Mirela Silva
Lumen: A Machine Learning Framework to Expose Influence Cues in Text
Jul 12, 2021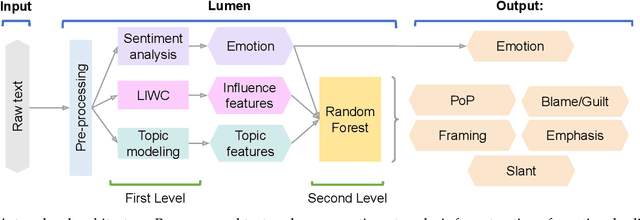
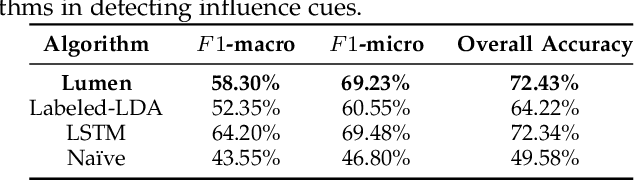
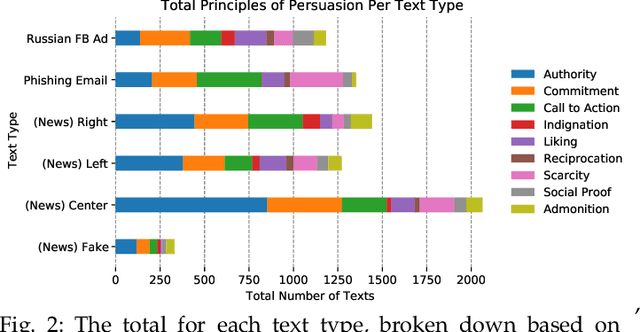
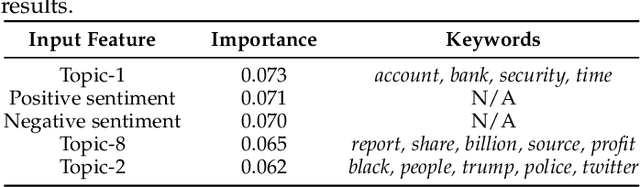
Abstract:Phishing and disinformation are popular social engineering attacks with attackers invariably applying influence cues in texts to make them more appealing to users. We introduce Lumen, a learning-based framework that exposes influence cues in text: (i) persuasion, (ii) framing, (iii) emotion, (iv) objectivity/subjectivity, (v) guilt/blame, and (vi) use of emphasis. Lumen was trained with a newly developed dataset of 3K texts comprised of disinformation, phishing, hyperpartisan news, and mainstream news. Evaluation of Lumen in comparison to other learning models showed that Lumen and LSTM presented the best F1-micro score, but Lumen yielded better interpretability. Our results highlight the promise of ML to expose influence cues in text, towards the goal of application in automatic labeling tools to improve the accuracy of human-based detection and reduce the likelihood of users falling for deceptive online content.
Predicting Different Types of Subtle Toxicity in Unhealthy Online Conversations
Jun 07, 2021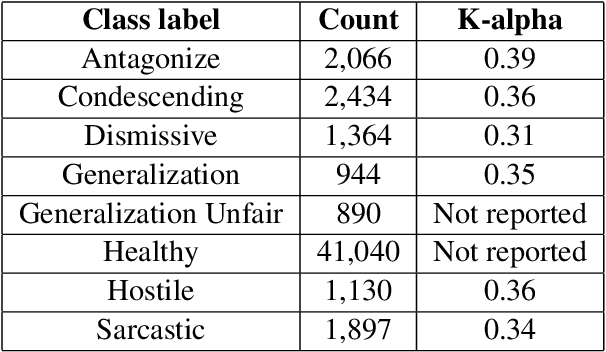
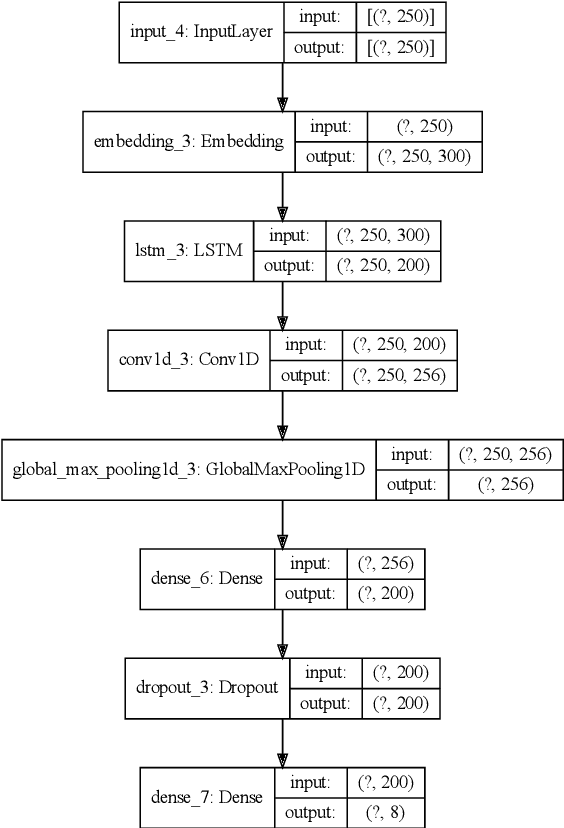
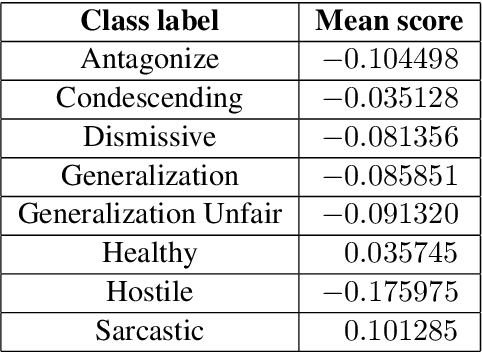
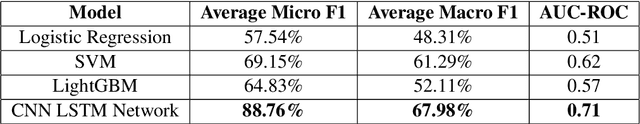
Abstract:This paper investigates the use of machine learning models for the classification of unhealthy online conversations containing one or more forms of subtler abuse, such as hostility, sarcasm, and generalization. We leveraged a public dataset of 44K online comments containing healthy and unhealthy comments labeled with seven forms of subtle toxicity. We were able to distinguish between these comments with a top micro F1-score, macro F1-score, and ROC-AUC of 88.76%, 67.98%, and 0.71, respectively. Hostile comments were easier to detect than other types of unhealthy comments. We also conducted a sentiment analysis which revealed that most types of unhealthy comments were associated with a slight negative sentiment, with hostile comments being the most negative ones.
Computer Users Have Unique Yet Temporally Inconsistent Computer Usage Profiles
May 20, 2021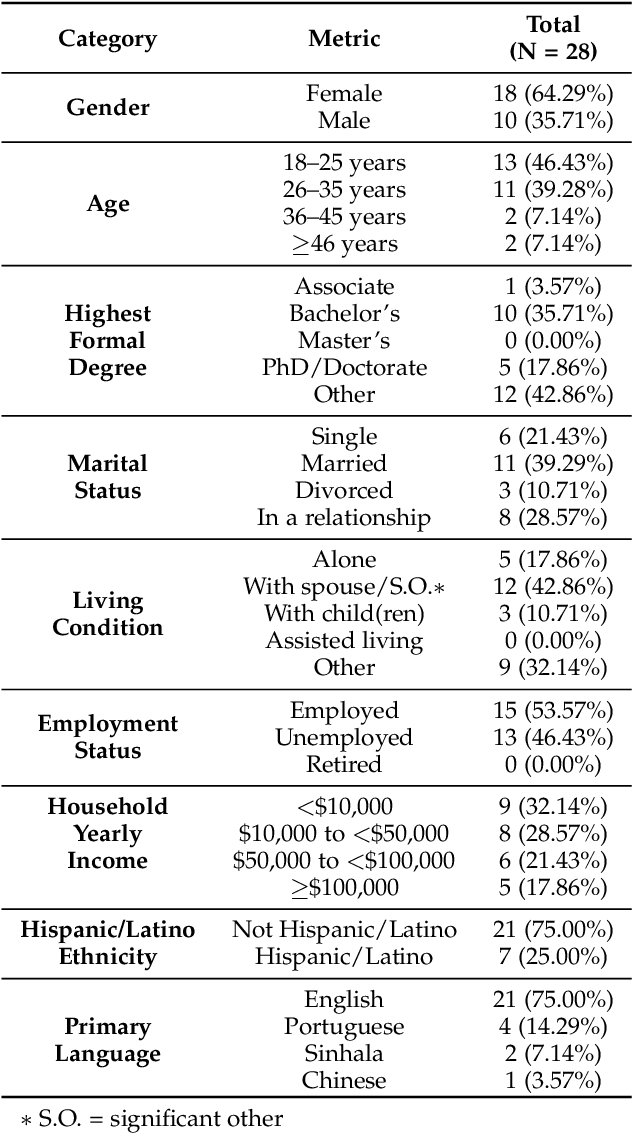
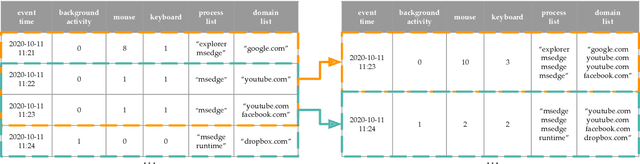
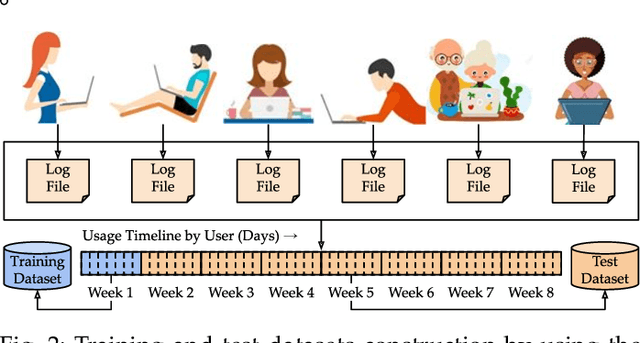
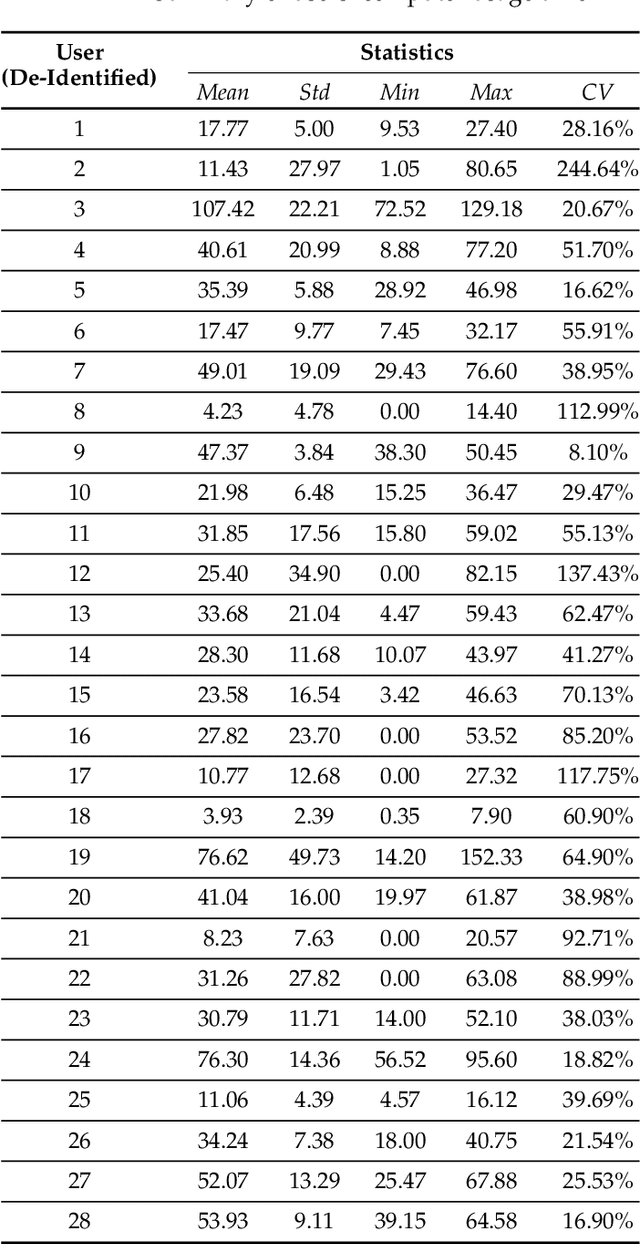
Abstract:This paper investigates whether computer usage profiles comprised of process-, network-, mouse- and keystroke-related events are unique and temporally consistent in a naturalistic setting, discussing challenges and opportunities of using such profiles in applications of continuous authentication. We collected ecologically-valid computer usage profiles from 28 MS Windows 10 computer users over 8 weeks and submitted this data to comprehensive machine learning analysis involving a diverse set of online and offline classifiers. We found that (i) computer usage profiles have the potential to uniquely characterize computer users (with a maximum F-score of 99.94%); (ii) network-related events were the most useful features to properly recognize profiles (95.14% of the top features distinguishing users being network-related); (iii) user profiles were mostly inconsistent over the 8-week data collection period, with 92.86% of users exhibiting drifts in terms of time and usage habits; and (iv) online models are better suited to handle computer usage profiles compared to offline models (maximum F-score for each approach was 95.99% and 99.94%, respectively).
Predicting Misinformation and Engagement in COVID-19 Twitter Discourse in the First Months of the Outbreak
Dec 23, 2020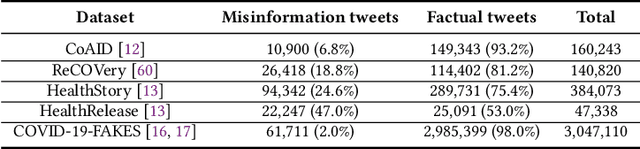
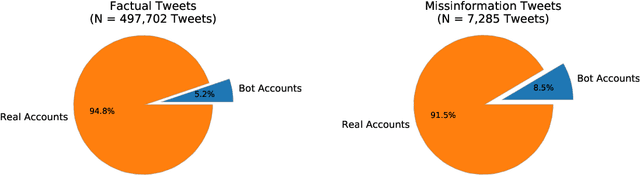
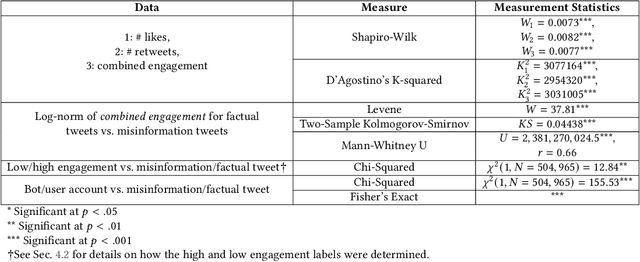
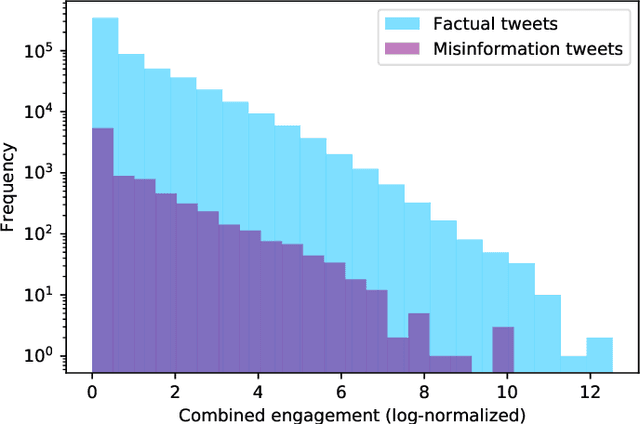
Abstract:Disinformation entails the purposeful dissemination of falsehoods towards a greater dubious agenda and the chaotic fracturing of a society. The general public has grown aware of the misuse of social media towards these nefarious ends, where even global public health crises have not been immune to misinformation (deceptive content spread without intended malice). In this paper, we examine nearly 505K COVID-19-related tweets from the initial months of the pandemic to understand misinformation as a function of bot-behavior and engagement. Using a correlation-based feature selection method, we selected the 11 most relevant feature subsets among over 170 features to distinguish misinformation from facts, and to predict highly engaging misinformation tweets about COVID-19. We achieved an average F-score of at least 72\% with ten popular multi-class classifiers, reinforcing the relevance of the selected features. We found that (i) real users tweet both facts and misinformation, while bots tweet proportionally more misinformation; (ii) misinformation tweets were less engaging than facts; (iii) the textual content of a tweet was the most important to distinguish fact from misinformation while (iv) user account metadata and human-like activity were most important to predict high engagement in factual and misinformation tweets; and (v) sentiment features were not relevant.
Facebook Ad Engagement in the Russian Active Measures Campaign of 2016
Dec 23, 2020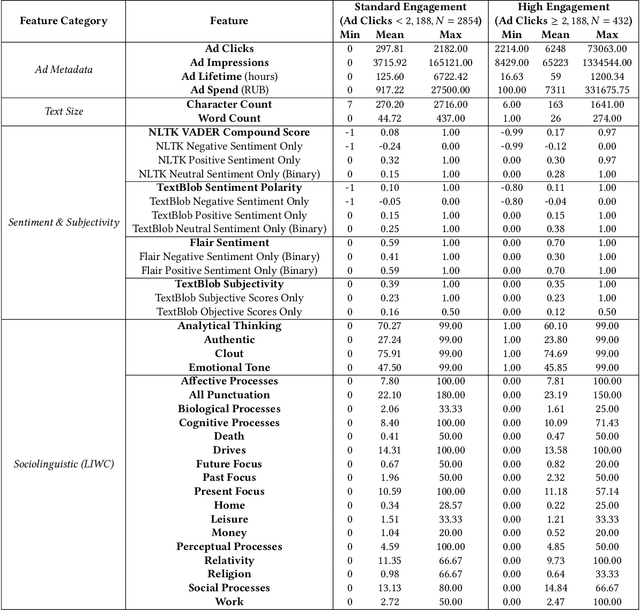
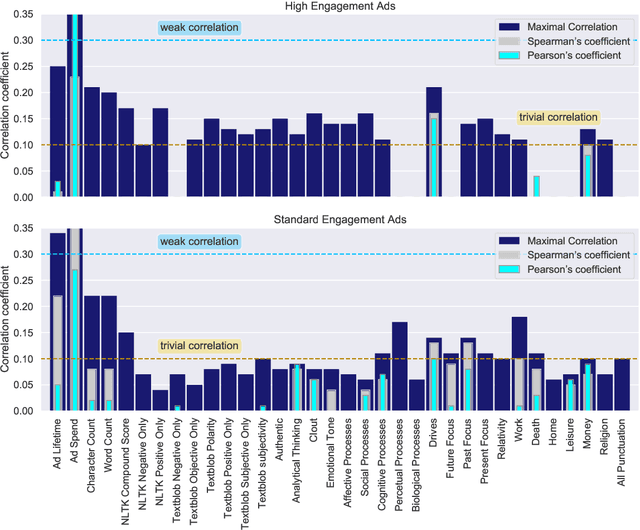
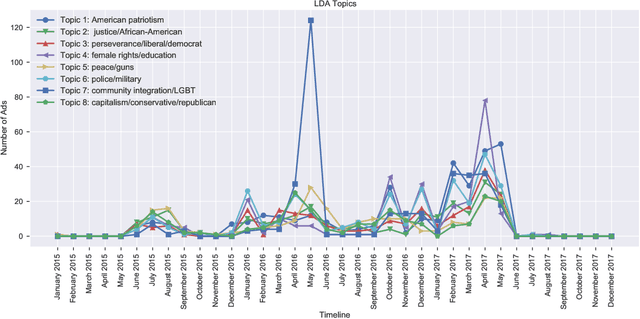
Abstract:This paper examines 3,517 Facebook ads created by Russia's Internet Research Agency (IRA) between June 2015 and August 2017 in its active measures disinformation campaign targeting the 2016 U.S. general election. We aimed to unearth the relationship between ad engagement (as measured by ad clicks) and 41 features related to ads' metadata, sociolinguistic structures, and sentiment. Our analysis was three-fold: (i) understand the relationship between engagement and features via correlation analysis; (ii) find the most relevant feature subsets to predict engagement via feature selection; and (iii) find the semantic topics that best characterize the dataset via topic modeling. We found that ad expenditure, text size, ad lifetime, and sentiment were the top features predicting users' engagement to the ads. Additionally, positive sentiment ads were more engaging than negative ads, and sociolinguistic features (e.g., use of religion-relevant words) were identified as highly important in the makeup of an engaging ad. Linear SVM and Logistic Regression classifiers achieved the highest mean F-scores (93.6% for both models), determining that the optimal feature subset contains 12 and 6 features, respectively. Finally, we corroborate the findings of related works that the IRA specifically targeted Americans on divisive ad topics (e.g., LGBT rights, African American reparations).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge