Study of the impact of climate change on precipitation in Paris area using method based on iterative multiscale dynamic time warping
Paper and Code
Oct 22, 2019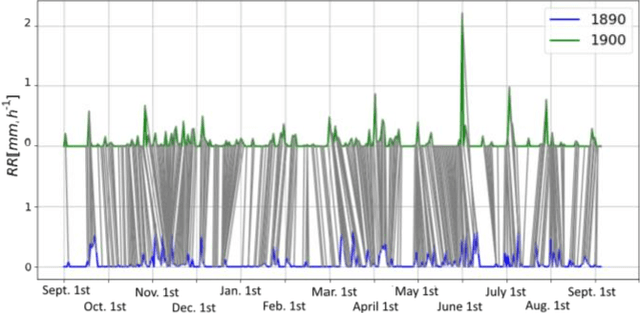
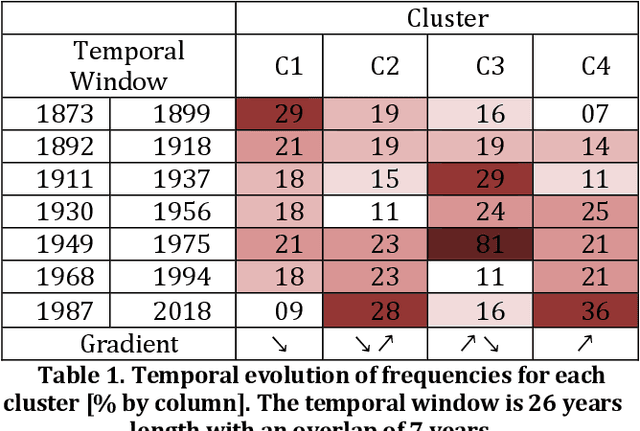
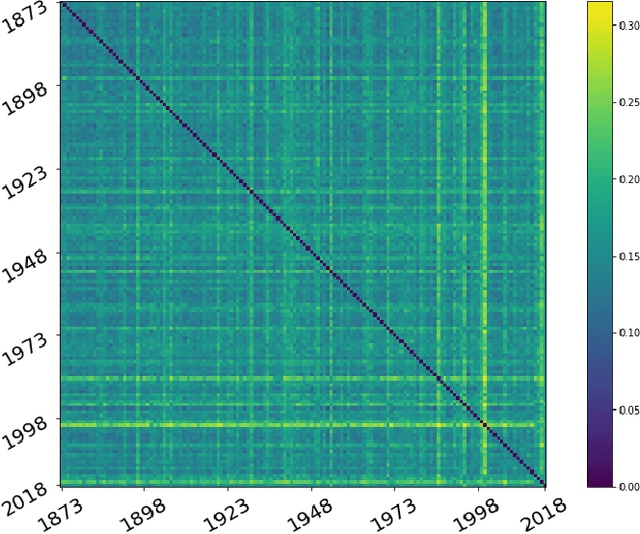
Studying the impact of climate change on precipitation is constrained by finding a way to evaluate the evolution of precipitation variability over time. Classical approaches (feature-based) have shown their limitations for this issue due to the intermittent and irregular nature of precipitation. In this study, we present a novel variant of the Dynamic time warping method quantifying the dissimilarity between two rainfall time series based on shapes comparisons, for clustering annual time series recorded at daily scale. This shape based approach considers the whole information (variability, trends and intermittency). We further labeled each cluster using a feature-based approach. While testing the proposed approach on the time series of Paris Montsouris, we found that the precipitation variability increased over the years in Paris area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge