Napoleon H. Reyes
Over the Edge of Chaos? Excess Complexity as a Roadblock to Artificial General Intelligence
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:In this study, we explored the progression trajectories of artificial intelligence (AI) systems through the lens of complexity theory. We challenged the conventional linear and exponential projections of AI advancement toward Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) underpinned by transformer-based architectures, and posited the existence of critical points, akin to phase transitions in complex systems, where AI performance might plateau or regress into instability upon exceeding a critical complexity threshold. We employed agent-based modelling (ABM) to simulate hypothetical scenarios of AI systems' evolution under specific assumptions, using benchmark performance as a proxy for capability and complexity. Our simulations demonstrated how increasing the complexity of the AI system could exceed an upper criticality threshold, leading to unpredictable performance behaviours. Additionally, we developed a practical methodology for detecting these critical thresholds using simulation data and stochastic gradient descent to fine-tune detection thresholds. This research offers a novel perspective on AI advancement that has a particular relevance to Large Language Models (LLMs), emphasising the need for a tempered approach to extrapolating AI's growth potential and underscoring the importance of developing more robust and comprehensive AI performance benchmarks.
Automating Research Synthesis with Domain-Specific Large Language Model Fine-Tuning
Apr 08, 2024



Abstract:This research pioneers the use of fine-tuned Large Language Models (LLMs) to automate Systematic Literature Reviews (SLRs), presenting a significant and novel contribution in integrating AI to enhance academic research methodologies. Our study employed the latest fine-tuning methodologies together with open-sourced LLMs, and demonstrated a practical and efficient approach to automating the final execution stages of an SLR process that involves knowledge synthesis. The results maintained high fidelity in factual accuracy in LLM responses, and were validated through the replication of an existing PRISMA-conforming SLR. Our research proposed solutions for mitigating LLM hallucination and proposed mechanisms for tracking LLM responses to their sources of information, thus demonstrating how this approach can meet the rigorous demands of scholarly research. The findings ultimately confirmed the potential of fine-tuned LLMs in streamlining various labor-intensive processes of conducting literature reviews. Given the potential of this approach and its applicability across all research domains, this foundational study also advocated for updating PRISMA reporting guidelines to incorporate AI-driven processes, ensuring methodological transparency and reliability in future SLRs. This study broadens the appeal of AI-enhanced tools across various academic and research fields, setting a new standard for conducting comprehensive and accurate literature reviews with more efficiency in the face of ever-increasing volumes of academic studies.
RGB-D And Thermal Sensor Fusion: A Systematic Literature Review
May 19, 2023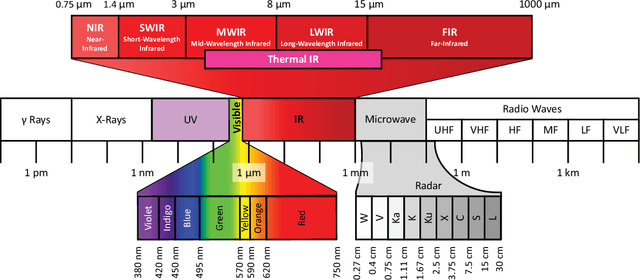
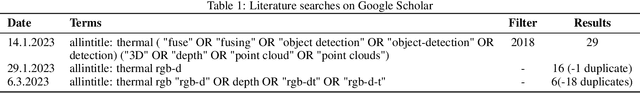
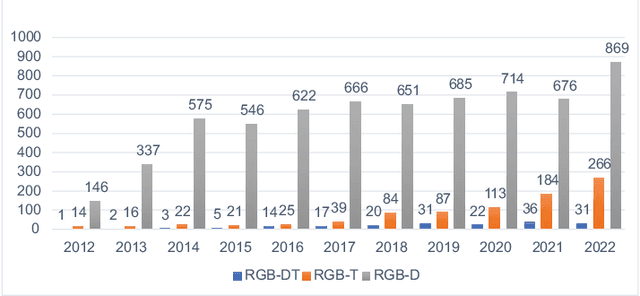
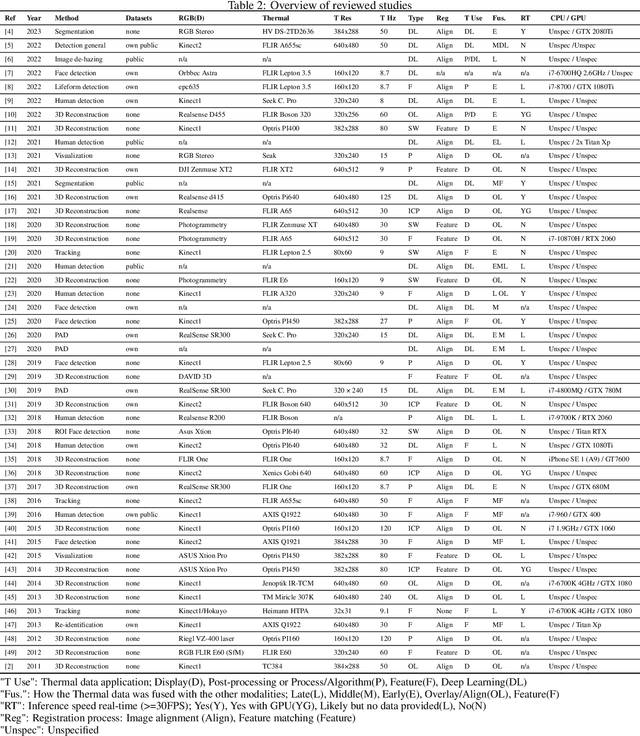
Abstract:In the last decade, the computer vision field has seen significant progress in multimodal data fusion and learning, where multiple sensors, including depth, infrared, and visual, are used to capture the environment across diverse spectral ranges. Despite these advancements, there has been no systematic and comprehensive evaluation of fusing RGB-D and thermal modalities to date. While autonomous driving using LiDAR, radar, RGB, and other sensors has garnered substantial research interest, along with the fusion of RGB and depth modalities, the integration of thermal cameras and, specifically, the fusion of RGB-D and thermal data, has received comparatively less attention. This might be partly due to the limited number of publicly available datasets for such applications. This paper provides a comprehensive review of both, state-of-the-art and traditional methods used in fusing RGB-D and thermal camera data for various applications, such as site inspection, human tracking, fault detection, and others. The reviewed literature has been categorised into technical areas, such as 3D reconstruction, segmentation, object detection, available datasets, and other related topics. Following a brief introduction and an overview of the methodology, the study delves into calibration and registration techniques, then examines thermal visualisation and 3D reconstruction, before discussing the application of classic feature-based techniques as well as modern deep learning approaches. The paper concludes with a discourse on current limitations and potential future research directions. It is hoped that this survey will serve as a valuable reference for researchers looking to familiarise themselves with the latest advancements and contribute to the RGB-DT research field.
Towards Asteroid Detection in Microlensing Surveys with Deep Learning
Nov 04, 2022
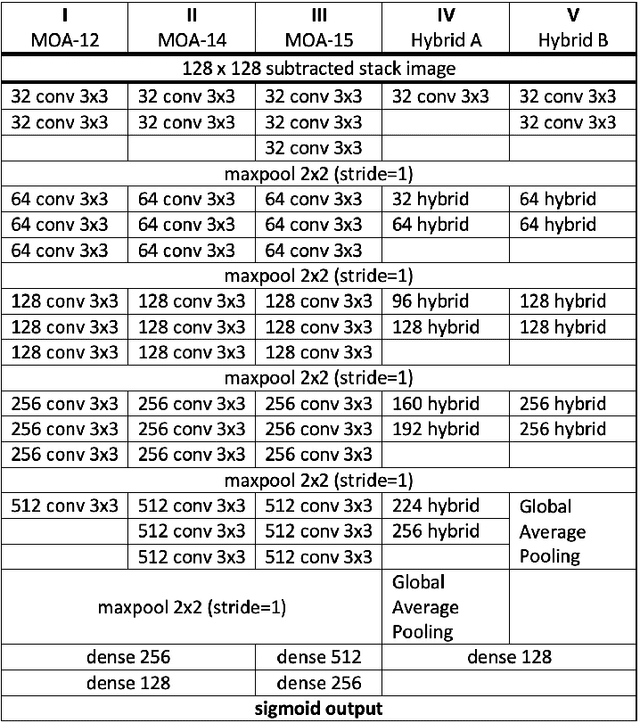
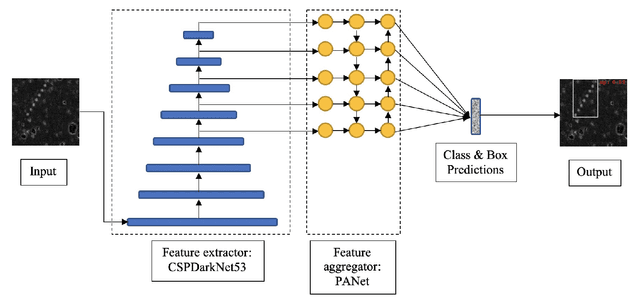
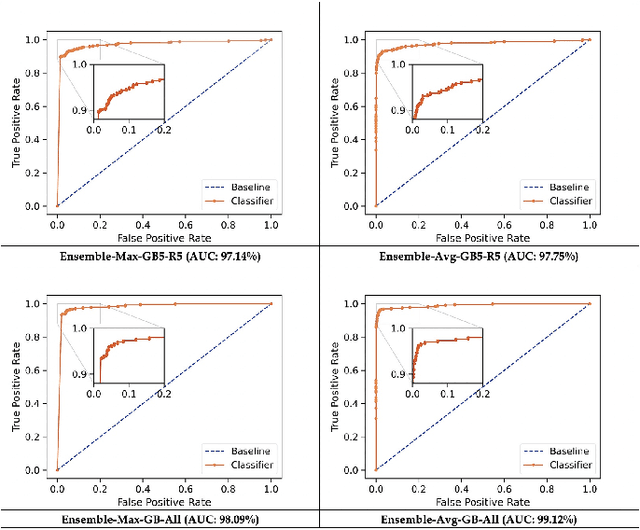
Abstract:Asteroids are an indelible part of most astronomical surveys though only a few surveys are dedicated to their detection. Over the years, high cadence microlensing surveys have amassed several terabytes of data while scanning primarily the Galactic Bulge and Magellanic Clouds for microlensing events and thus provide a treasure trove of opportunities for scientific data mining. In particular, numerous asteroids have been observed by visual inspection of selected images. This paper presents novel deep learning-based solutions for the recovery and discovery of asteroids in the microlensing data gathered by the MOA project. Asteroid tracklets can be clearly seen by combining all the observations on a given night and these tracklets inform the structure of the dataset. Known asteroids were identified within these composite images and used for creating the labelled datasets required for supervised learning. Several custom CNN models were developed to identify images with asteroid tracklets. Model ensembling was then employed to reduce the variance in the predictions as well as to improve the generalisation error, achieving a recall of 97.67%. Furthermore, the YOLOv4 object detector was trained to localize asteroid tracklets, achieving a mean Average Precision (mAP) of 90.97%. These trained networks will be applied to 16 years of MOA archival data to find both known and unknown asteroids that have been observed by the survey over the years. The methodologies developed can be adapted for use by other surveys for asteroid recovery and discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge