Muthuraman Chidambaram
Learning Cross-Lingual Sentence Representations via a Multi-task Dual-Encoder Model
Oct 30, 2018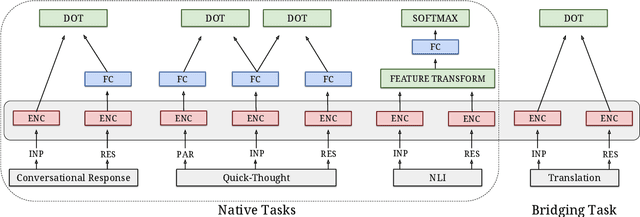
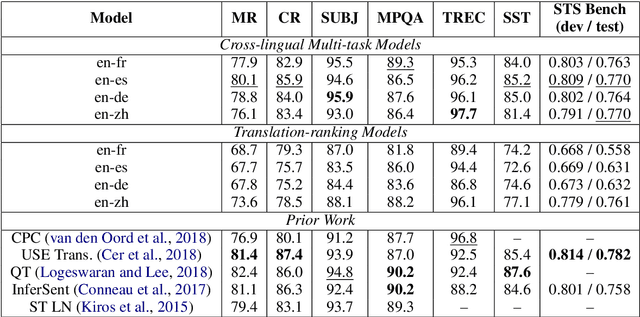
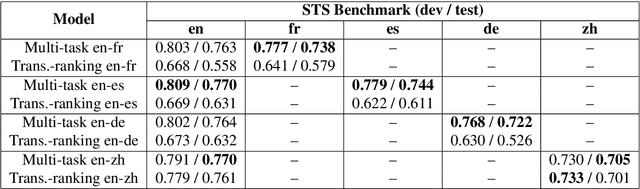
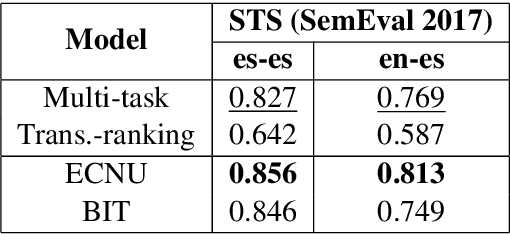
Abstract:Neural language models have been shown to achieve an impressive level of performance on a number of language processing tasks. The majority of these models, however, are limited to producing predictions for only English texts due to limited amounts of labeled data available in other languages. One potential method for overcoming this issue is learning cross-lingual text representations that can be used to transfer the performance from training on English tasks to non-English tasks, despite little to no task-specific non-English data. In this paper, we explore a natural setup for learning cross-lingual sentence representations: the dual-encoder. We provide a comprehensive evaluation of our cross-lingual representations on a number of monolingual, cross-lingual, and zero-shot/few-shot learning tasks, and also give an analysis of different learned cross-lingual embedding spaces.
Style Transfer Generative Adversarial Networks: Learning to Play Chess Differently
May 07, 2017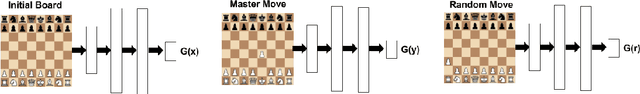
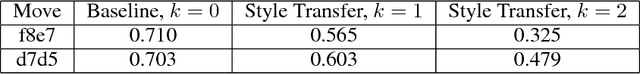
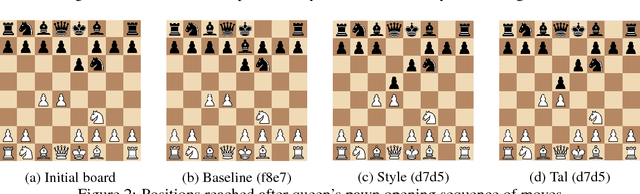
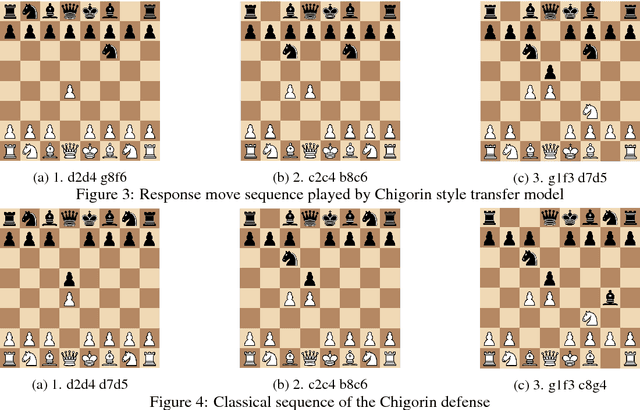
Abstract:The idea of style transfer has largely only been explored in image-based tasks, which we attribute in part to the specific nature of loss functions used for style transfer. We propose a general formulation of style transfer as an extension of generative adversarial networks, by using a discriminator to regularize a generator with an otherwise separate loss function. We apply our approach to the task of learning to play chess in the style of a specific player, and present empirical evidence for the viability of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge