Nai-Wei Lo
Deep Learning-Based Arrhythmia Detection Using RR-Interval Framed Electrocardiograms
Dec 01, 2020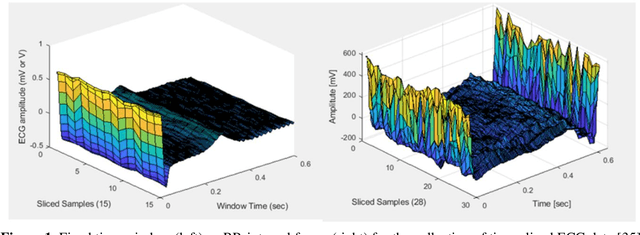
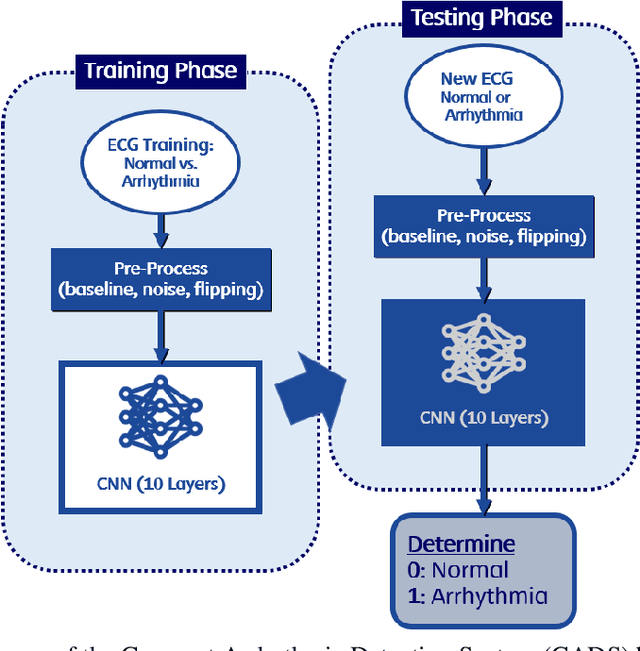
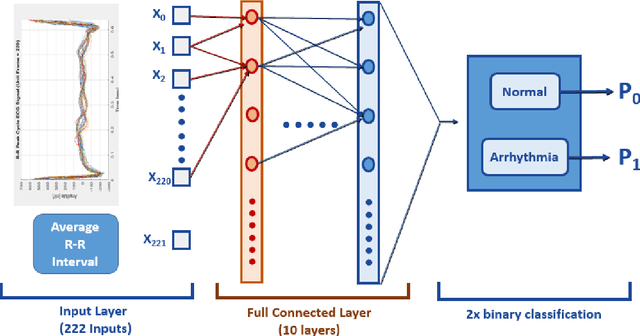
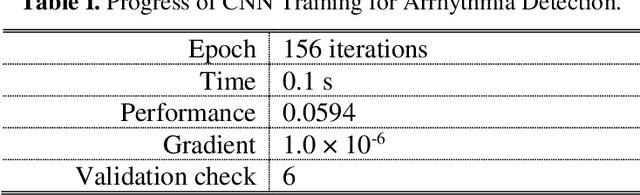
Abstract:Deep learning applied to electrocardiogram (ECG) data can be used to achieve personal authentication in biometric security applications, but it has not been widely used to diagnose cardiovascular disorders. We developed a deep learning model for the detection of arrhythmia in which time-sliced ECG data representing the distance between successive R-peaks are used as the input for a convolutional neural network (CNN). The main objective is developing the compact deep learning based detect system which minimally uses the dataset but delivers the confident accuracy rate of the Arrhythmia detection. This compact system can be implemented in wearable devices or real-time monitoring equipment because the feature extraction step is not required for complex ECG waveforms, only the R-peak data is needed. The results of both tests indicated that the Compact Arrhythmia Detection System (CADS) matched the performance of conventional systems for the detection of arrhythmia in two consecutive test runs. All features of the CADS are fully implemented and publicly available in MATLAB.
A Machine Learning Framework for Biometric Authentication using Electrocardiogram
Apr 09, 2019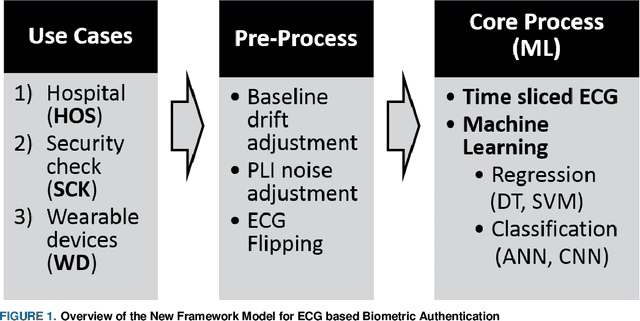
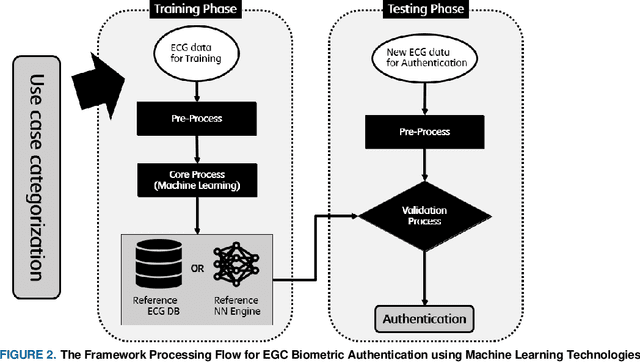
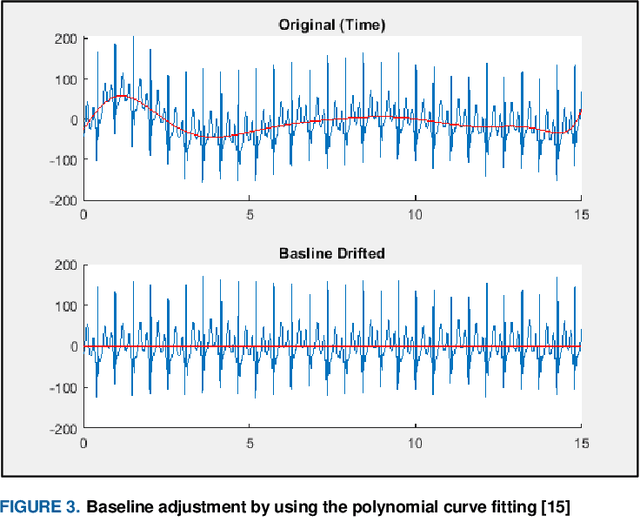
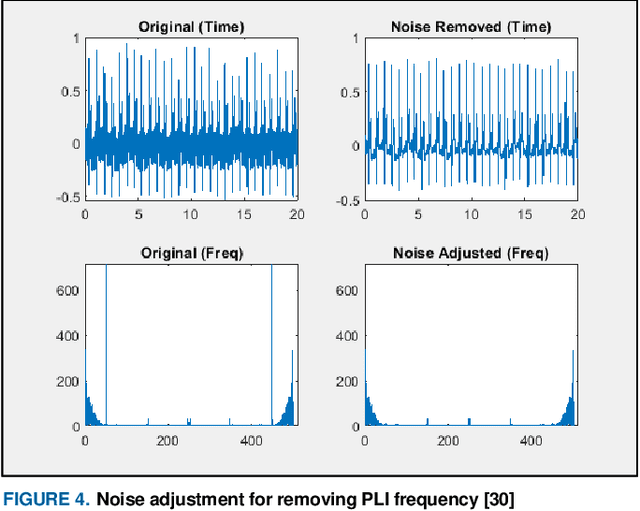
Abstract:This paper introduces a framework for how to appropriately adopt and adjust Machine Learning (ML) techniques used to construct Electrocardiogram (ECG) based biometric authentication schemes. The proposed framework can help investigators and developers on ECG based biometric authentication mechanisms define the boundaries of required datasets and get training data with good quality. To determine the boundaries of datasets, use case analysis is adopted. Based on various application scenarios on ECG based authentication, three distinct use cases (or authentication categories) are developed. With more qualified training data given to corresponding machine learning schemes, the precision on ML-based ECG biometric authentication mechanisms is increased in consequence. ECG time slicing technique with the R-peak anchoring is utilized in this framework to acquire ML training data with good quality. In the proposed framework four new measure metrics are introduced to evaluate the quality of ML training and testing data. In addition, a Matlab toolbox, containing all proposed mechanisms, metrics and sample data with demonstrations using various ML techniques, is developed and publicly available for further investigation. For developing ML-based ECG biometric authentication, the proposed framework can guide researchers to prepare the proper ML setups and the ML training datasets along with three identified user case scenarios. For researchers adopting ML techniques to design new schemes in other research domains, the proposed framework is still useful for generating ML-based training and testing datasets with good quality and utilizing new measure metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge