Mohamed Djallel Dilmi
Self-Reinforcement Attention Mechanism For Tabular Learning
May 19, 2023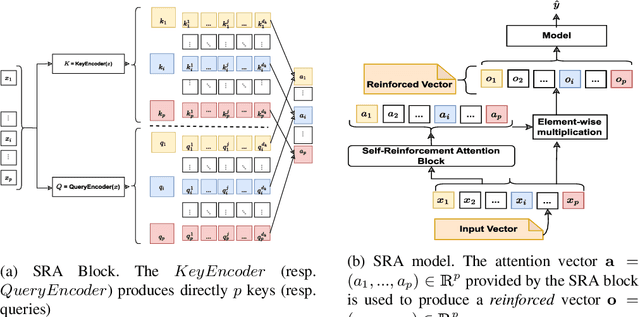
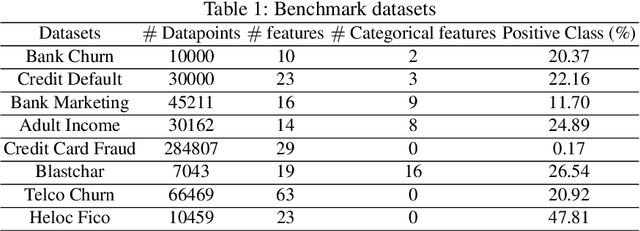
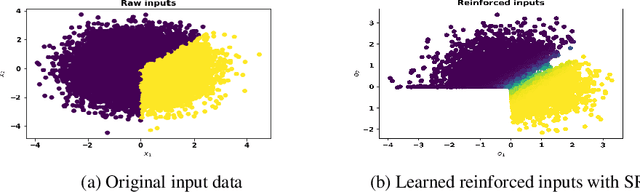
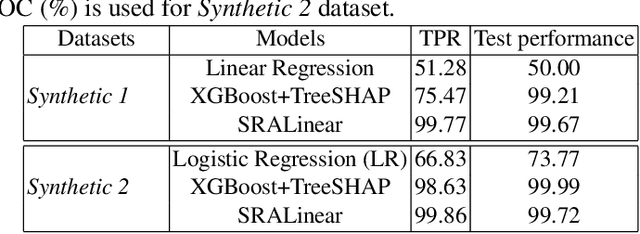
Abstract:Apart from the high accuracy of machine learning models, what interests many researchers in real-life problems (e.g., fraud detection, credit scoring) is to find hidden patterns in data; particularly when dealing with their challenging imbalanced characteristics. Interpretability is also a key requirement that needs to accompany the used machine learning model. In this concern, often, intrinsically interpretable models are preferred to complex ones, which are in most cases black-box models. Also, linear models are used in some high-risk fields to handle tabular data, even if performance must be sacrificed. In this paper, we introduce Self-Reinforcement Attention (SRA), a novel attention mechanism that provides a relevance of features as a weight vector which is used to learn an intelligible representation. This weight is then used to reinforce or reduce some components of the raw input through element-wise vector multiplication. Our results on synthetic and real-world imbalanced data show that our proposed SRA block is effective in end-to-end combination with baseline models.
Epigenetics Algorithms: Self-Reinforcement-Attention mechanism to regulate chromosomes expression
Mar 15, 2023Abstract:Genetic algorithms are a well-known example of bio-inspired heuristic methods. They mimic natural selection by modeling several operators such as mutation, crossover, and selection. Recent discoveries about Epigenetics regulation processes that occur "on top of" or "in addition to" the genetic basis for inheritance involve changes that affect and improve gene expression. They raise the question of improving genetic algorithms (GAs) by modeling epigenetics operators. This paper proposes a new epigenetics algorithm that mimics the epigenetics phenomenon known as DNA methylation. The novelty of our epigenetics algorithms lies primarily in taking advantage of attention mechanisms and deep learning, which fits well with the genes enhancing/silencing concept. The paper develops theoretical arguments and presents empirical studies to exhibit the capability of the proposed epigenetics algorithms to solve more complex problems efficiently than has been possible with simple GAs; for example, facing two Non-convex (multi-peaks) optimization problems as presented in this paper, the proposed epigenetics algorithm provides good performances and shows an excellent ability to overcome the lack of local optimum and thus find the global optimum.
Study of the impact of climate change on precipitation in Paris area using method based on iterative multiscale dynamic time warping
Oct 22, 2019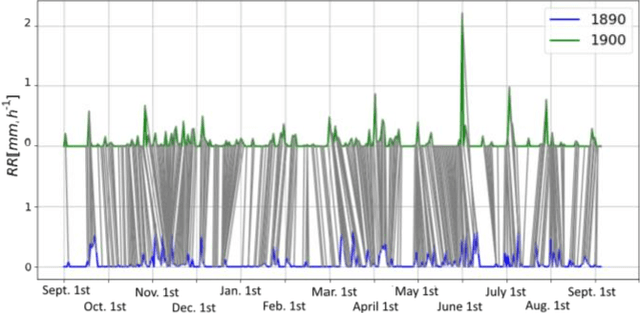
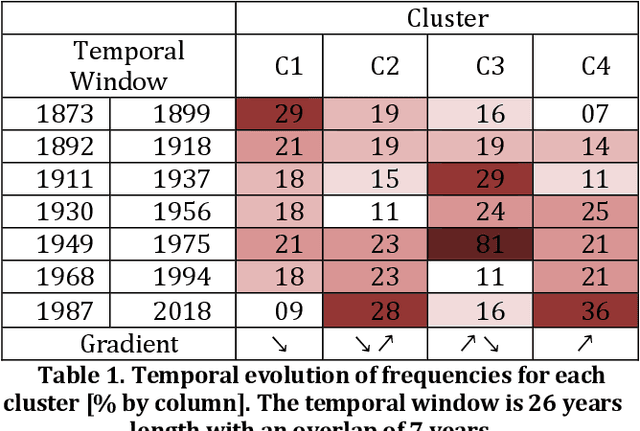
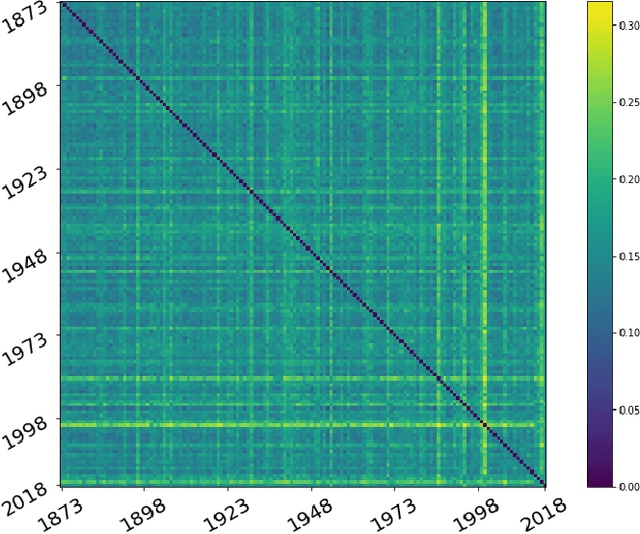
Abstract:Studying the impact of climate change on precipitation is constrained by finding a way to evaluate the evolution of precipitation variability over time. Classical approaches (feature-based) have shown their limitations for this issue due to the intermittent and irregular nature of precipitation. In this study, we present a novel variant of the Dynamic time warping method quantifying the dissimilarity between two rainfall time series based on shapes comparisons, for clustering annual time series recorded at daily scale. This shape based approach considers the whole information (variability, trends and intermittency). We further labeled each cluster using a feature-based approach. While testing the proposed approach on the time series of Paris Montsouris, we found that the precipitation variability increased over the years in Paris area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge