Mu Tian
A dynamic interactive learning framework for automated 3D medical image segmentation
Dec 11, 2023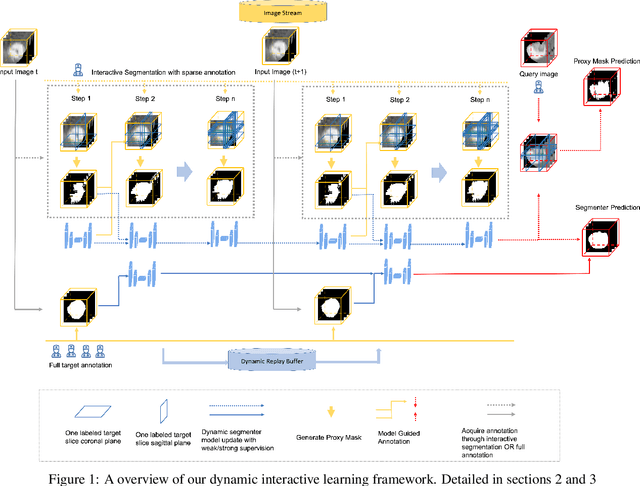
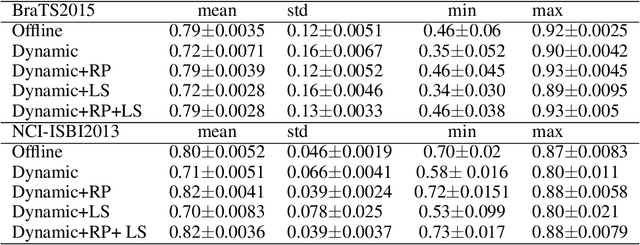
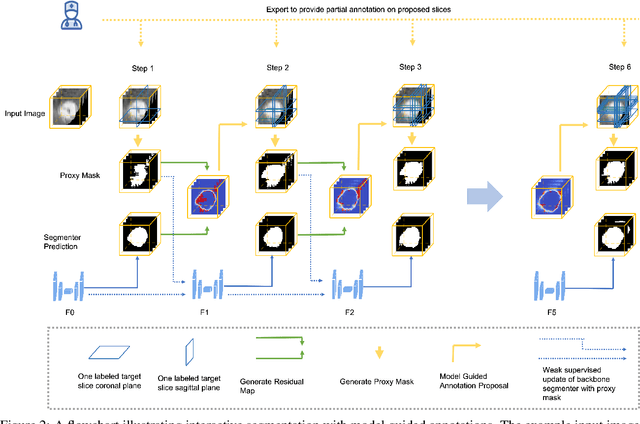
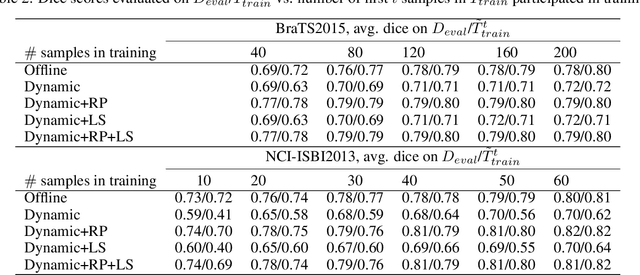
Abstract:Many deep learning based automated medical image segmentation systems, in reality, face difficulties in deployment due to the cost of massive data annotation and high latency in model iteration. We propose a dynamic interactive learning framework that addresses these challenges by integrating interactive segmentation into end-to-end weak supervised learning with streaming tasks. We develop novel replay and label smoothing schemes that overcome catastrophic forgetting and improve online learning robustness. For each image, our multi-round interactive segmentation module simultaneously optimizes both front-end predictions and deep learning segmenter. In each round, a 3D "proxy mask" is propagated from sparse user inputs based on image registration, serving as weak supervision that enable knowledge distillation from the unknown ground truth. In return, the trained segmenter explicitly guides next step's user interventions according to a spatial residual map from consecutive front or back-end predictions. Evaluation on 3D segmentation tasks (NCI-ISBI2013 and BraTS2015) shows that our framework generates online learning performances that match offline training benchmark. In addition, with a 62% reduction in total annotation efforts, our framework produces competitive dice scores comparing to online and offline learning which equipped with full ground truth. Furthermore, such a framework, with its flexibility and responsiveness, could be deployed behind hospital firewall that guarantees data security and easy maintenance.
AttenScribble: Attentive Similarity Learning for Scribble-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Dec 11, 2023Abstract:The success of deep networks in medical image segmentation relies heavily on massive labeled training data. However, acquiring dense annotations is a time-consuming process. Weakly-supervised methods normally employ less expensive forms of supervision, among which scribbles started to gain popularity lately thanks to its flexibility. However, due to lack of shape and boundary information, it is extremely challenging to train a deep network on scribbles that generalizes on unlabeled pixels. In this paper, we present a straightforward yet effective scribble supervised learning framework. Inspired by recent advances of transformer based segmentation, we create a pluggable spatial self-attention module which could be attached on top of any internal feature layers of arbitrary fully convolutional network (FCN) backbone. The module infuses global interaction while keeping the efficiency of convolutions. Descended from this module, we construct a similarity metric based on normalized and symmetrized attention. This attentive similarity leads to a novel regularization loss that imposes consistency between segmentation prediction and visual affinity. This attentive similarity loss optimizes the alignment of FCN encoders, attention mapping and model prediction. Ultimately, the proposed FCN+Attention architecture can be trained end-to-end guided by a combination of three learning objectives: partial segmentation loss, a customized masked conditional random fields and the proposed attentive similarity loss. Extensive experiments on public datasets (ACDC and CHAOS) showed that our framework not just out-performs existing state-of-the-art, but also delivers close performance to fully-supervised benchmark. Code will be available upon publication.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge