Minglei Ma
Two-Path GMM-ResNet and GMM-SENet for ASV Spoofing Detection
Jul 08, 2024Abstract:The automatic speaker verification system is sometimes vulnerable to various spoofing attacks. The 2-class Gaussian Mixture Model classifier for genuine and spoofed speech is usually used as the baseline for spoofing detection. However, the GMM classifier does not separately consider the scores of feature frames on each Gaussian component. In addition, the GMM accumulates the scores on all frames independently, and does not consider their correlations. We propose the two-path GMM-ResNet and GMM-SENet models for spoofing detection, whose input is the Gaussian probability features based on two GMMs trained on genuine and spoofed speech respectively. The models consider not only the score distribution on GMM components, but also the relationship between adjacent frames. A two-step training scheme is applied to improve the system robustness. Experiments on the ASVspoof 2019 show that the LFCC+GMM-ResNet system can relatively reduce min-tDCF and EER by 76.1% and 76.3% on logical access scenario compared with the GMM, and the LFCC+GMM-SENet system by 94.4% and 95.4% on physical access scenario. After score fusion, the systems give the second-best results on both scenarios.
GMM-ResNet2: Ensemble of Group ResNet Networks for Synthetic Speech Detection
Jul 02, 2024
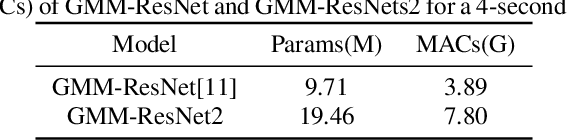

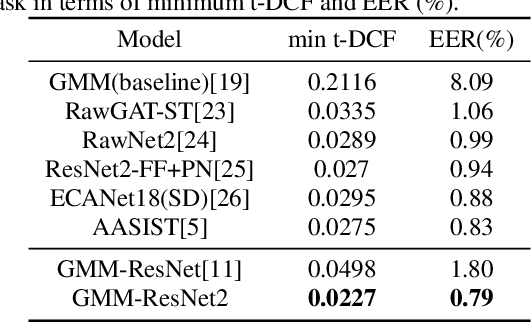
Abstract:Deep learning models are widely used for speaker recognition and spoofing speech detection. We propose the GMM-ResNet2 for synthesis speech detection. Compared with the previous GMM-ResNet model, GMM-ResNet2 has four improvements. Firstly, the different order GMMs have different capabilities to form smooth approximations to the feature distribution, and multiple GMMs are used to extract multi-scale Log Gaussian Probability features. Secondly, the grouping technique is used to improve the classification accuracy by exposing the group cardinality while reducing both the number of parameters and the training time. The final score is obtained by ensemble of all group classifier outputs using the averaging method. Thirdly, the residual block is improved by including one activation function and one batch normalization layer. Finally, an ensemble-aware loss function is proposed to integrate the independent loss functions of all ensemble members. On the ASVspoof 2019 LA task, the GMM-ResNet2 achieves a minimum t-DCF of 0.0227 and an EER of 0.79\%. On the ASVspoof 2021 LA task, the GMM-ResNet2 achieves a minimum t-DCF of 0.2362 and an EER of 2.19\%, and represents a relative reductions of 31.4\% and 76.3\% compared with the LFCC-LCNN baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge