Nandhini Subramanian
Panoptic Segmentation: A Review
Nov 19, 2021

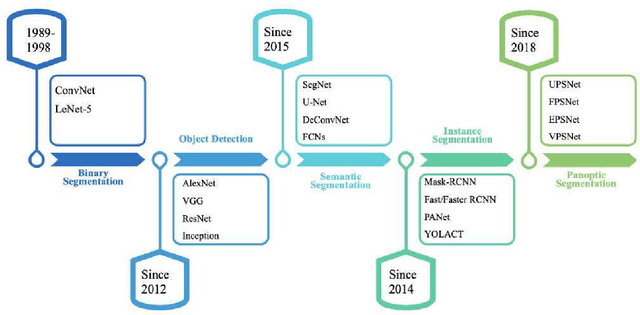

Abstract:Image segmentation for video analysis plays an essential role in different research fields such as smart city, healthcare, computer vision and geoscience, and remote sensing applications. In this regard, a significant effort has been devoted recently to developing novel segmentation strategies; one of the latest outstanding achievements is panoptic segmentation. The latter has resulted from the fusion of semantic and instance segmentation. Explicitly, panoptic segmentation is currently under study to help gain a more nuanced knowledge of the image scenes for video surveillance, crowd counting, self-autonomous driving, medical image analysis, and a deeper understanding of the scenes in general. To that end, we present in this paper the first comprehensive review of existing panoptic segmentation methods to the best of the authors' knowledge. Accordingly, a well-defined taxonomy of existing panoptic techniques is performed based on the nature of the adopted algorithms, application scenarios, and primary objectives. Moreover, the use of panoptic segmentation for annotating new datasets by pseudo-labeling is discussed. Moving on, ablation studies are carried out to understand the panoptic methods from different perspectives. Moreover, evaluation metrics suitable for panoptic segmentation are discussed, and a comparison of the performance of existing solutions is provided to inform the state-of-the-art and identify their limitations and strengths. Lastly, the current challenges the subject technology faces and the future trends attracting considerable interest in the near future are elaborated, which can be a starting point for the upcoming research studies. The papers provided with code are available at: https://github.com/elharroussomar/Awesome-Panoptic-Segmentation
An encoder-decoder-based method for COVID-19 lung infection segmentation
Jul 04, 2020



Abstract:The novelty of the COVID-19 disease and the speed of spread has created a colossal chaos, impulse among researchers worldwide to exploit all the resources and capabilities to understand and analyze characteristics of the coronavirus in term of the ways it spreads and virus incubation time. For that, the existing medical features like CT and X-ray images are used. For example, CT-scan images can be used for the detection of lung infection. But the challenges of these features such as the quality of the image and infection characteristics limitate the effectiveness of these features. Using artificial intelligence (AI) tools and computer vision algorithms, the accuracy of detection can be more accurate and can help to overcome these issues. This paper proposes a multi-task deep-learning-based method for lung infection segmentation using CT-scan images. Our proposed method starts by segmenting the lung regions that can be infected. Then, segmenting the infections in these regions. Also, to perform a multi-class segmentation the proposed model is trained using the two-stream inputs. The multi-task learning used in this paper allows us to overcome shortage of labeled data. Also, the multi-input stream allows the model to do the learning on many features that can improve the results. To evaluate the proposed method, many features have been used. Also, from the experiments, the proposed method can segment lung infections with a high degree performance even with shortage of data and labeled images. In addition, comparing with the state-of-the-art method our method achieves good performance results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge