Mohamed Elgaar
Linguistic Blind Spots in Clinical Decision Extraction
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Extracting medical decisions from clinical notes is a key step for clinical decision support and patient-facing care summaries. We study how the linguistic characteristics of clinical decisions vary across decision categories and whether these differences explain extraction failures. Using MedDec discharge summaries annotated with decision categories from the Decision Identification and Classification Taxonomy for Use in Medicine (DICTUM), we compute seven linguistic indices for each decision span and analyze span-level extraction recall of a standard transformer model. We find clear category-specific signatures: drug-related and problem-defining decisions are entity-dense and telegraphic, whereas advice and precaution decisions contain more narrative, with higher stopword and pronoun proportions and more frequent hedging and negation cues. On the validation split, exact-match recall is 48%, with large gaps across linguistic strata: recall drops from 58% to 24% from the lowest to highest stopword-proportion bins, and spans containing hedging or negation cues are less likely to be recovered. Under a relaxed overlap-based match criterion, recall increases to 71%, indicating that many errors are span boundary disagreements rather than complete misses. Overall, narrative-style spans--common in advice and precaution decisions--are a consistent blind spot under exact matching, suggesting that downstream systems should incorporate boundary-tolerant evaluation and extraction strategies for clinical decisions.
Curriculum Learning for LLM Pretraining: An Analysis of Learning Dynamics
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Curriculum learning changes the order of pre-training data, but it remains unclear whether it changes the learning trajectory or mainly reorders exposure over a fixed trajectory. We train Pythia models (14M-410M parameters) for 300B tokens under three linguistically motivated curricula-Age-of-Acquisition, word frequency, and Verb Variation (VV)-and compare each against Random ordering; at 1B parameters we compare Random and VV. Across orderings, training follows a shared sequence of latent phases, while curricula mainly change within-phase data exposure. In smaller models (up to 160M parameters), Random ordering exhibits higher gradient noise and stronger late-training output-head spectral saturation, alongside lower final accuracy; curricula reduce both effects at matched compute. At larger scales, saturation differences are smaller and curriculum gains shrink. We formalize the link between difficulty pacing and optimization stability in an idealized analysis based on gradient-variance control, and our results point to a practical takeaway: curricula help by stabilizing within-phase optimization rather than by creating new phases.
P-Masking: Power Law Masking Improves Multi-attribute Controlled Generation
Oct 31, 2024Abstract:We introduce LingGen, a novel approach for controlled text generation that offers precise control over a wide array of linguistic attributes, even as the number of attributes varies. LingGen employs a dynamic P-MASKING strategy, which samples masking rates from a power law distribution during training. This innovative approach enables the model to develop robust representations and adapt its attribute control capabilities across a variable number of attributes, from a single attribute to multiple complex configurations. The P-MASKING technique enhances LingGen's ability to manage different levels of attribute visibility, resulting in superior performance in multi-attribute generation tasks. Our experiments demonstrate that LingGen surpasses current state-of-the-art models in both attribute control accuracy and text fluency, particularly excelling in scenarios with varying attribute demands. Additionally, our ablation studies highlight the effectiveness of P-MASKING and the influence of different base language models on performance. These findings demonstrate LingGen's potential for applications requiring precise and adaptable control over multiple linguistic attributes in text generation.
Multi-Attribute Linguistic Tuning for Controlled Paraphrase Generation
Oct 31, 2024Abstract:We present a novel approach to paraphrase generation that enables precise control and fine-tuning of 40 linguistic attributes for English. Our model is an encoder-decoder architecture that takes as input a source sentence and desired linguistic attributes, and produces paraphrases of the source that satisfy the desired attributes. To guarantee high-quality outputs at inference time, our method is equipped with a quality control mechanism that gradually adjusts the embedding of linguistic attributes to find the nearest and most attainable configuration of desired attributes for paraphrase generation. We evaluate the effectiveness of our method by comparing it to recent controllable generation models. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms baselines in generating paraphrases that satisfy desired linguistic attributes.
MedDec: A Dataset for Extracting Medical Decisions from Discharge Summaries
Aug 23, 2024
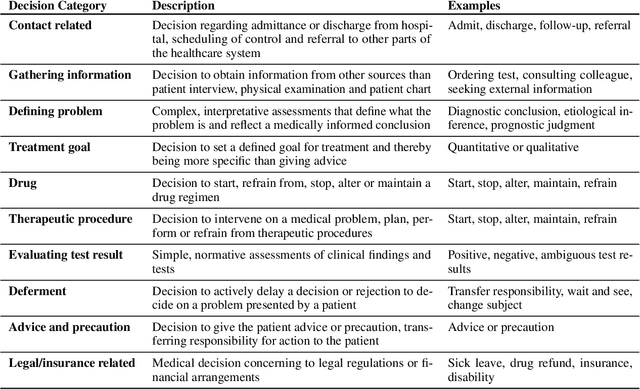
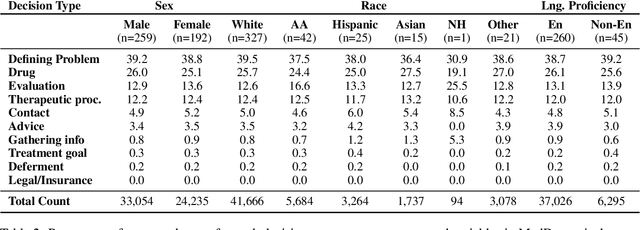
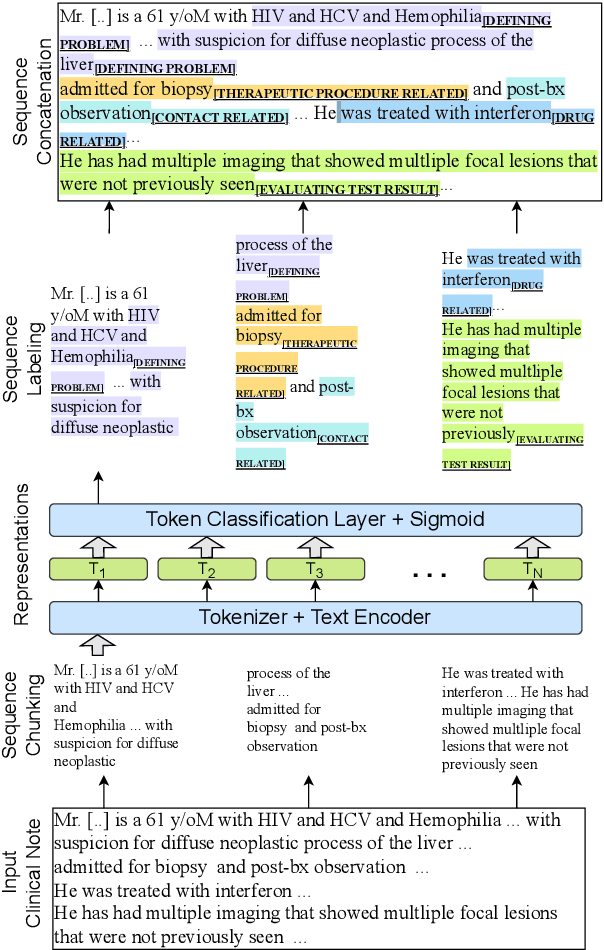
Abstract:Medical decisions directly impact individuals' health and well-being. Extracting decision spans from clinical notes plays a crucial role in understanding medical decision-making processes. In this paper, we develop a new dataset called "MedDec", which contains clinical notes of eleven different phenotypes (diseases) annotated by ten types of medical decisions. We introduce the task of medical decision extraction, aiming to jointly extract and classify different types of medical decisions within clinical notes. We provide a comprehensive analysis of the dataset, develop a span detection model as a baseline for this task, evaluate recent span detection approaches, and employ a few metrics to measure the complexity of data samples. Our findings shed light on the complexities inherent in clinical decision extraction and enable future work in this area of research. The dataset and code are available through https://github.com/CLU-UML/MedDec.
CogniVoice: Multimodal and Multilingual Fusion Networks for Mild Cognitive Impairment Assessment from Spontaneous Speech
Jul 18, 2024Abstract:Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) is a medical condition characterized by noticeable declines in memory and cognitive abilities, potentially affecting individual's daily activities. In this paper, we introduce CogniVoice, a novel multilingual and multimodal framework to detect MCI and estimate Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores by analyzing speech data and its textual transcriptions. The key component of CogniVoice is an ensemble multimodal and multilingual network based on ``Product of Experts'' that mitigates reliance on shortcut solutions. Using a comprehensive dataset containing both English and Chinese languages from TAUKADIAL challenge, CogniVoice outperforms the best performing baseline model on MCI classification and MMSE regression tasks by 2.8 and 4.1 points in F1 and RMSE respectively, and can effectively reduce the performance gap across different language groups by 0.7 points in F1.
Ling-CL: Understanding NLP Models through Linguistic Curricula
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:We employ a characterization of linguistic complexity from psycholinguistic and language acquisition research to develop data-driven curricula to understand the underlying linguistic knowledge that models learn to address NLP tasks. The novelty of our approach is in the development of linguistic curricula derived from data, existing knowledge about linguistic complexity, and model behavior during training. By analyzing several benchmark NLP datasets, our curriculum learning approaches identify sets of linguistic metrics (indices) that inform the challenges and reasoning required to address each task. Our work will inform future research in all NLP areas, allowing linguistic complexity to be considered early in the research and development process. In addition, our work prompts an examination of gold standards and fair evaluation in NLP.
HuCurl: Human-induced Curriculum Discovery
Jul 14, 2023Abstract:We introduce the problem of curriculum discovery and describe a curriculum learning framework capable of discovering effective curricula in a curriculum space based on prior knowledge about sample difficulty. Using annotation entropy and loss as measures of difficulty, we show that (i): the top-performing discovered curricula for a given model and dataset are often non-monotonic as opposed to monotonic curricula in existing literature, (ii): the prevailing easy-to-hard or hard-to-easy transition curricula are often at the risk of underperforming, and (iii): the curricula discovered for smaller datasets and models perform well on larger datasets and models respectively. The proposed framework encompasses some of the existing curriculum learning approaches and can discover curricula that outperform them across several NLP tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge