Michael Scriney
Analysis of Individual Conversational Volatility in Tandem Telecollaboration for Second Language Learning
Jun 28, 2022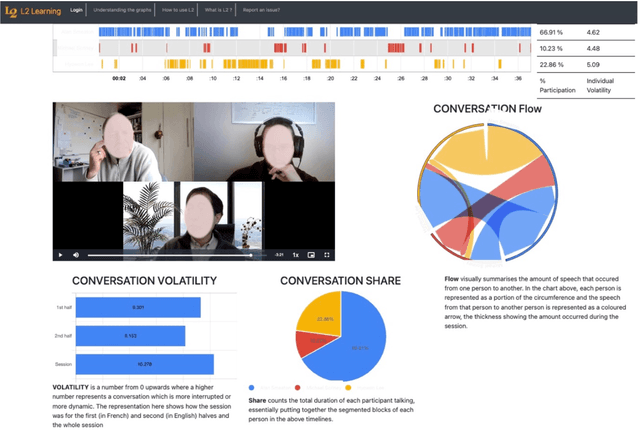
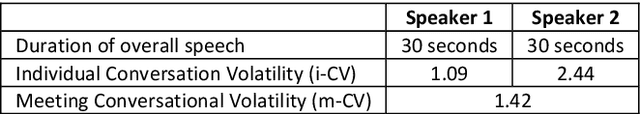
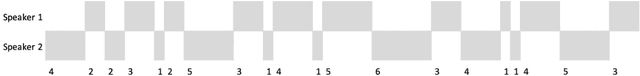

Abstract:Second language learning can be enabled by tandem collaboration where students are grouped into video conference calls while learning the native language of other student(s) on the calls. This places students in an online environment where the more outgoing can actively contribute and engage in dialogue while those more shy and unsure of their second language skills can sit back and coast through the calls. We have built and deployed the L2L system which records timings of conversational utterances from all participants in a call. We generate visualisations including participation rates and timelines for each student in each call and present these on a dashboard. We have recently developed a measure called personal conversational volatility for how dynamic has been each student's contribution to the dialogue in each call. We present an analysis of conversational volatility measures for a sample of 19 individual English-speaking students from our University who are learning Frenchm, in each of 86 tandem telecollaboration calls over one teaching semester. Our analysis shows there is a need to look into the nature of the interactions and see if the choices of discussion topics assigned to them were too difficult for some students and that may have influenced their engagement in some way.
Facilitating reflection in teletandem through automatically generated conversation metrics and playback video
Nov 18, 2021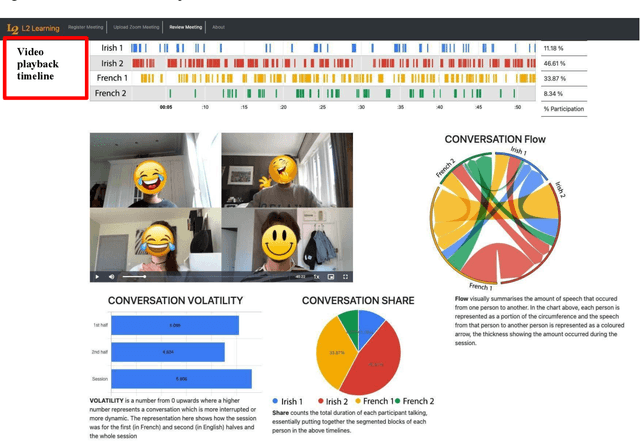
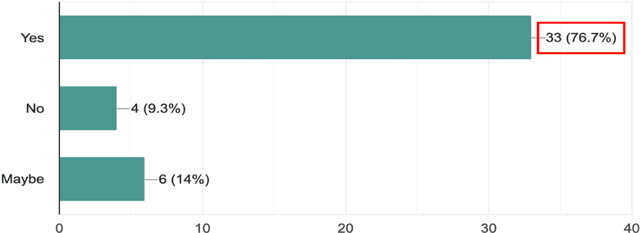
Abstract:This pilot study focuses on a tool called L2L that allows second language (L2) learners to visualise and analyse their Zoom interactions with native speakers. L2L uses the Zoom transcript to automatically generate conversation metrics and its playback feature with timestamps allows students to replay any chosen portion of the conversation for post-session reflection and self-review. This exploratory study investigates a seven-week teletandem project, where undergraduate students from an Irish University learning French (B2) interacted with their peers from a French University learning English (B2+) via Zoom. The data collected from a survey (N=43) and semi-structured interviews (N=35) show that the quantitative conversation metrics and qualitative review of the synchronous content helped raise students' confidence levels while engaging with native speakers. Furthermore, it allowed them to set tangible goals to improve their participation, and be more aware of what, why and how they are learning.
* 5 pages
Attention Based Video Summaries of Live Online Zoom Classes
Jan 15, 2021Abstract:This paper describes a system developed to help University students get more from their online lectures, tutorials, laboratory and other live sessions. We do this by logging their attention levels on their laptops during live Zoom sessions and providing them with personalised video summaries of those live sessions. Using facial attention analysis software we create personalised video summaries composed of just the parts where a student's attention was below some threshold. We can also factor in other criteria into video summary generation such as parts where the student was not paying attention while others in the class were, and parts of the video that other students have replayed extensively which a given student has not. Attention and usage based video summaries of live classes are a form of personalised content, they are educational video segments recommended to highlight important parts of live sessions, useful in both topic understanding and in exam preparation. The system also allows a Professor to review the aggregated attention levels of those in a class who attended a live session and logged their attention levels. This allows her to see which parts of the live activity students were paying most, and least, attention to. The Help-Me-Watch system is deployed and in use at our University in a way that protects student's personal data, operating in a GDPR-compliant way.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge