Nauros Romim
BD-SHS: A Benchmark Dataset for Learning to Detect Online Bangla Hate Speech in Different Social Contexts
Jun 01, 2022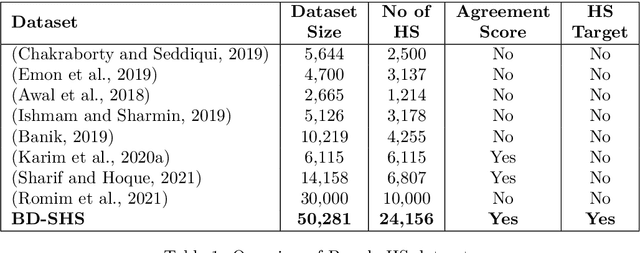
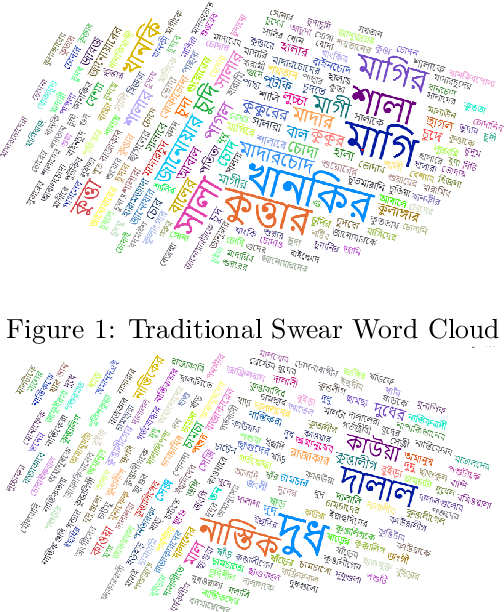
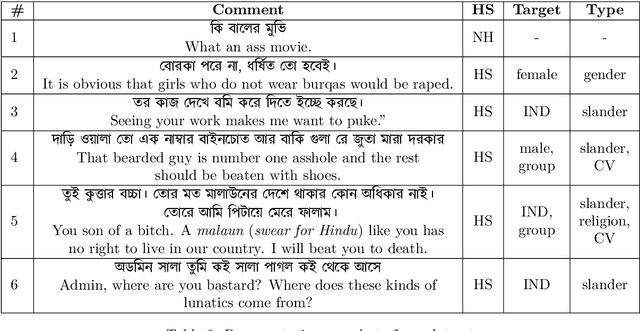
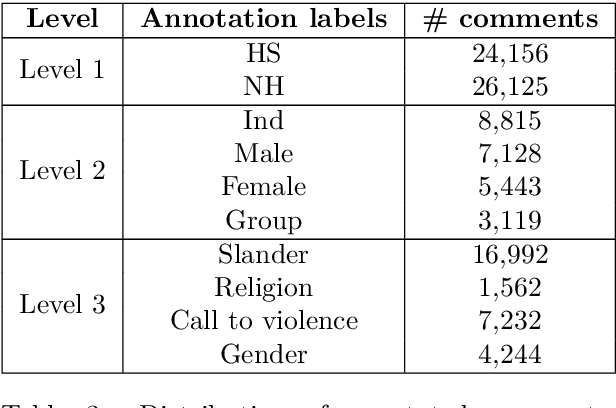
Abstract:Social media platforms and online streaming services have spawned a new breed of Hate Speech (HS). Due to the massive amount of user-generated content on these sites, modern machine learning techniques are found to be feasible and cost-effective to tackle this problem. However, linguistically diverse datasets covering different social contexts in which offensive language is typically used are required to train generalizable models. In this paper, we identify the shortcomings of existing Bangla HS datasets and introduce a large manually labeled dataset BD-SHS that includes HS in different social contexts. The labeling criteria were prepared following a hierarchical annotation process, which is the first of its kind in Bangla HS to the best of our knowledge. The dataset includes more than 50,200 offensive comments crawled from online social networking sites and is at least 60% larger than any existing Bangla HS datasets. We present the benchmark result of our dataset by training different NLP models resulting in the best one achieving an F1-score of 91.0%. In our experiments, we found that a word embedding trained exclusively using 1.47 million comments from social media and streaming sites consistently resulted in better modeling of HS detection in comparison to other pre-trained embeddings. Our dataset and all accompanying codes is publicly available at github.com/naurosromim/hate-speech-dataset-for-Bengali-social-media
HS-BAN: A Benchmark Dataset of Social Media Comments for Hate Speech Detection in Bangla
Dec 03, 2021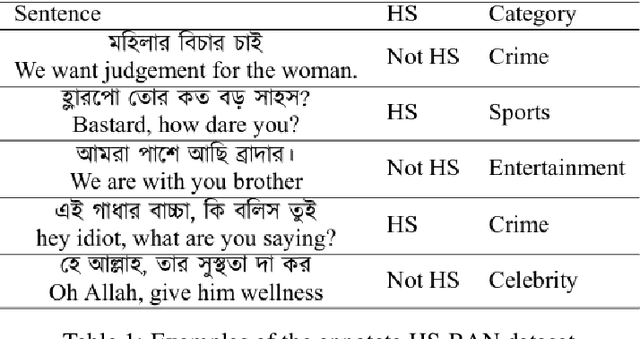
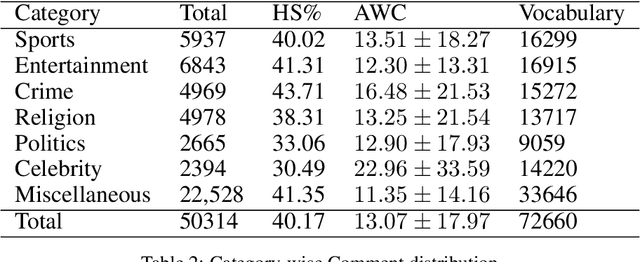
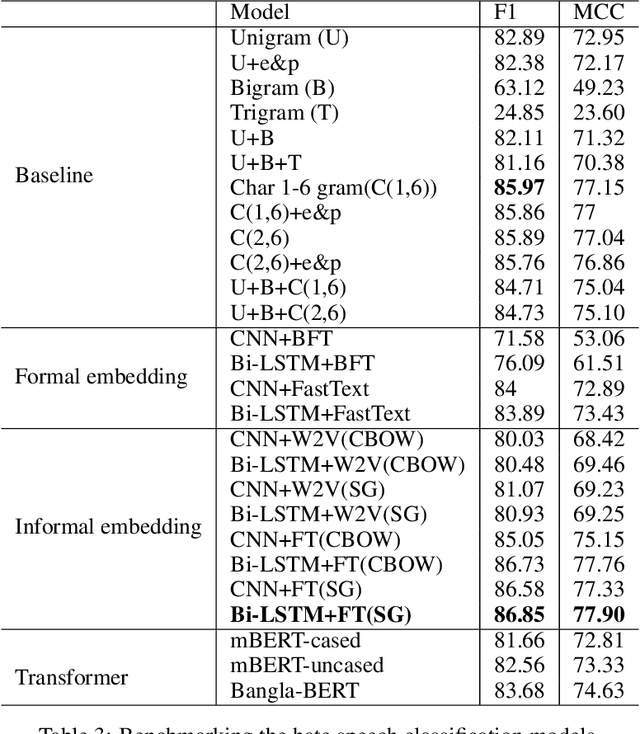
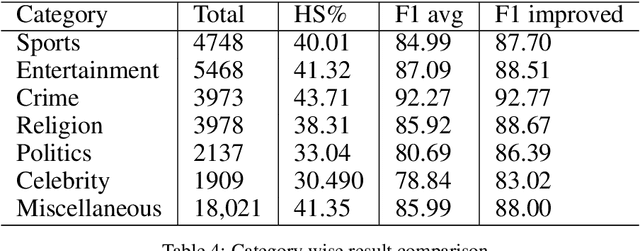
Abstract:In this paper, we present HS-BAN, a binary class hate speech (HS) dataset in Bangla language consisting of more than 50,000 labeled comments, including 40.17% hate and rest are non hate speech. While preparing the dataset a strict and detailed annotation guideline was followed to reduce human annotation bias. The HS dataset was also preprocessed linguistically to extract different types of slang currently people write using symbols, acronyms, or alternative spellings. These slang words were further categorized into traditional and non-traditional slang lists and included in the results of this paper. We explored traditional linguistic features and neural network-based methods to develop a benchmark system for hate speech detection for the Bangla language. Our experimental results show that existing word embedding models trained with informal texts perform better than those trained with formal text. Our benchmark shows that a Bi-LSTM model on top of the FastText informal word embedding achieved 86.78% F1-score. We will make the dataset available for public use.
Hate Speech detection in the Bengali language: A dataset and its baseline evaluation
Dec 17, 2020



Abstract:Social media sites such as YouTube and Facebook have become an integral part of everyone's life and in the last few years, hate speech in the social media comment section has increased rapidly. Detection of hate speech on social media websites faces a variety of challenges including small imbalanced data sets, the findings of an appropriate model and also the choice of feature analysis method. further more, this problem is more severe for the Bengali speaking community due to the lack of gold standard labelled datasets. This paper presents a new dataset of 30,000 user comments tagged by crowd sourcing and varified by experts. All the comments are collected from YouTube and Facebook comment section and classified into seven categories: sports, entertainment, religion, politics, crime, celebrity and TikTok & meme. A total of 50 annotators annotated each comment three times and the majority vote was taken as the final annotation. Nevertheless, we have conducted base line experiments and several deep learning models along with extensive pre-trained Bengali word embedding such as Word2Vec, FastText and BengFastText on this dataset to facilitate future research opportunities. The experiment illustrated that although all deep learning models performed well, SVM achieved the best result with 87.5% accuracy. Our core contribution is to make this benchmark dataset available and accessible to facilitate further research in the field of in the field of Bengali hate speech detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge