Neda Hassanpour
Pathway Activity Analysis and Metabolite Annotation for Untargeted Metabolomics using Probabilistic Modeling
Dec 12, 2019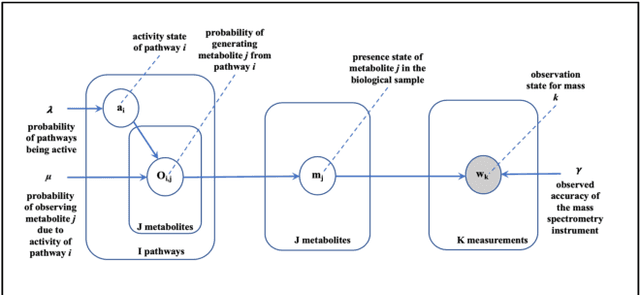
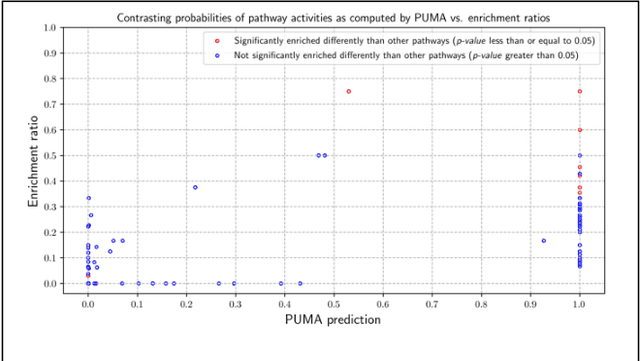
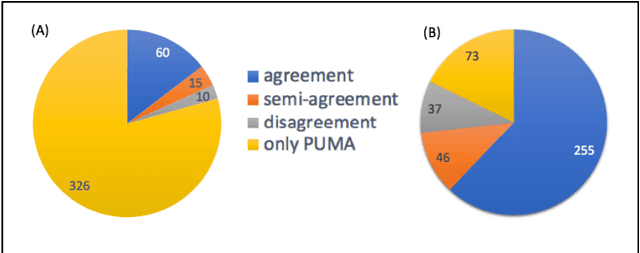
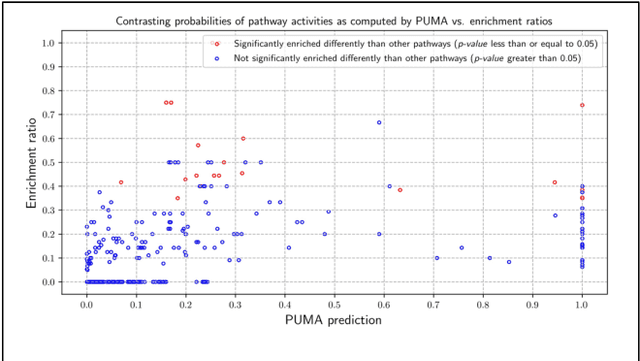
Abstract:Motivation: Untargeted metabolomics comprehensively characterizes small molecules and elucidates activities of biochemical pathways within a biological sample. Despite computational advances, interpreting collected measurements and determining their biological role remains a challenge. Results: To interpret measurements, we present an inference-based approach, termed Probabilistic modeling for Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis (PUMA). Our approach captures measurements and known information about the sample under study in a generative model and uses stochastic sampling to compute posterior probability distributions. PUMA predicts the likelihood of pathways being active, and then derives a probabilistic annotation, which assigns chemical identities to the measurements. PUMA is validated on synthetic datasets. When applied to test cases, the resulting pathway activities are biologically meaningful and distinctly different from those obtained using statistical pathway enrichment techniques. Annotation results are in agreement to those obtained using other tools that utilize additional information in the form of spectral signatures. Importantly, PUMA annotates many additional measurements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge