Neil John Ortega
Efficient Generation of Parameterised Quantum Circuits from Large Texts
May 19, 2025Abstract:Quantum approaches to natural language processing (NLP) are redefining how linguistic information is represented and processed. While traditional hybrid quantum-classical models rely heavily on classical neural networks, recent advancements propose a novel framework, DisCoCirc, capable of directly encoding entire documents as parameterised quantum circuits (PQCs), besides enjoying some additional interpretability and compositionality benefits. Following these ideas, this paper introduces an efficient methodology for converting large-scale texts into quantum circuits using tree-like representations of pregroup diagrams. Exploiting the compositional parallels between language and quantum mechanics, grounded in symmetric monoidal categories, our approach enables faithful and efficient encoding of syntactic and discourse relationships in long and complex texts (up to 6410 words in our experiments) to quantum circuits. The developed system is provided to the community as part of the augmented open-source quantum NLP package lambeq Gen II.
A Pattern Language for Machine Learning Tasks
Jul 02, 2024
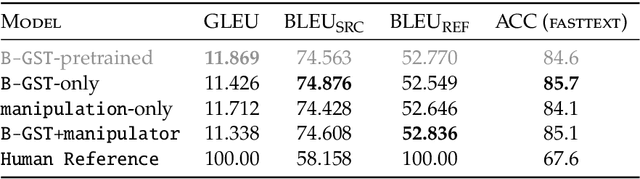
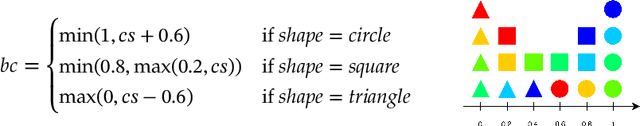

Abstract:Idealised as universal approximators, learners such as neural networks can be viewed as "variable functions" that may become one of a range of concrete functions after training. In the same way that equations constrain the possible values of variables in algebra, we may view objective functions as constraints on the behaviour of learners. We extract the equivalences perfectly optimised objective functions impose, calling them "tasks". For these tasks, we develop a formal graphical language that allows us to: (1) separate the core tasks of a behaviour from its implementation details; (2) reason about and design behaviours model-agnostically; and (3) simply describe and unify approaches in machine learning across domains. As proof-of-concept, we design a novel task that enables converting classifiers into generative models we call "manipulators", which we implement by directly translating task specifications into code. The resulting models exhibit capabilities such as style transfer and interpretable latent-space editing, without the need for custom architectures, adversarial training or random sampling. We formally relate the behaviour of manipulators to GANs, and empirically demonstrate their competitive performance with VAEs. We report on experiments across vision and language domains aiming to characterise manipulators as approximate Bayesian inversions of discriminative classifiers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge