Moritz Heusinger
CEREMADE
Federated Learning -- Methods, Applications and beyond
Dec 22, 2022Abstract:In recent years the applications of machine learning models have increased rapidly, due to the large amount of available data and technological progress.While some domains like web analysis can benefit from this with only minor restrictions, other fields like in medicine with patient data are strongerregulated. In particular \emph{data privacy} plays an important role as recently highlighted by the trustworthy AI initiative of the EU or general privacy regulations in legislation. Another major challenge is, that the required training \emph{data is} often \emph{distributed} in terms of features or samples and unavailable for classicalbatch learning approaches. In 2016 Google came up with a framework, called \emph{Federated Learning} to solve both of these problems. We provide a brief overview on existing Methods and Applications in the field of vertical and horizontal \emph{Federated Learning}, as well as \emph{Fderated Transfer Learning}.
Reactive Soft Prototype Computing for Concept Drift Streams
Jul 10, 2020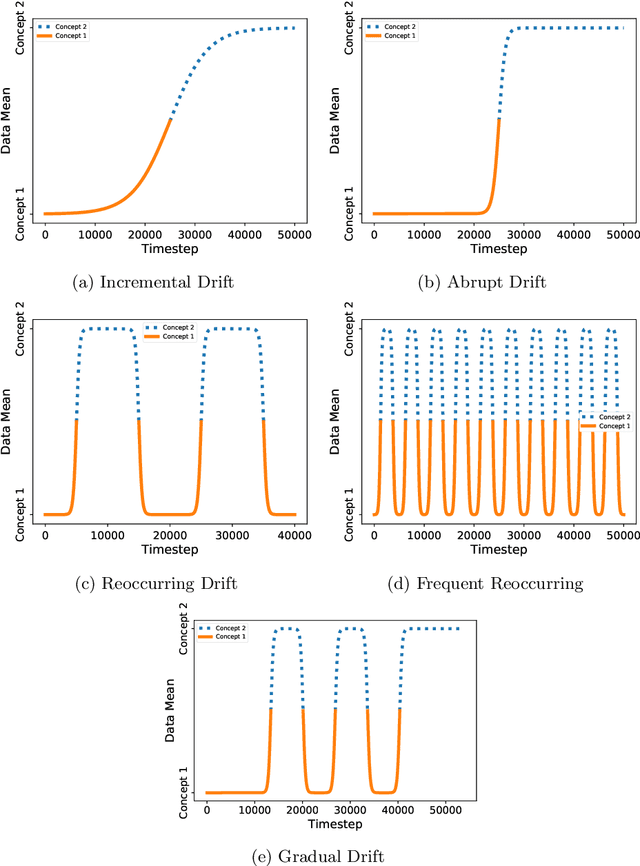
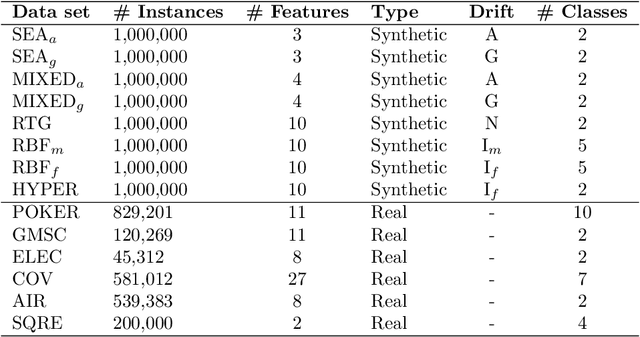
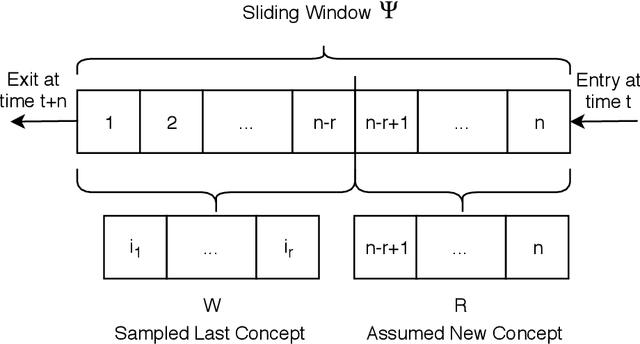
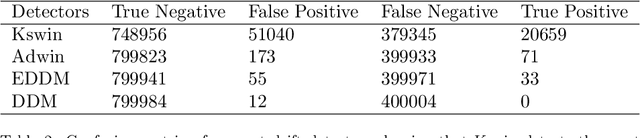
Abstract:The amount of real-time communication between agents in an information system has increased rapidly since the beginning of the decade. This is because the use of these systems, e. g. social media, has become commonplace in today's society. This requires analytical algorithms to learn and predict this stream of information in real-time. The nature of these systems is non-static and can be explained, among other things, by the fast pace of trends. This creates an environment in which algorithms must recognize changes and adapt. Recent work shows vital research in the field, but mainly lack stable performance during model adaptation. In this work, a concept drift detection strategy followed by a prototype-based adaptation strategy is proposed. Validated through experimental results on a variety of typical non-static data, our solution provides stable and quick adjustments in times of change.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge