Najibesadat Sadati
Representation Learning with Autoencoders for Electronic Health Records: A Comparative Study
Sep 20, 2019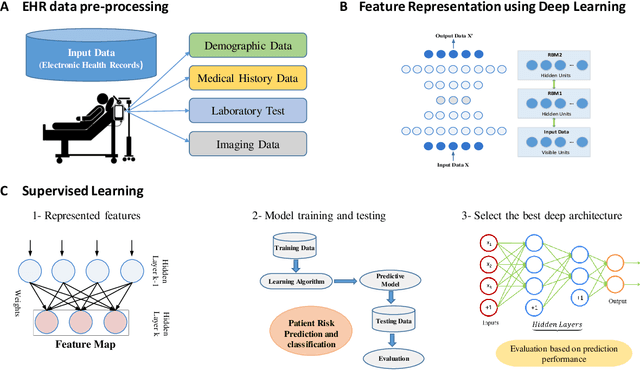
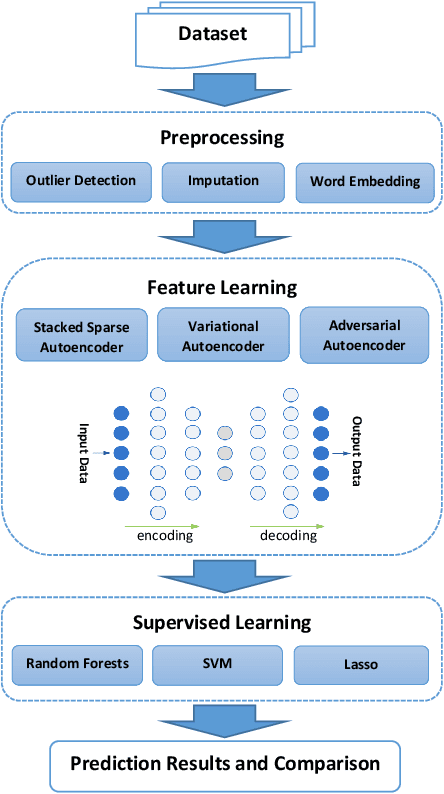
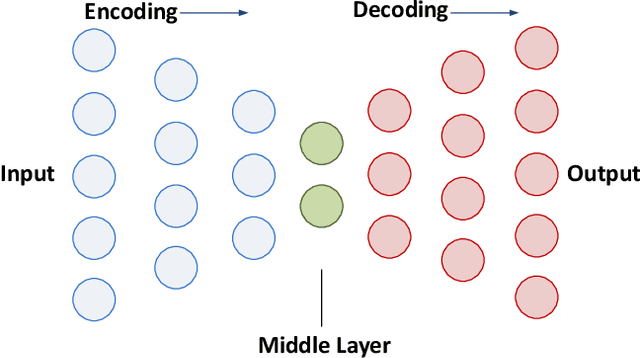
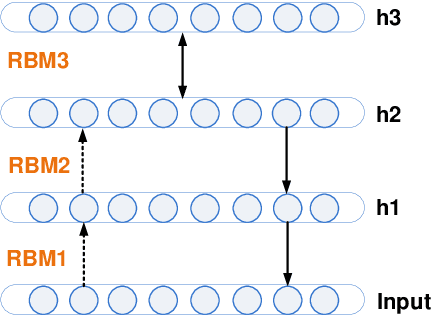
Abstract:Increasing volume of Electronic Health Records (EHR) in recent years provides great opportunities for data scientists to collaborate on different aspects of healthcare research by applying advanced analytics to these EHR clinical data. A key requirement however is obtaining meaningful insights from high dimensional, sparse and complex clinical data. Data science approaches typically address this challenge by performing feature learning in order to build more reliable and informative feature representations from clinical data followed by supervised learning. In this paper, we propose a predictive modeling approach based on deep learning based feature representations and word embedding techniques. Our method uses different deep architectures (stacked sparse autoencoders, deep belief network, adversarial autoencoders and variational autoencoders) for feature representation in higher-level abstraction to obtain effective and robust features from EHRs, and then build prediction models on top of them. Our approach is particularly useful when the unlabeled data is abundant whereas labeled data is scarce. We investigate the performance of representation learning through a supervised learning approach. Our focus is to present a comparative study to evaluate the performance of different deep architectures through supervised learning and provide insights in the choice of deep feature representation techniques. Our experiments demonstrate that for small data sets, stacked sparse autoencoder demonstrates a superior generality performance in prediction due to sparsity regularization whereas variational autoencoders outperform the competing approaches for large data sets due to its capability of learning the representation distribution
A Deep Active Survival Analysis Approach for Precision Treatment Recommendations: Application of Prostate Cancer
Apr 10, 2018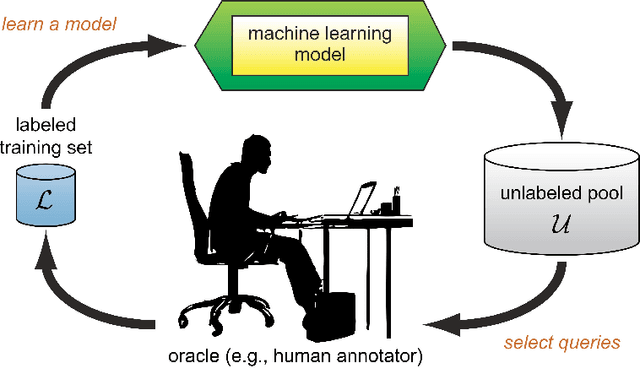
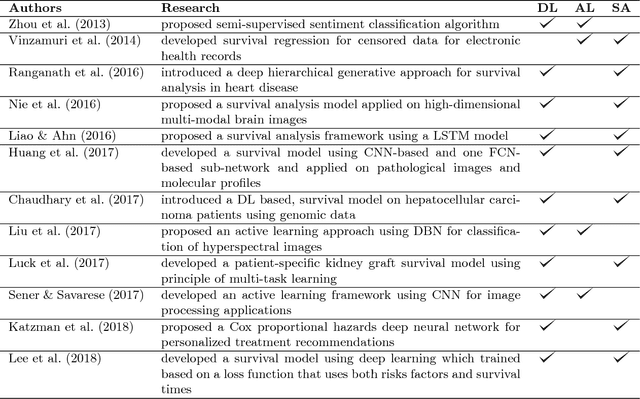
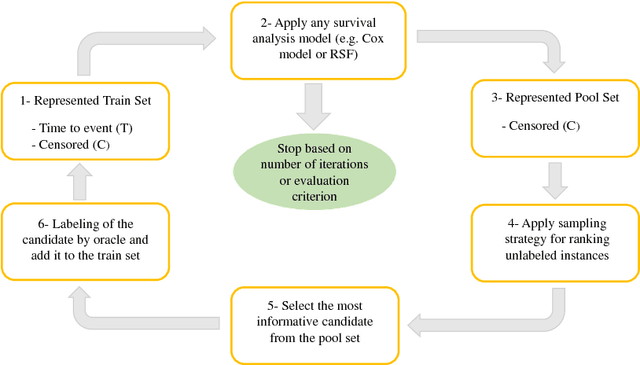
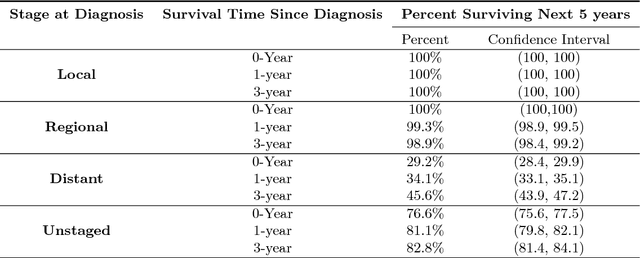
Abstract:Survival analysis has been developed and applied in the number of areas including manufacturing, finance, economics and healthcare. In healthcare domain, usually clinical data are high-dimensional, sparse and complex and sometimes there exists few amount of time-to-event (labeled) instances. Therefore building an accurate survival model from electronic health records is challenging. With this motivation, we address this issue and provide a new survival analysis framework using deep learning and active learning with a novel sampling strategy. First, our approach provides better representation with lower dimensions from clinical features using labeled (time-to-event) and unlabeled (censored) instances and then actively trains the survival model by labeling the censored data using an oracle. As a clinical assistive tool, we introduce a simple effective treatment recommendation approach based on our survival model. In the experimental study, we apply our approach on SEER-Medicare data related to prostate cancer among African-Americans and white patients. The results indicate that our approach outperforms significantly than baseline models.
A Predictive Approach Using Deep Feature Learning for Electronic Medical Records: A Comparative Study
Jan 06, 2018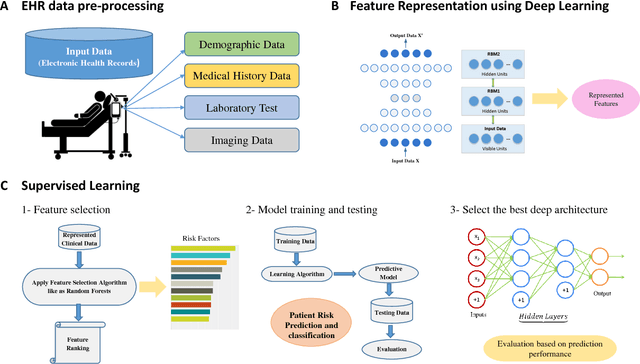

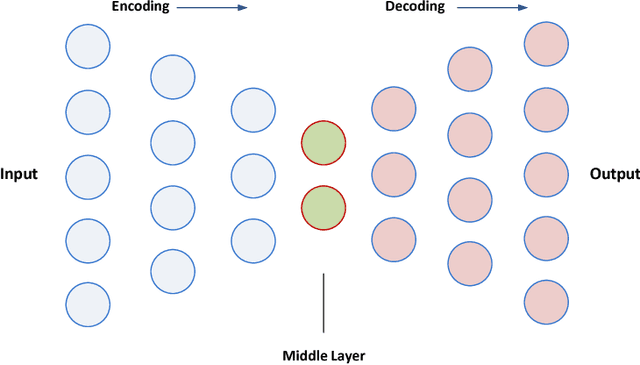
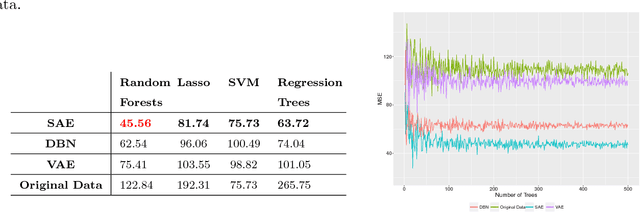
Abstract:Massive amount of electronic medical records accumulating from patients and populations motivates clinicians and data scientists to collaborate for the advanced analytics to extract knowledge that is essential to address the extensive personalized insights needed for patients, clinicians, providers, scientists, and health policy makers. In this paper, we propose a new predictive approach based on feature representation using deep feature learning and word embedding techniques. Our method uses different deep architectures for feature representation in higher-level abstraction to obtain effective and more robust features from EMRs, and then build prediction models on the top of them. Our approach is particularly useful when the unlabeled data is abundant whereas labeled one is scarce. We investigate the performance of representation learning through a supervised approach. First, we apply our method on a small dataset related to a specific precision medicine problem, which focuses on prediction of left ventricular mass indexed to body surface area (LVMI) as an indicator of heart damage risk in a vulnerable demographic subgroup (African-Americans). Then we use two large datasets from eICU collaborative research database to predict the length of stay in Cardiac-ICU and Neuro-ICU based on high dimensional features. Finally we provide a comparative study and show that our predictive approach leads to better results in comparison with others.
SUBIC: A Supervised Bi-Clustering Approach for Precision Medicine
Sep 26, 2017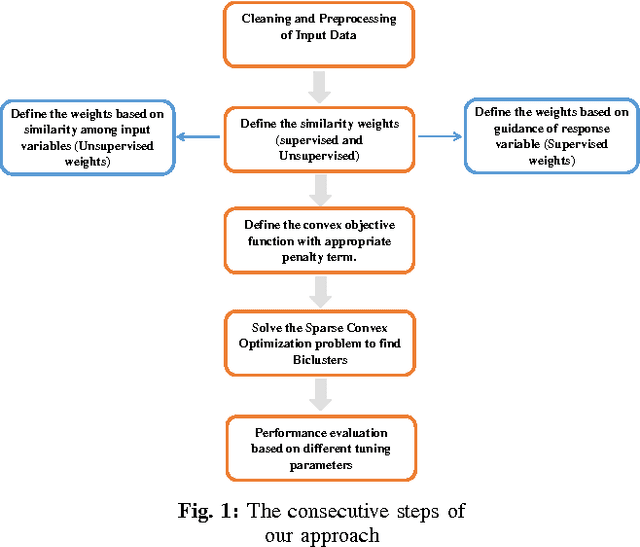
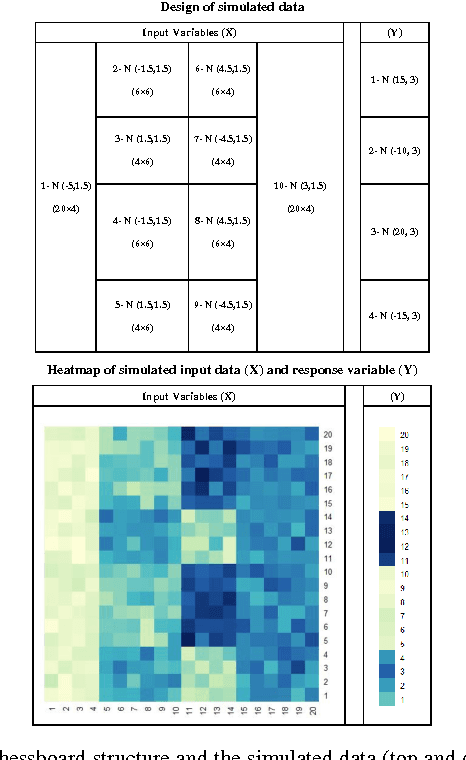
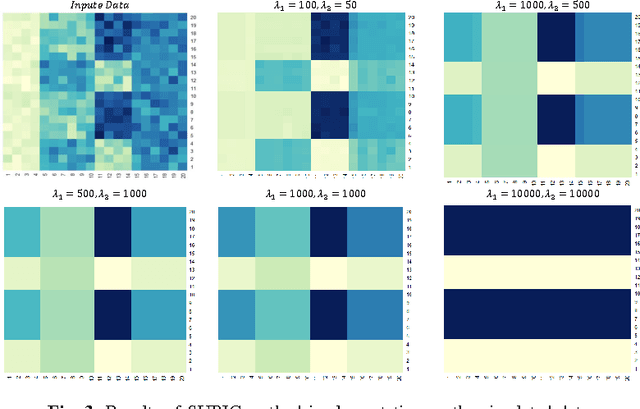
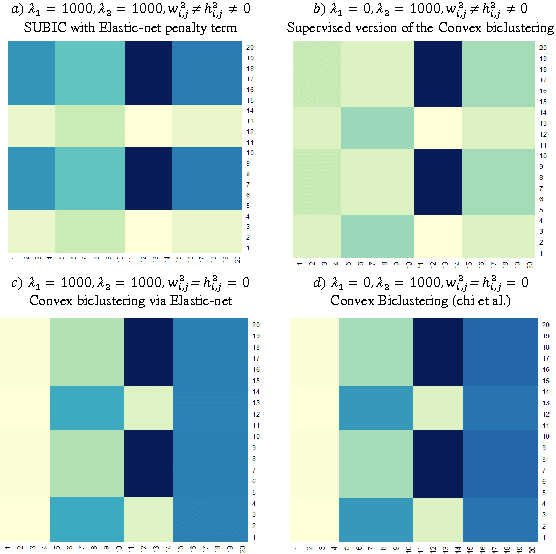
Abstract:Traditional medicine typically applies one-size-fits-all treatment for the entire patient population whereas precision medicine develops tailored treatment schemes for different patient subgroups. The fact that some factors may be more significant for a specific patient subgroup motivates clinicians and medical researchers to develop new approaches to subgroup detection and analysis, which is an effective strategy to personalize treatment. In this study, we propose a novel patient subgroup detection method, called Supervised Biclustring (SUBIC) using convex optimization and apply our approach to detect patient subgroups and prioritize risk factors for hypertension (HTN) in a vulnerable demographic subgroup (African-American). Our approach not only finds patient subgroups with guidance of a clinically relevant target variable but also identifies and prioritizes risk factors by pursuing sparsity of the input variables and encouraging similarity among the input variables and between the input and target variables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge