Mohammad Aminisharifabad
Statistical Method to Model the Quality Inconsistencies of the Welding Process
Feb 24, 2019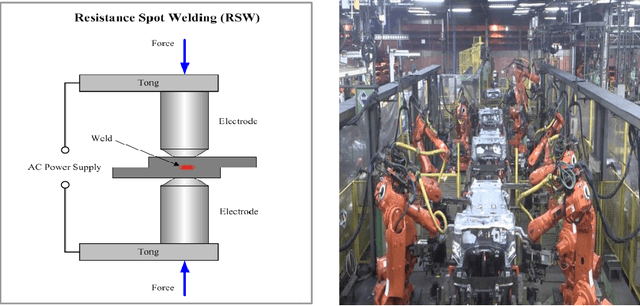
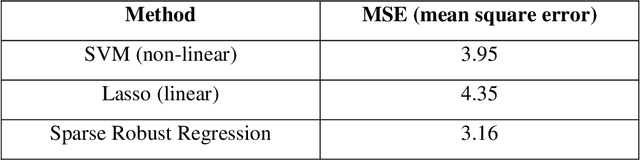
Abstract:Resistance Spot Welding (RSW) is an important manufacturing process that attracts increasing attention in automotive industry. However, due to the complexity of the manufacturing process, the corresponding product quality shows significant inconsistencies even under the same process setup. This paper develops a statistical method to capture the inconsistence of welding quality measurements (e.g., nugget width) based on process parameters to efficiently monitor product quality. The proposed method provides engineering efficiency and cost saving benefit through reduction of physical testing required for weldability and verification. The developed method is applied to the real-world welding process.
Exact Learning of RNA Energy Parameters From Structure
Oct 15, 2013


Abstract:We consider the problem of exact learning of parameters of a linear RNA energy model from secondary structure data. A necessary and sufficient condition for learnability of parameters is derived, which is based on computing the convex hull of union of translated Newton polytopes of input sequences. The set of learned energy parameters is characterized as the convex cone generated by the normal vectors to those facets of the resulting polytope that are incident to the origin. In practice, the sufficient condition may not be satisfied by the entire training data set; hence, computing a maximal subset of training data for which the sufficient condition is satisfied is often desired. We show that problem is NP-hard in general for an arbitrary dimensional feature space. Using a randomized greedy algorithm, we select a subset of RNA STRAND v2.0 database that satisfies the sufficient condition for separate A-U, C-G, G-U base pair counting model. The set of learned energy parameters includes experimentally measured energies of A-U, C-G, and G-U pairs; hence, our parameter set is in agreement with the Turner parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge