Verstaevel
IRIT-SMAC
Analyzing Shapley Additive Explanations to Understand Anomaly Detection Algorithm Behaviors and Their Complementarity
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Unsupervised anomaly detection is a challenging problem due to the diversity of data distributions and the lack of labels. Ensemble methods are often adopted to mitigate these challenges by combining multiple detectors, which can reduce individual biases and increase robustness. Yet building an ensemble that is genuinely complementary remains challenging, since many detectors rely on similar decision cues and end up producing redundant anomaly scores. As a result, the potential of ensemble learning is often limited by the difficulty of identifying models that truly capture different types of irregularities. To address this, we propose a methodology for characterizing anomaly detectors through their decision mechanisms. Using SHapley Additive exPlanations, we quantify how each model attributes importance to input features, and we use these attribution profiles to measure similarity between detectors. We show that detectors with similar explanations tend to produce correlated anomaly scores and identify largely overlapping anomalies. Conversely, explanation divergence reliably indicates complementary detection behavior. Our results demonstrate that explanation-driven metrics offer a different criterion than raw outputs for selecting models in an ensemble. However, we also demonstrate that diversity alone is insufficient; high individual model performance remains a prerequisite for effective ensembles. By explicitly targeting explanation diversity while maintaining model quality, we are able to construct ensembles that are more diverse, more complementary, and ultimately more effective for unsupervised anomaly detection.
Adaptive Agents in Spatial Double-Auction Markets: Modeling the Emergence of Industrial Symbiosis
Dec 19, 2025



Abstract:Industrial symbiosis fosters circularity by enabling firms to repurpose residual resources, yet its emergence is constrained by socio-spatial frictions that shape costs, matching opportunities, and market efficiency. Existing models often overlook the interaction between spatial structure, market design, and adaptive firm behavior, limiting our understanding of where and how symbiosis arises. We develop an agent-based model where heterogeneous firms trade byproducts through a spatially embedded double-auction market, with prices and quantities emerging endogenously from local interactions. Leveraging reinforcement learning, firms adapt their bidding strategies to maximize profit while accounting for transport costs, disposal penalties, and resource scarcity. Simulation experiments reveal the economic and spatial conditions under which decentralized exchanges converge toward stable and efficient outcomes. Counterfactual regret analysis shows that sellers' strategies approach a near Nash equilibrium, while sensitivity analysis highlights how spatial structures and market parameters jointly govern circularity. Our model provides a basis for exploring policy interventions that seek to align firm incentives with sustainability goals, and more broadly demonstrates how decentralized coordination can emerge from adaptive agents in spatially constrained markets.
* AAMAS CC-BY 4.0 licence. Adaptive Agents in Spatial Double-Auction Markets: Modeling the Emergence of Industrial Symbiosis. Full paper. In Proc. of the 25th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS 2026), Paphos, Cyprus, May 25 - 29, 2026, IFAAMAS, 10 pages
Data-Driven Global Sensitivity Analysis for Engineering Design Based on Individual Conditional Expectations
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Explainable machine learning techniques have gained increasing attention in engineering applications, especially in aerospace design and analysis, where understanding how input variables influence data-driven models is essential. Partial Dependence Plots (PDPs) are widely used for interpreting black-box models by showing the average effect of an input variable on the prediction. However, their global sensitivity metric can be misleading when strong interactions are present, as averaging tends to obscure interaction effects. To address this limitation, we propose a global sensitivity metric based on Individual Conditional Expectation (ICE) curves. The method computes the expected feature importance across ICE curves, along with their standard deviation, to more effectively capture the influence of interactions. We provide a mathematical proof demonstrating that the PDP-based sensitivity is a lower bound of the proposed ICE-based metric under truncated orthogonal polynomial expansion. In addition, we introduce an ICE-based correlation value to quantify how interactions modify the relationship between inputs and the output. Comparative evaluations were performed on three cases: a 5-variable analytical function, a 5-variable wind-turbine fatigue problem, and a 9-variable airfoil aerodynamics case, where ICE-based sensitivity was benchmarked against PDP, SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP), and Sobol' indices. The results show that ICE-based feature importance provides richer insights than the traditional PDP-based approach, while visual interpretations from PDP, ICE, and SHAP complement one another by offering multiple perspectives.
Modèles de Substitution pour les Modèles à base d'Agents : Enjeux, Méthodes et Applications
May 17, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent simulations enables the modeling and analyses of the dynamic behaviors and interactions of autonomous entities evolving in complex environments. Agent-based models (ABM) are widely used to study emergent phenomena arising from local interactions. However, their high computational cost poses a significant challenge, particularly for large-scale simulations requiring extensive parameter exploration, optimization, or uncertainty quantification. The increasing complexity of ABM limits their feasibility for real-time decision-making and large-scale scenario analysis. To address these limitations, surrogate models offer an efficient alternative by learning approximations from sparse simulation data. These models provide cheap-to-evaluate predictions, significantly reducing computational costs while maintaining accuracy. Various machine learning techniques, including regression models, neural networks, random forests and Gaussian processes, have been applied to construct robust surrogates. Moreover, uncertainty quantification and sensitivity analysis play a crucial role in enhancing model reliability and interpretability. This article explores the motivations, methods, and applications of surrogate modeling for ABM, emphasizing the trade-offs between accuracy, computational efficiency, and interpretability. Through a case study on a segregation model, we highlight the challenges associated with building and validating surrogate models, comparing different approaches and evaluating their performance. Finally, we discuss future perspectives on integrating surrogate models within ABM to improve scalability, explainability, and real-time decision support across various fields such as ecology, urban planning and economics.
How to solve a classification problem using a cooperative tiling Multi-Agent System?
Sep 15, 2022



Abstract:Adaptive Multi-Agent Systems (AMAS) transform dynamic problems into problems of local cooperation between agents. We present smapy, an ensemble based AMAS implementation for mobility prediction, whose agents are provided with machine learning models in addition to their cooperation rules. With a detailed methodology, we propose a framework to transform a classification problem into a cooperative tiling of the input variable space. We show that it is possible to use linear classifiers for online non-linear classification on three benchmark toy problems chosen for their different levels of linear separability, if they are integrated in a cooperative Multi-Agent structure. The results obtained show a significant improvement of the performance of linear classifiers in non-linear contexts in terms of classification accuracy and decision boundaries, thanks to the cooperative approach.
An ensemble Multi-Agent System for non-linear classification
Sep 14, 2022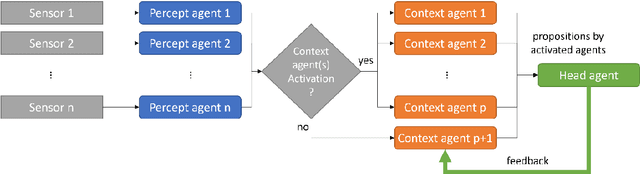
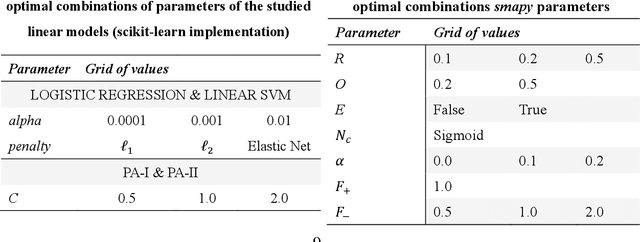
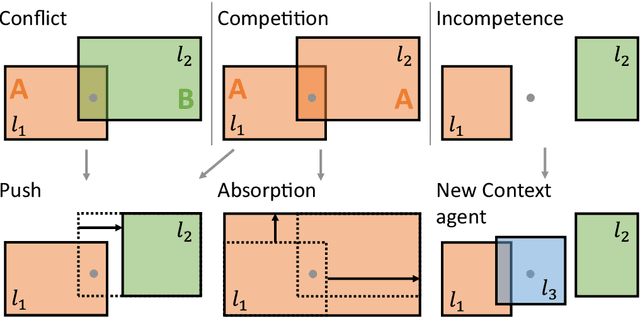
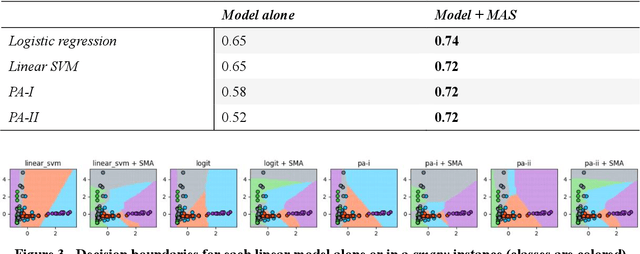
Abstract:Self-Adaptive Multi-Agent Systems (AMAS) transform machine learning problems into problems of local cooperation between agents. We present smapy, an ensemble based AMAS implementation for mobility prediction, whose agents are provided with machine learning models in addition to their cooperation rules. With a detailed methodology, we show that it is possible to use linear models for nonlinear classification on a benchmark transport mode detection dataset, if they are integrated in a cooperative multi-agent structure. The results obtained show a significant improvement of the performance of linear models in non-linear contexts thanks to the multi-agent approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge