Muhammad Kamran
Transformer Based Building Boundary Reconstruction using Attraction Field Maps
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:In recent years, the number of remote satellites orbiting the Earth has grown significantly, streaming vast amounts of high-resolution visual data to support diverse applications across civil, public, and military domains. Among these applications, the generation and updating of spatial maps of the built environment have become critical due to the extensive coverage and detailed imagery provided by satellites. However, reconstructing spatial maps from satellite imagery is a complex computer vision task, requiring the creation of high-level object representations, such as primitives, to accurately capture the built environment. While the past decade has witnessed remarkable advancements in object detection and representation using visual data, primitives-based object representation remains a persistent challenge in computer vision. Consequently, high-quality spatial maps often rely on labor-intensive and manual processes. This paper introduces a novel deep learning methodology leveraging Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) to address these challenges in building footprint reconstruction. The proposed approach enhances performance by incorporating geometric regularity into building boundaries, integrating multi-scale and multi-resolution features, and embedding Attraction Field Maps into the network. These innovations provide a scalable and precise solution for automated building footprint extraction from a single satellite image, paving the way for impactful applications in urban planning, disaster management, and large-scale spatial analysis. Our model, Decoupled-PolyGCN, outperforms existing methods by 6% in AP and 10% in AR, demonstrating its ability to deliver accurate and regularized building footprints across diverse and challenging scenarios.
Enhancing Polygonal Building Segmentation via Oriented Corners
Jul 17, 2024Abstract:The growing demand for high-resolution maps across various applications has underscored the necessity of accurately segmenting building vectors from overhead imagery. However, current deep neural networks often produce raster data outputs, leading to the need for extensive post-processing that compromises the fidelity, regularity, and simplicity of building representations. In response, this paper introduces a novel deep convolutional neural network named OriCornerNet, which directly extracts delineated building polygons from input images. Specifically, our approach involves a deep model that predicts building footprint masks, corners, and orientation vectors that indicate directions toward adjacent corners. These predictions are then used to reconstruct an initial polygon, followed by iterative refinement using a graph convolutional network that leverages semantic and geometric features. Our method inherently generates simplified polygons by initializing the refinement process with predicted corners. Also, including geometric information from oriented corners contributes to producing more regular and accurate results. Performance evaluations conducted on SpaceNet Vegas and CrowdAI-small datasets demonstrate the competitive efficacy of our approach compared to the state-of-the-art in building segmentation from overhead imagery.
Boundary Regularized Building Footprint Extraction From Satellite Images Using Deep Neural Network
Jun 23, 2020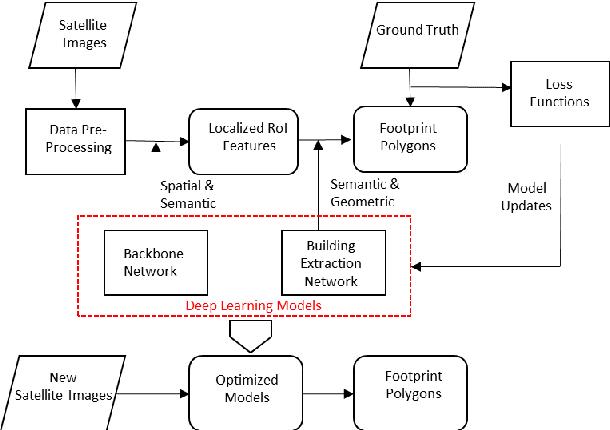
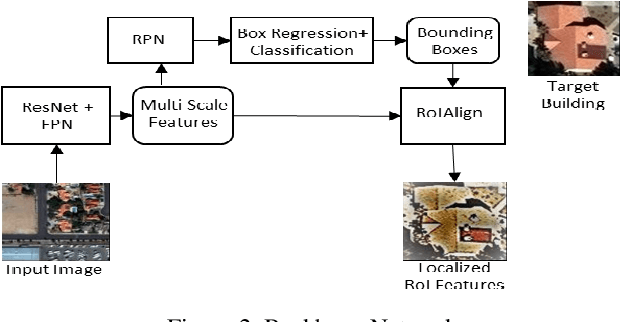
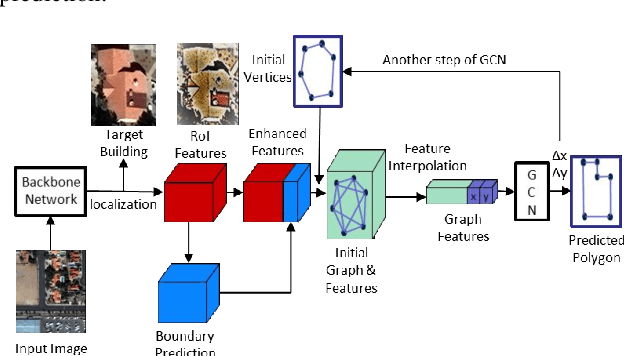
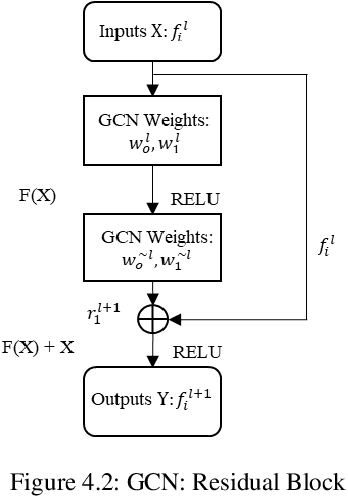
Abstract:In recent years, an ever-increasing number of remote satellites are orbiting the Earth which streams vast amount of visual data to support a wide range of civil, public and military applications. One of the key information obtained from satellite imagery is to produce and update spatial maps of built environment due to its wide coverage with high resolution data. However, reconstructing spatial maps from satellite imagery is not a trivial vision task as it requires reconstructing a scene or object with high-level representation such as primitives. For the last decade, significant advancement in object detection and representation using visual data has been achieved, but the primitive-based object representation still remains as a challenging vision task. Thus, a high-quality spatial map is mainly produced through complex labour-intensive processes. In this paper, we propose a novel deep neural network, which enables to jointly detect building instance and regularize noisy building boundary shapes from a single satellite imagery. The proposed deep learning method consists of a two-stage object detection network to produce region of interest (RoI) features and a building boundary extraction network using graph models to learn geometric information of the polygon shapes. Extensive experiments show that our model can accomplish multi-tasks of object localization, recognition, semantic labelling and geometric shape extraction simultaneously. In terms of building extraction accuracy, computation efficiency and boundary regularization performance, our model outperforms the state-of-the-art baseline models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge