Michael Horton
A Practical Index Structure Supporting Fréchet Proximity Queries Among Trajectories
May 28, 2020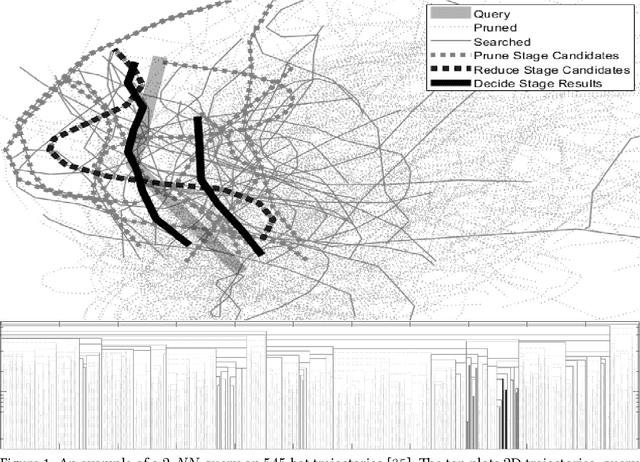
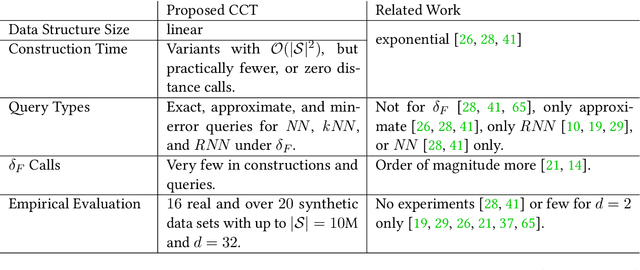
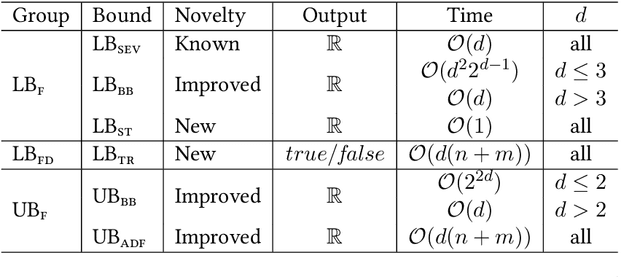
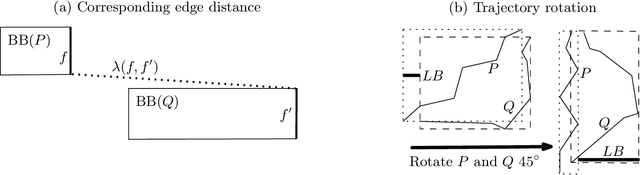
Abstract:We present a scalable approach for range and $k$ nearest neighbor queries under computationally expensive metrics, like the continuous Fr\'echet distance on trajectory data. Based on clustering for metric indexes, we obtain a dynamic tree structure whose size is linear in the number of trajectories, regardless of the trajectory's individual sizes or the spatial dimension, which allows one to exploit low `intrinsic dimensionality' of data sets for effective search space pruning. Since the distance computation is expensive, generic metric indexing methods are rendered impractical. We present strategies that (i) improve on known upper and lower bound computations, (ii) build cluster trees without any or very few distance calls, and (iii) search using bounds for metric pruning, interval orderings for reduction, and randomized pivoting for reporting the final results. We analyze the efficiency and effectiveness of our methods with extensive experiments on diverse synthetic and real-world data sets. The results show improvement over state-of-the-art methods for exact queries, and even further speed-ups are achieved for queries that may return approximate results. Surprisingly, the majority of exact nearest-neighbor queries on real data sets are answered without any distance computations.
Classification of Passes in Football Matches using Spatiotemporal Data
Jul 18, 2014
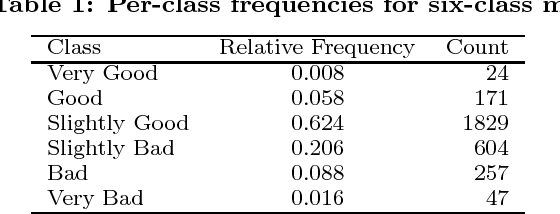
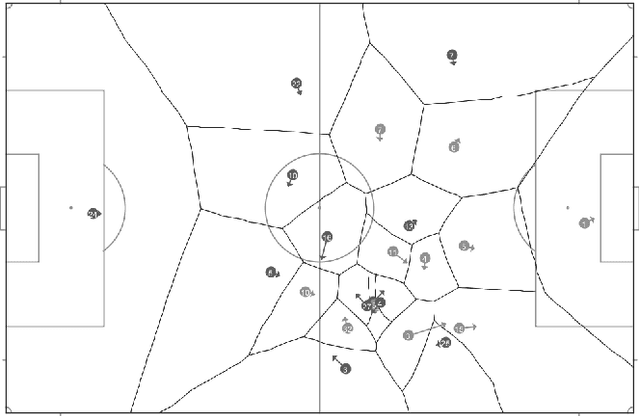
Abstract:A knowledgeable observer of a game of football (soccer) can make a subjective evaluation of the quality of passes made between players during the game. We investigate the problem of producing an automated system to make the same evaluation of passes. We present a model that constructs numerical predictor variables from spatiotemporal match data using feature functions based on methods from computational geometry, and then learns a classification function from labelled examples of the predictor variables. Furthermore, the learned classifiers are analysed to determine if there is a relationship between the complexity of the algorithm that computed the predictor variable and the importance of the variable to the classifier. Experimental results show that we are able to produce a classifier with 85.8% accuracy on classifying passes as Good, OK or Bad, and that the predictor variables computed using complex methods from computational geometry are of moderate importance to the learned classifiers. Finally, we show that the inter-rater agreement on pass classification between the machine classifier and a human observer is of similar magnitude to the agreement between two observers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge