Muhammad Hanif Lashari
Enhanced Position Estimation in Tactile Internet-Enabled Remote Robotic Surgery Using MOESP-Based Kalman Filter
Jan 27, 2025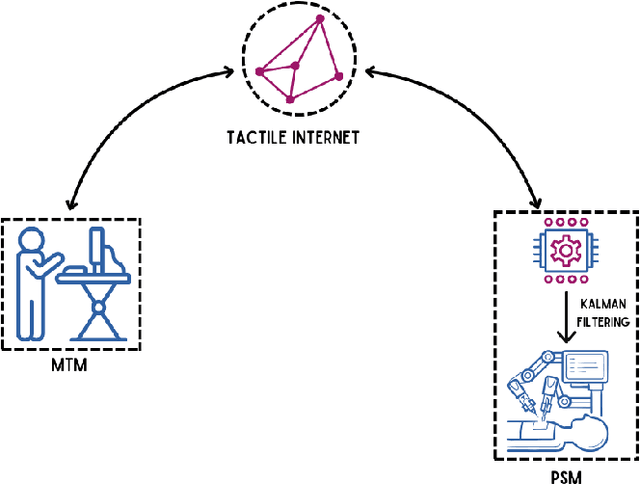
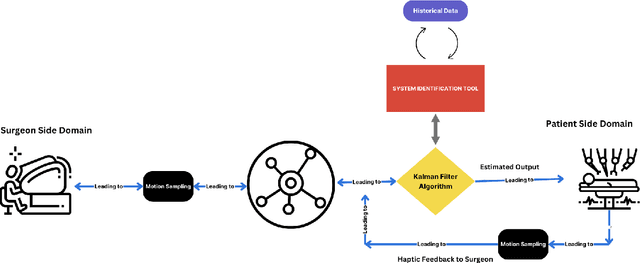


Abstract:Accurately estimating the position of a patient's side robotic arm in real time during remote surgery is a significant challenge, especially within Tactile Internet (TI) environments. This paper presents a new and efficient method for position estimation using a Kalman Filter (KF) combined with the Multivariable Output-Error State Space (MOESP) method for system identification. Unlike traditional approaches that require prior knowledge of the system's dynamics, this study uses the JIGSAW dataset, a comprehensive collection of robotic surgical data, along with input from the Master Tool Manipulator (MTM) to derive the state-space model directly. The MOESP method allows accurate modeling of the Patient Side Manipulator (PSM) dynamics without prior system models, improving the KF's performance under simulated network conditions, including delays, jitter, and packet loss. These conditions mimic real-world challenges in Tactile Internet applications. The findings demonstrate the KF's improved resilience and accuracy in state estimation, achieving over 95 percent accuracy despite network-induced uncertainties.
A Predictive Approach for Enhancing Accuracy in Remote Robotic Surgery Using Informer Model
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Precise and real-time estimation of the robotic arm's position on the patient's side is essential for the success of remote robotic surgery in Tactile Internet (TI) environments. This paper presents a prediction model based on the Transformer-based Informer framework for accurate and efficient position estimation. Additionally, it combines a Four-State Hidden Markov Model (4-State HMM) to simulate realistic packet loss scenarios. The proposed approach addresses challenges such as network delays, jitter, and packet loss to ensure reliable and precise operation in remote surgical applications. The method integrates the optimization problem into the Informer model by embedding constraints such as energy efficiency, smoothness, and robustness into its training process using a differentiable optimization layer. The Informer framework uses features such as ProbSparse attention, attention distilling, and a generative-style decoder to focus on position-critical features while maintaining a low computational complexity of O(L log L). The method is evaluated using the JIGSAWS dataset, achieving a prediction accuracy of over 90 percent under various network scenarios. A comparison with models such as TCN, RNN, and LSTM demonstrates the Informer framework's superior performance in handling position prediction and meeting real-time requirements, making it suitable for Tactile Internet-enabled robotic surgery.
Enhancing Precision in Tactile Internet-Enabled Remote Robotic Surgery: Kalman Filter Approach
Jun 06, 2024Abstract:Accurately estimating the position of a patient's side robotic arm in real time in a remote surgery task is a significant challenge, particularly in Tactile Internet (TI) environments. This paper presents a Kalman Filter (KF) based computationally efficient position estimation method. The study also assume no prior knowledge of the dynamic system model of the robotic arm system. Instead, The JIGSAW dataset, which is a comprehensive collection of robotic surgical data, and the Master Tool Manipulator's (MTM) input are utilized to learn the system model using System Identification (SI) toolkit available in Matlab. We further investigate the effectiveness of KF to determine the position of the Patient Side Manipulator (PSM) under simulated network conditions that include delays, jitter, and packet loss. These conditions reflect the typical challenges encountered in real-world Tactile Internet applications. The results of the study highlight KF's resilience and effectiveness in achieving accurate state estimation despite network-induced uncertainties with over 90\% estimation accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge