Moez Ben HajHmida
Learning Word Representations for Tunisian Sentiment Analysis
Oct 14, 2020
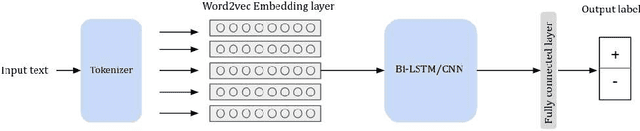

Abstract:Tunisians on social media tend to express themselves in their local dialect using Latin script (TUNIZI). This raises an additional challenge to the process of exploring and recognizing online opinions. To date, very little work has addressed TUNIZI sentiment analysis due to scarce resources for training an automated system. In this paper, we focus on the Tunisian dialect sentiment analysis used on social media. Most of the previous work used machine learning techniques combined with handcrafted features. More recently, Deep Neural Networks were widely used for this task, especially for the English language. In this paper, we explore the importance of various unsupervised word representations (word2vec, BERT) and we investigate the use of Convolutional Neural Networks and Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory. Without using any kind of handcrafted features, our experimental results on two publicly available datasets showed comparable performances to other languages.
A review of sentiment analysis research in Arabic language
May 25, 2020



Abstract:Sentiment analysis is a task of natural language processing which has recently attracted increasing attention. However, sentiment analysis research has mainly been carried out for the English language. Although Arabic is ramping up as one of the most used languages on the Internet, only a few studies have focused on Arabic sentiment analysis so far. In this paper, we carry out an in-depth qualitative study of the most important research works in this context by presenting limits and strengths of existing approaches. In particular, we survey both approaches that leverage machine translation or transfer learning to adapt English resources to Arabic and approaches that stem directly from the Arabic language.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge