Naiyu Wang
DEPT: Deep Extreme Point Tracing for Ultrasound Image Segmentation
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Automatic medical image segmentation plays a crucial role in computer aided diagnosis. However, fully supervised learning approaches often require extensive and labor-intensive annotation efforts. To address this challenge, weakly supervised learning methods, particularly those using extreme points as supervisory signals, have the potential to offer an effective solution. In this paper, we introduce Deep Extreme Point Tracing (DEPT) integrated with Feature-Guided Extreme Point Masking (FGEPM) algorithm for ultrasound image segmentation. Notably, our method generates pseudo labels by identifying the lowest-cost path that connects all extreme points on the feature map-based cost matrix. Additionally, an iterative training strategy is proposed to refine pseudo labels progressively, enabling continuous network improvement. Experimental results on two public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method. The performance of our method approaches that of the fully supervised method and outperforms several existing weakly supervised methods.
A Practical Cross-Device Federated Learning Framework over 5G Networks
Apr 18, 2022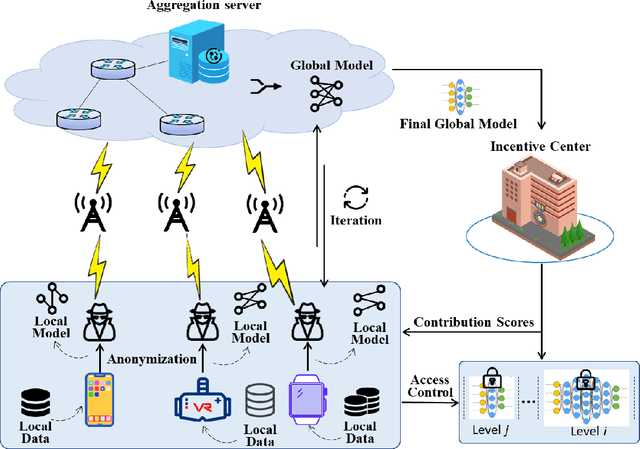
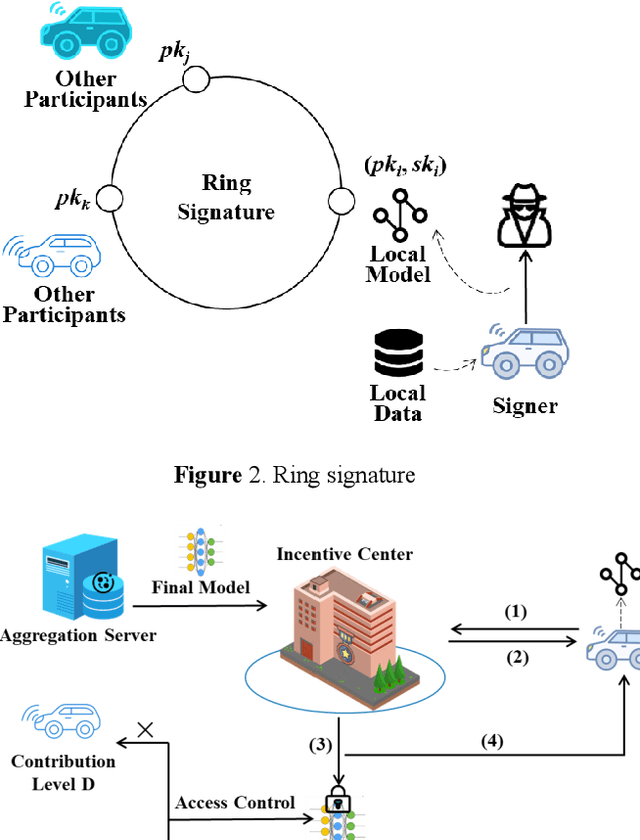
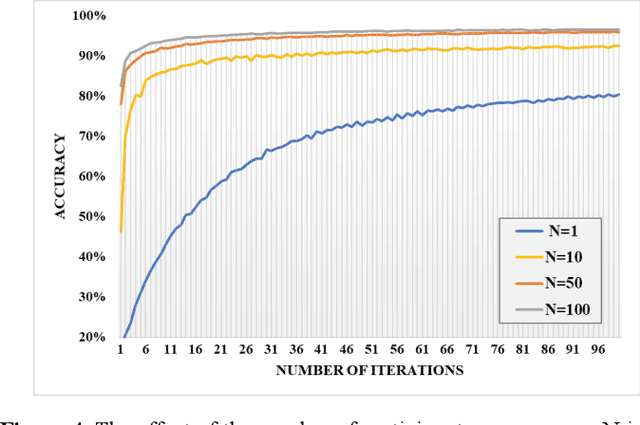
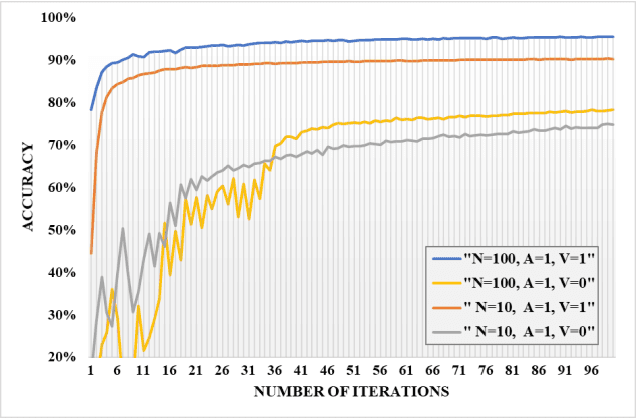
Abstract:The concept of federated learning (FL) was first proposed by Google in 2016. Thereafter, FL has been widely studied for the feasibility of application in various fields due to its potential to make full use of data without compromising the privacy. However, limited by the capacity of wireless data transmission, the employment of federated learning on mobile devices has been making slow progress in practical. The development and commercialization of the 5th generation (5G) mobile networks has shed some light on this. In this paper, we analyze the challenges of existing federated learning schemes for mobile devices and propose a novel cross-device federated learning framework, which utilizes the anonymous communication technology and ring signature to protect the privacy of participants while reducing the computation overhead of mobile devices participating in FL. In addition, our scheme implements a contribution-based incentive mechanism to encourage mobile users to participate in FL. We also give a case study of autonomous driving. Finally, we present the performance evaluation of the proposed scheme and discuss some open issues in federated learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge