Michel Meneses
Conditional Online Learning for Keyword Spotting
May 19, 2023Abstract:Modern approaches for keyword spotting rely on training deep neural networks on large static datasets with i.i.d. distributions. However, the resulting models tend to underperform when presented with changing data regimes in real-life applications. This work investigates a simple but effective online continual learning method that updates a keyword spotter on-device via SGD as new data becomes available. Contrary to previous research, this work focuses on learning the same KWS task, which covers most commercial applications. During experiments with dynamic audio streams in different scenarios, that method improves the performance of a pre-trained small-footprint model by 34%. Moreover, experiments demonstrate that, compared to a naive online learning implementation, conditional model updates based on its performance in a small hold-out set drawn from the training distribution mitigate catastrophic forgetting.
Learning to associate detections for real-time multiple object tracking
Jul 12, 2020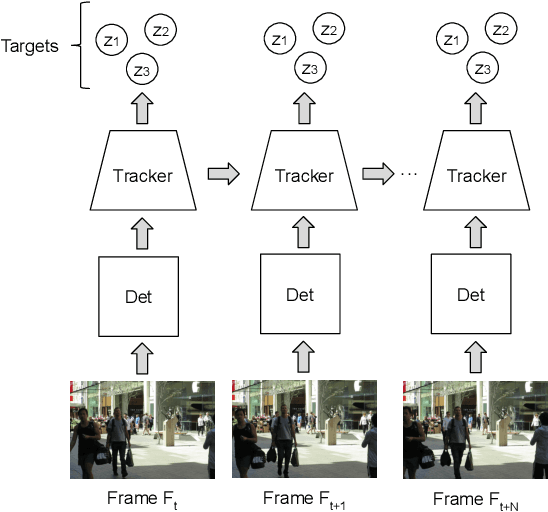
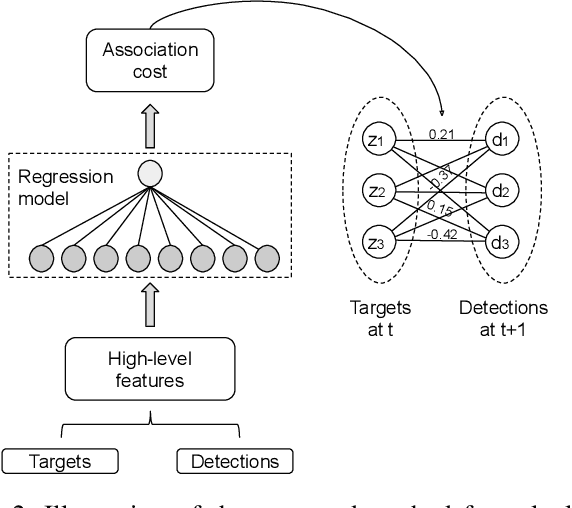
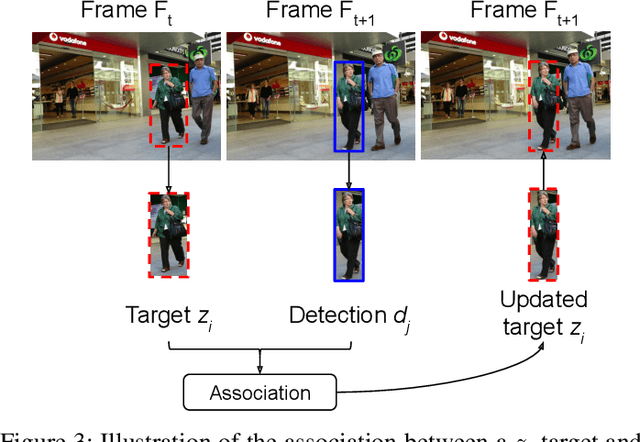
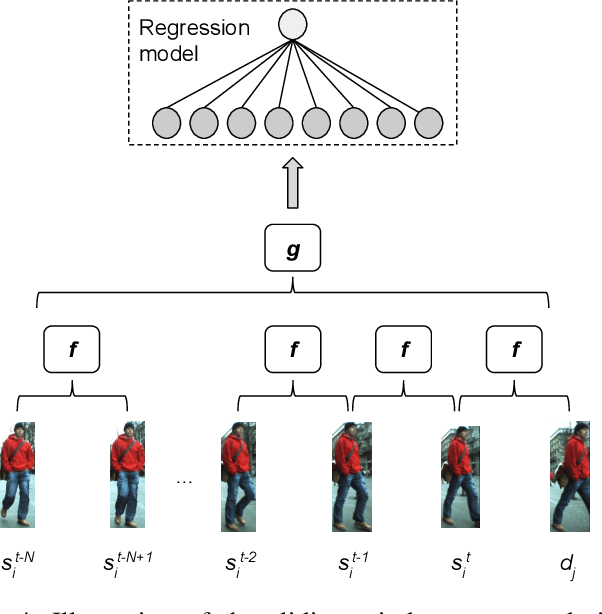
Abstract:With the recent advances in the object detection research field, tracking-by-detection has become the leading paradigm adopted by multi-object tracking algorithms. By extracting different features from detected objects, those algorithms can estimate the objects' similarities and association patterns along successive frames. However, since similarity functions applied by tracking algorithms are handcrafted, it is difficult to employ them in new contexts. In this study, it is investigated the use of artificial neural networks to learning a similarity function that can be used among detections. During training, the networks were introduced to correct and incorrect association patterns, sampled from a pedestrian tracking data set. For such, different motion and appearance features combinations have been explored. Finally, a trained network has been inserted into a multiple-object tracking framework, which has been assessed on the MOT Challenge benchmark. Throughout the experiments, the proposed tracker matched the results obtained by state-of-the-art methods, it has run 58\% faster than a recent and similar method, used as baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge