Mitsuo Yoshida
Feature Selective Likelihood Ratio Estimator for Low- and Zero-frequency N-grams
Nov 05, 2021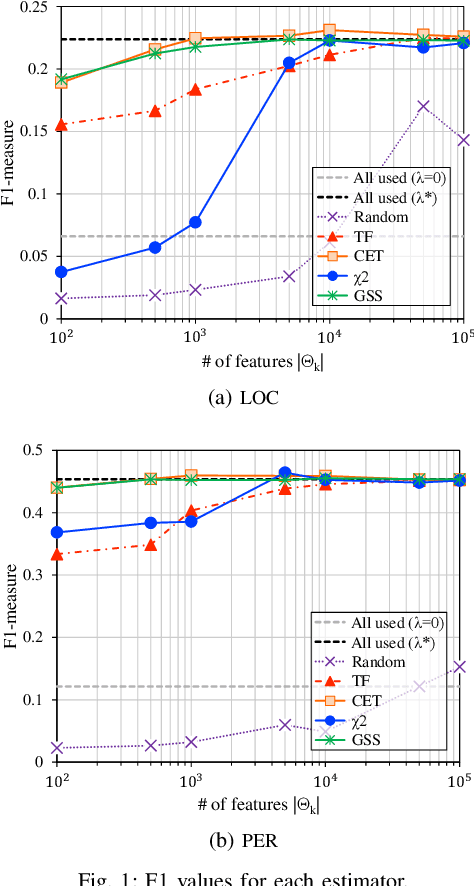
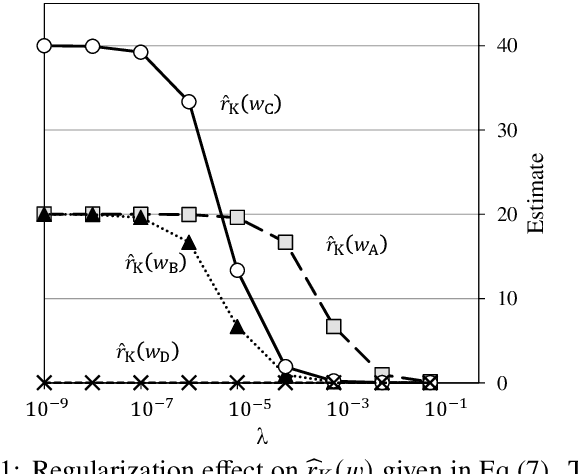
Abstract:In natural language processing (NLP), the likelihood ratios (LRs) of N-grams are often estimated from the frequency information. However, a corpus contains only a fraction of the possible N-grams, and most of them occur infrequently. Hence, we desire an LR estimator for low- and zero-frequency N-grams. One way to achieve this is to decompose the N-grams into discrete values, such as letters and words, and take the product of the LRs for the values. However, because this method deals with a large number of discrete values, the running time and memory usage for estimation are problematic. Moreover, use of unnecessary discrete values causes deterioration of the estimation accuracy. Therefore, this paper proposes combining the aforementioned method with the feature selection method used in document classification, and shows that our estimator provides effective and efficient estimation results for low- and zero-frequency N-grams.
Unified Likelihood Ratio Estimation for High- to Zero-frequency N-grams
Oct 03, 2021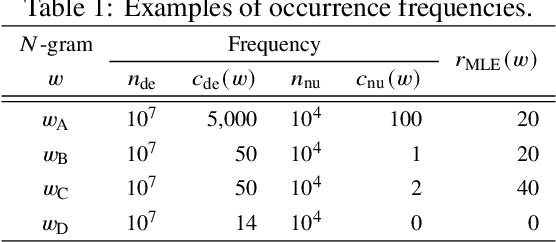
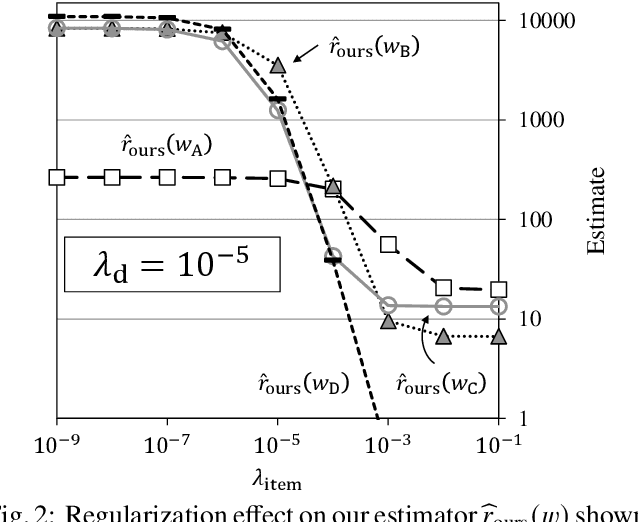
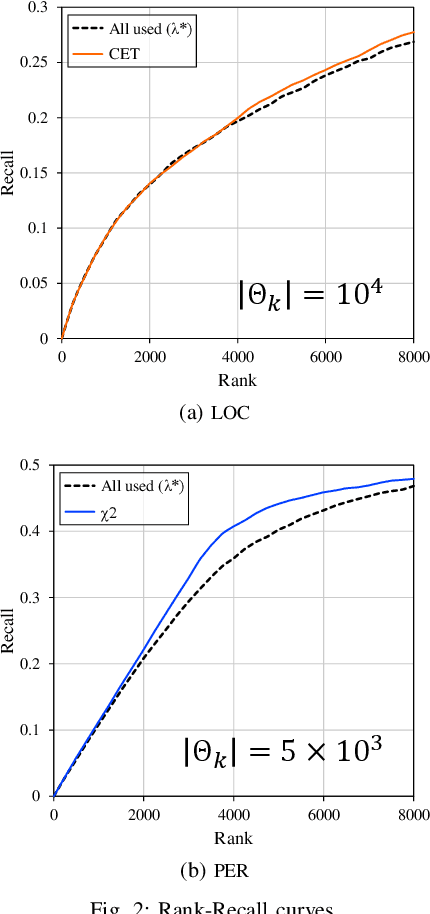
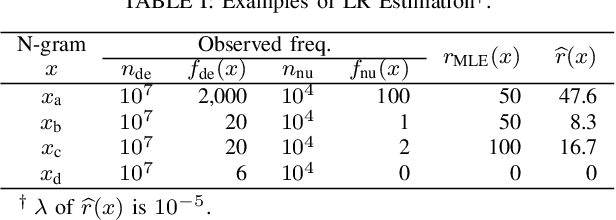
Abstract:Likelihood ratios (LRs), which are commonly used for probabilistic data processing, are often estimated based on the frequency counts of individual elements obtained from samples. In natural language processing, an element can be a continuous sequence of $N$ items, called an $N$-gram, in which each item is a word, letter, etc. In this paper, we attempt to estimate LRs based on $N$-gram frequency information. A naive estimation approach that uses only $N$-gram frequencies is sensitive to low-frequency (rare) $N$-grams and not applicable to zero-frequency (unobserved) $N$-grams; these are known as the low- and zero-frequency problems, respectively. To address these problems, we propose a method for decomposing $N$-grams into item units and then applying their frequencies along with the original $N$-gram frequencies. Our method can obtain the estimates of unobserved $N$-grams by using the unit frequencies. Although using only unit frequencies ignores dependencies between items, our method takes advantage of the fact that certain items often co-occur in practice and therefore maintains their dependencies by using the relevant $N$-gram frequencies. We also introduce a regularization to achieve robust estimation for rare $N$-grams. Our experimental results demonstrate that our method is effective at solving both problems and can effectively control dependencies.
* 17 pages, 8 figures
Analysis of Short Dwell Time in Relation to User Interest in a News Application
Dec 27, 2020



Abstract:Dwell time has been widely used in various fields to evaluate content quality and user engagement. Although many studies shown that content with long dwell time is good quality, contents with short dwell time have not been discussed in detail. We hypothesize that content with short dwell time is not always low quality and does not always have low user engagement, but is instead related to user interest. The purpose of this study is to clarify the meanings of short dwell time browsing in mobile news application. First, we analyze the relation of short dwell time to user interest using large scale user behavior logs from a mobile news application. This analysis was conducted on a vector space based on users click histories and then users and articles were mapped in the same space. The users with short dwell time are concentrated on a specific position in this space; thus, the length of dwell time is related to their interest. Moreover, we also analyze the characteristics of short dwell time browsing by excluding these browses from their click histories. Surprisingly, excluding short dwell time click history, it was found that short dwell time click history included some aspect of user interest in 30.87% of instances where the cluster of users changed. These findings demonstrate that short dwell time does not always indicate a low level of user engagement, but also level of user interest.
The metrics of keywords to understand the difference between Retweet and Like in each category
Dec 27, 2020



Abstract:The purpose of this study is to clarify what kind of news is easily retweeted and what kind of news is easily Liked. We believe these actions, retweeting and Liking, have different meanings for users. Understanding this difference is important for understanding people's interest in Twitter. To analyze the difference between retweets (RT) and Likes on Twitter in detail, we focus on word appearances in news titles. First, we calculate basic statistics and confirm that tweets containing news URLs have different RT and Like tendencies compared to other tweets. Next, we compared RTs and Likes for each category and confirmed that the tendency of categories is different. Therefore, we propose metrics for clarifying the differences in each action for each category used in the $\chi$-square test in order to perform an analysis focusing on the topic. The proposed metrics are more useful than simple counts and TF-IDF for extracting meaningful words to understand the difference between RTs and Likes. We analyzed each category using the proposed metrics and quantitatively confirmed that the difference in the role of retweeting and Liking appeared in the content depending on the category. Moreover, by aggregating tweets chronologically, the results showed the trend of RT and Like as a list of words and clarified how the characteristic words of each week were related to current events for retweeting and Liking.
Journal Name Extraction from Japanese Scientific News Articles
Jun 11, 2019



Abstract:In Japanese scientific news articles, although the research results are described clearly, the article's sources tend to be uncited. This makes it difficult for readers to know the details of the research. In this paper, we address the task of extracting journal names from Japanese scientific news articles. We hypothesize that a journal name is likely to occur in a specific context. To support the hypothesis, we construct a character-based method and extract journal names using this method. This method only uses the left and right context features of journal names. The results of the journal name extractions suggest that the distribution hypothesis plays an important role in identifying the journal names.
Polysemy Detection in Distributed Representation of Word Sense
Sep 26, 2017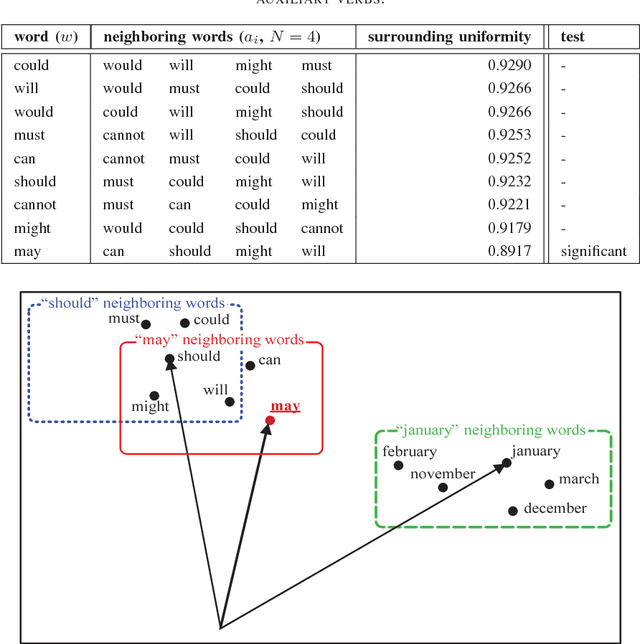
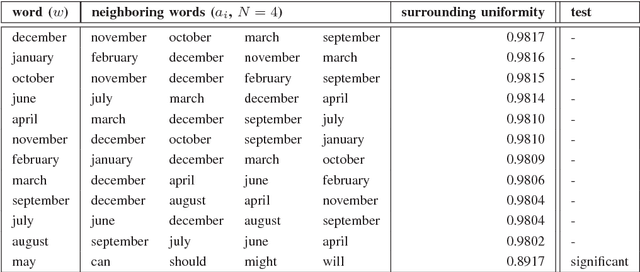

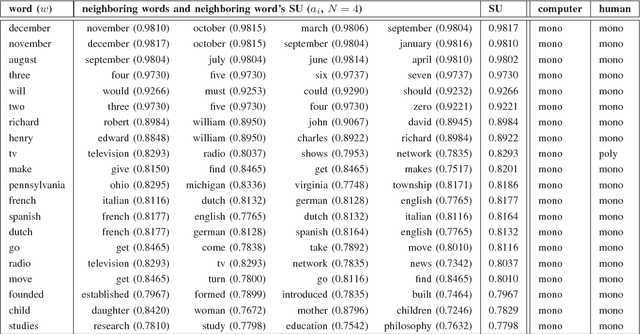
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a statistical test to determine whether a given word is used as a polysemic word or not. The statistic of the word in this test roughly corresponds to the fluctuation in the senses of the neighboring words a nd the word itself. Even though the sense of a word corresponds to a single vector, we discuss how polysemy of the words affects the position of vectors. Finally, we also explain the method to detect this effect.
Realizing Half-Diminished Reality from Video Stream of Manipulating Objects
Sep 25, 2017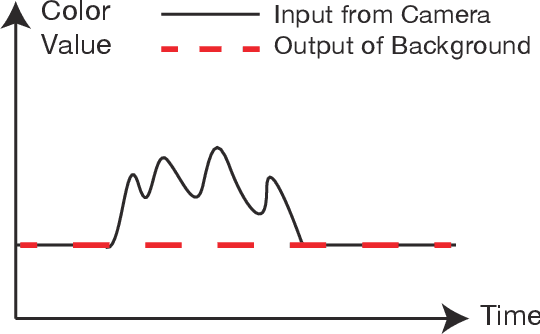
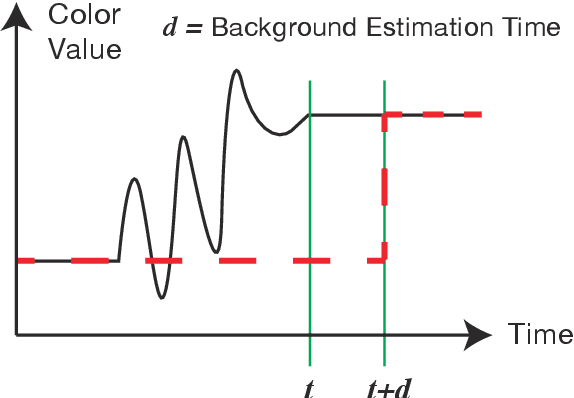

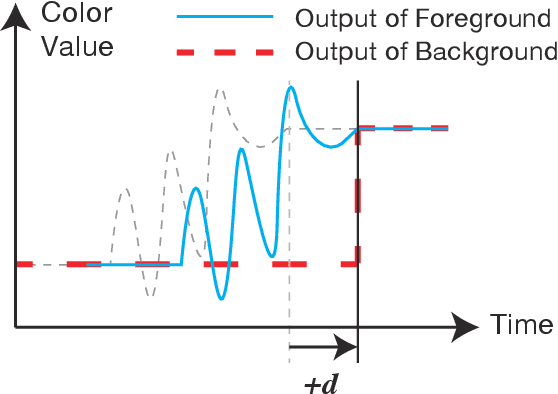
Abstract:When we watch a video, in which human hands manipulate objects, these hands may obscure some parts of those objects. We are willing to make clear how the objects are manipulated by making the image of hands semi-transparent, and showing the complete images of the hands and the object. By carefully choosing a Half-Diminished Reality method, this paper proposes a method that can process the video in real time and verifies that the proposed method works well.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge