Muhammad Umer Anwaar
On Leveraging Variational Graph Embeddings for Open World Compositional Zero-Shot Learning
Apr 23, 2022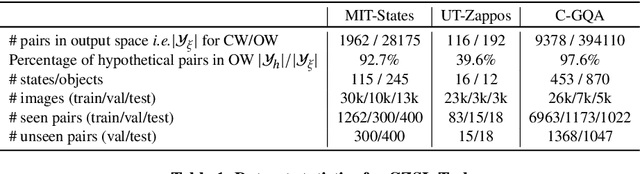
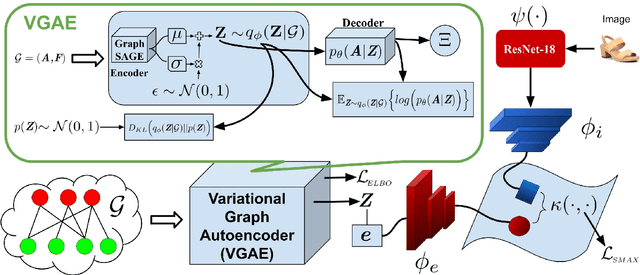
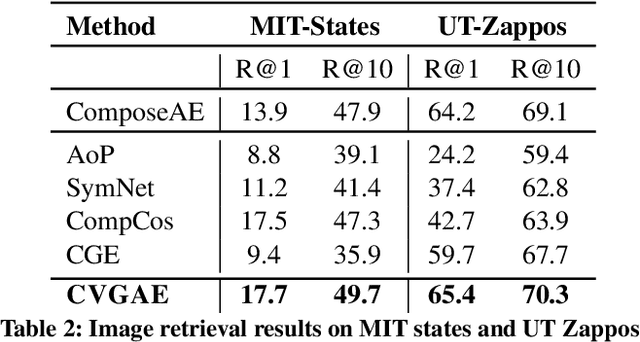
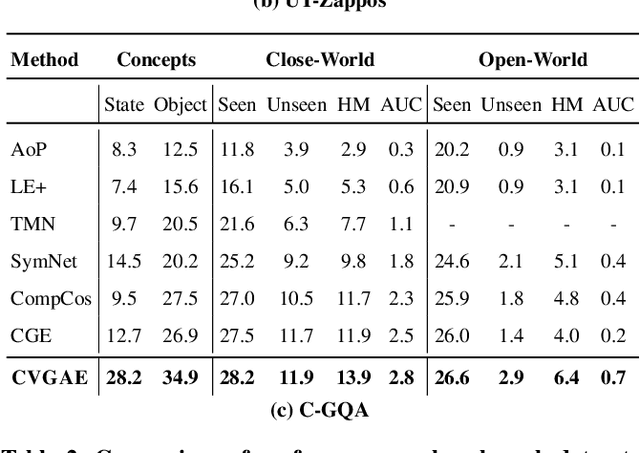
Abstract:Humans are able to identify and categorize novel compositions of known concepts. The task in Compositional Zero-Shot learning (CZSL) is to learn composition of primitive concepts, i.e. objects and states, in such a way that even their novel compositions can be zero-shot classified. In this work, we do not assume any prior knowledge on the feasibility of novel compositions i.e.open-world setting, where infeasible compositions dominate the search space. We propose a Compositional Variational Graph Autoencoder (CVGAE) approach for learning the variational embeddings of the primitive concepts (nodes) as well as feasibility of their compositions (via edges). Such modelling makes CVGAE scalable to real-world application scenarios. This is in contrast to SOTA method, CGE, which is computationally very expensive. e.g.for benchmark C-GQA dataset, CGE requires 3.94 x 10^5 nodes, whereas CVGAE requires only 1323 nodes. We learn a mapping of the graph and image embeddings onto a common embedding space. CVGAE adopts a deep metric learning approach and learns a similarity metric in this space via bi-directional contrastive loss between projected graph and image embeddings. We validate the effectiveness of our approach on three benchmark datasets.We also demonstrate via an image retrieval task that the representations learnt by CVGAE are better suited for compositional generalization.
Variational Embeddings for Community Detection and Node Representation
Jan 11, 2021

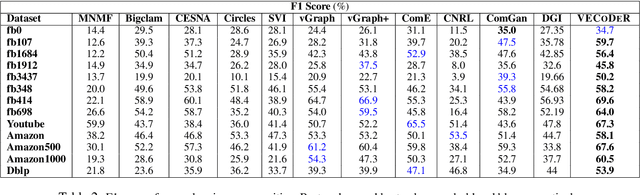
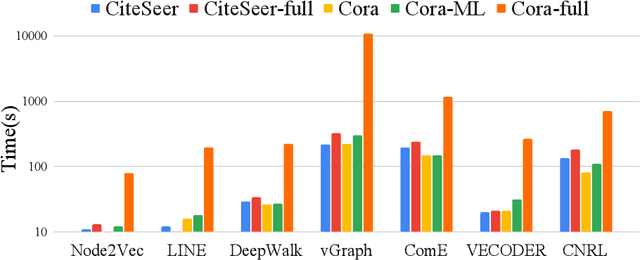
Abstract:In this paper, we study how to simultaneously learn two highly correlated tasks of graph analysis, i.e., community detection and node representation learning. We propose an efficient generative model called VECoDeR for jointly learning Variational Embeddings for Community Detection and node Representation. VECoDeR assumes that every node can be a member of one or more communities. The node embeddings are learned in such a way that connected nodes are not only "closer" to each other but also share similar community assignments. A joint learning framework leverages community-aware node embeddings for better community detection. We demonstrate on several graph datasets that VECoDeR effectively out-performs many competitive baselines on all three tasks i.e. node classification, overlapping community detection and non-overlapping community detection. We also show that VECoDeR is computationally efficient and has quite robust performance with varying hyperparameters.
Metapath- and Entity-aware Graph Neural Network for Recommendation
Oct 22, 2020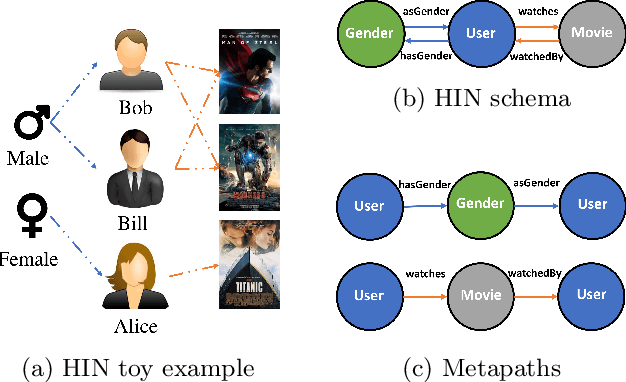
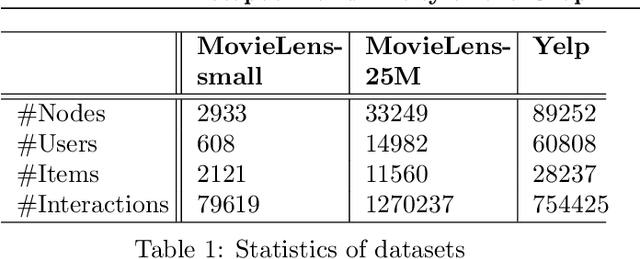
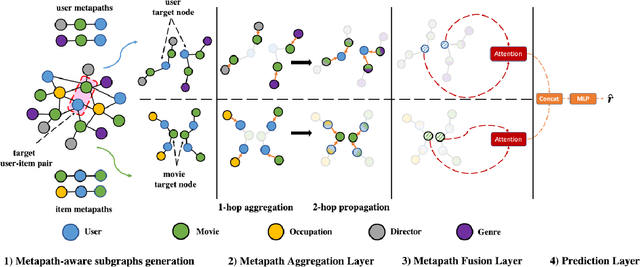
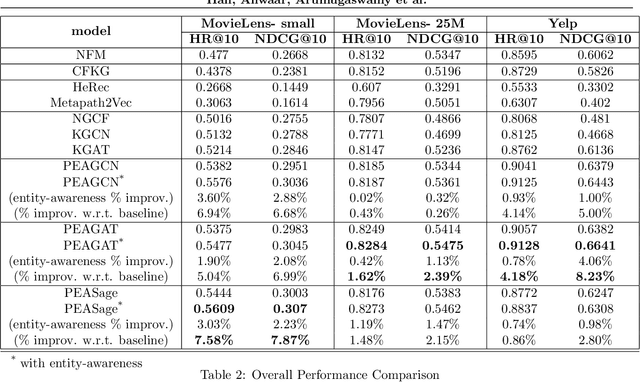
Abstract:Due to the shallow structure, classic graph neural networks (GNNs) failed in modelling high-order graph structures that deliver critical insights of task relevant relations. The negligence of those insights lead to insufficient distillation of collaborative signals in recommender systems. In this paper, we propose PEAGNN, a unified GNN framework tailored for recommendation tasks, which is capable of exploiting the rich semantics in metapaths. PEAGNN trains multilayer GNNs to perform metapath-aware information aggregation on collaborative subgraphs, $h$-hop subgraphs around the target user-item pairs. After the attentive fusion of aggregated information from different metapaths, a graph-level representation is then extracted for matching score prediction. To leverage the local structure of collaborative subgraphs, we present entity-awareness that regularizes node embedding with the presence of features in a contrastive manner. Moreover, PEAGNN is compatible with the mainstream GNN structures such as GCN, GAT and GraphSage. The empirical analysis on three public datasets demonstrate that our model outperforms or is at least on par with other competitive baselines. Further analysis indicates that trained PEAGNN automatically derives meaningful metapath combinations from the given metapaths.
Compositional Learning of Image-Text Query for Image Retrieval
Jun 28, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the problem of retrieving images from a database based on a multi-modal (image-text) query. Specifically, the query text prompts some modification in the query image and the task is to retrieve images with the desired modifications. For instance, a user of an E-Commerce platform is interested in buying a dress, which should look similar to her friend's dress, but the dress should be of white color with a ribbon sash. In this case, we would like the algorithm to retrieve some dresses with desired modifications in the query dress. We propose an autoencoder based model, ComposeAE, to learn the composition of image and text query for retrieving images. We adopt a deep metric learning approach and learn a metric that pushes composition of source image and text query closer to the target images. We also propose a rotational symmetry constraint on the optimization problem. Our approach is able to outperform the state-of-the-art method TIRG \cite{TIRG} on three benchmark datasets, namely: MIT-States, Fashion200k and Fashion IQ. In order to ensure fair comparison, we introduce strong baselines by enhancing TIRG method. To ensure reproducibility of the results, we publish our code here: \url{https://anonymous.4open.science/r/d1babc3c-0e72-448a-8594-b618bae876dc/}.
Counterfactual Learning from Logs for Improved Ranking of E-Commerce Products
Jul 24, 2019



Abstract:Improved search quality enhances users' satisfaction, which directly impacts sales growth of an E-Commerce (E-Com) platform. Learning to Rank (LTR) algorithms require relevance judgments on products for learning. In real commercial scenarios, getting such judgments poses an immense challenge in application of LTR algorithms. In the literature, it is proposed to employ user feedback signals such as clicks, orders etc to generate relevance judgments. It is done by aggregating the logged data and calculating click rate, order rate etc of products, for each query in the logs. In this paper, we advocate counterfactual risk minimization (CRM) approach which circumvents the need of such data pre-processing and is better suited for learning from logged data, i.e. contextual bandit feedback. Due to unavailability of public E-Com LTR dataset, we provide Mercateo dataset from our E-Com platform. This dataset contains information of queries from real users, actions taken by the policy running on the system, probability of these actions and feedback of users on those actions. Our commercial dataset contains more than 10 million click log entries and 1 million order logs from a catalogue of about 3.5 million products and 3000 queries. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work which examines effectiveness of CRM approach in learning ranking model from real-world logged data. Our empirical evaluation shows that CRM approach is able to learn directly from logged contextual-bandit feedback. Our method outperforms full-information loss on deep neural network model as well as traditional ranking models like LambdaMART. These findings have significant implications for improving the quality of search in E-Com platforms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge