Meysam Tavakoli
CONRep: Uncertainty-Aware Vision-Language Report Drafting Using Conformal Prediction
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Automated radiology report drafting (ARRD) using vision-language models (VLMs) has advanced rapidly, yet most systems lack explicit uncertainty estimates, limiting trust and safe clinical deployment. We propose CONRep, a model-agnostic framework that integrates conformal prediction (CP) to provide statistically grounded uncertainty quantification for VLM-generated radiology reports. CONRep operates at both the label level, by calibrating binary predictions for predefined findings, and the sentence level, by assessing uncertainty in free-text impressions via image-text semantic alignment. We evaluate CONRep using both generative and contrastive VLMs on public chest X-ray datasets. Across both settings, outputs classified as high confidence consistently show significantly higher agreement with radiologist annotations and ground-truth impressions than low-confidence outputs. By enabling calibrated confidence stratification without modifying underlying models, CONRep improves the transparency, reliability, and clinical usability of automated radiology reporting systems.
Medical image registration using unsupervised deep neural network: A scoping literature review
Aug 03, 2022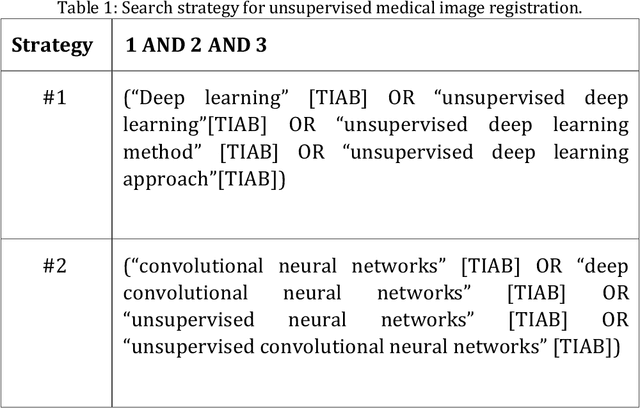
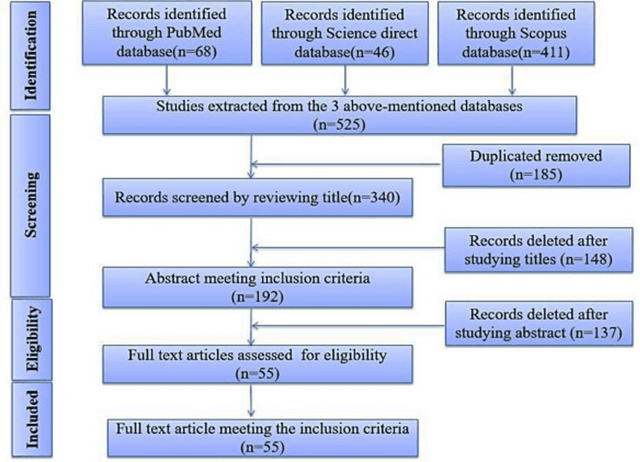
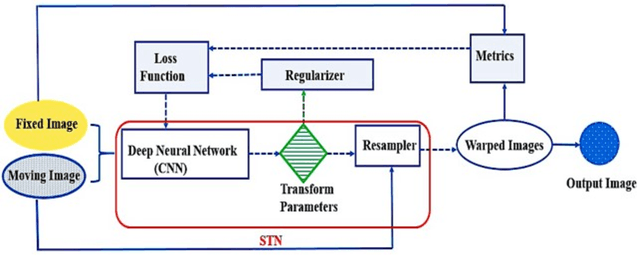
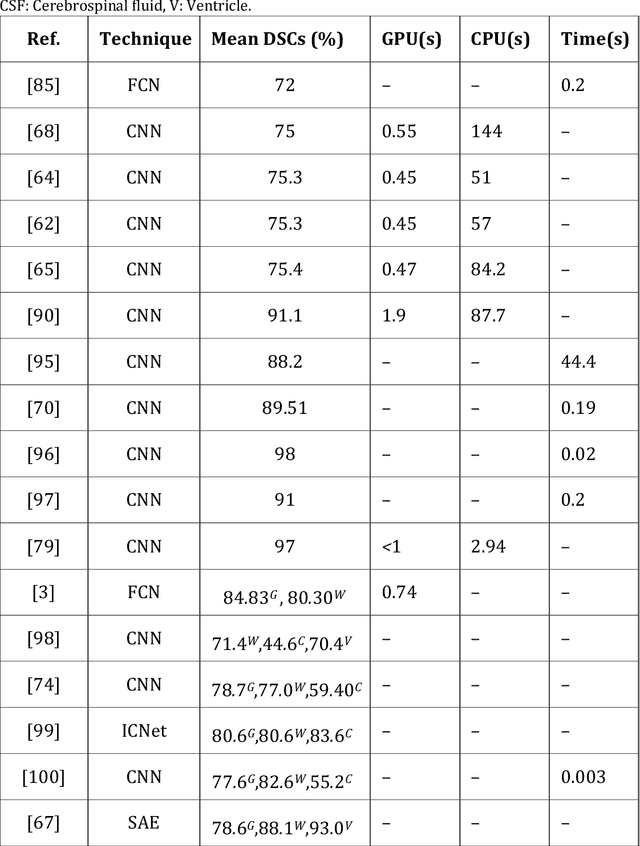
Abstract:In medicine, image registration is vital in image-guided interventions and other clinical applications. However, it is a difficult subject to be addressed which by the advent of machine learning, there have been considerable progress in algorithmic performance has recently been achieved for medical image registration in this area. The implementation of deep neural networks provides an opportunity for some medical applications such as conducting image registration in less time with high accuracy, playing a key role in countering tumors during the operation. The current study presents a comprehensive scoping review on the state-of-the-art literature of medical image registration studies based on unsupervised deep neural networks is conducted, encompassing all the related studies published in this field to this date. Here, we have tried to summarize the latest developments and applications of unsupervised deep learning-based registration methods in the medical field. Fundamental and main concepts, techniques, statistical analysis from different viewpoints, novelties, and future directions are elaborately discussed and conveyed in the current comprehensive scoping review. Besides, this review hopes to help those active readers, who are riveted by this field, achieve deep insight into this exciting field.
A comprehensive survey on computer-aided diagnostic systems in diabetic retinopathy screening
Aug 03, 2022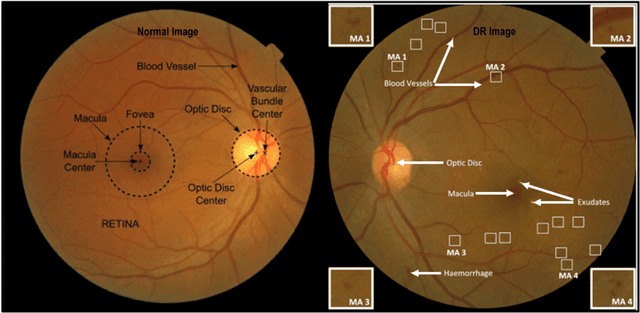

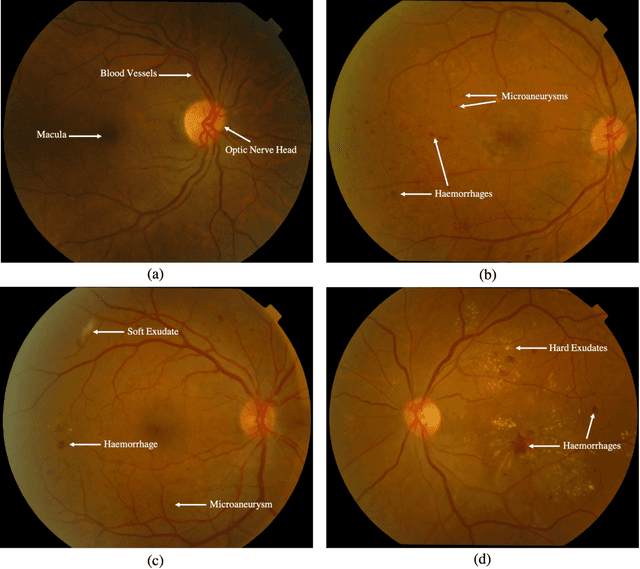
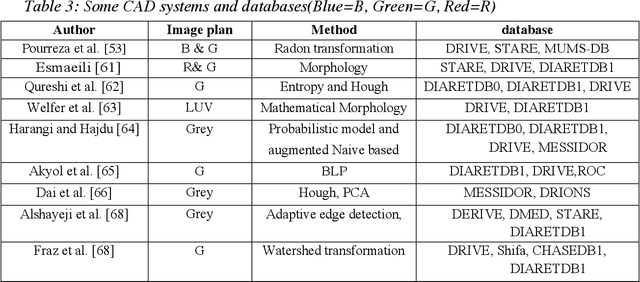
Abstract:Diabetes Mellitus (DM) can lead to significant microvasculature disruptions that eventually causes diabetic retinopathy (DR), or complications in the eye due to diabetes. If left unchecked, this disease can increase over time and eventually cause complete vision loss. The general method to detect such optical developments is through examining the vessels, optic nerve head, microaneurysms, haemorrhage, exudates, etc. from retinal images. Ultimately this is limited by the number of experienced ophthalmologists and the vastly growing number of DM cases. To enable earlier and efficient DR diagnosis, the field of ophthalmology requires robust computer aided diagnosis (CAD) systems. Our review is intended for anyone, from student to established researcher, who wants to understand what can be accomplished with CAD systems and their algorithms to modeling and where the field of retinal image processing in computer vision and pattern recognition is headed. For someone just getting started, we place a special emphasis on the logic, strengths and shortcomings of different databases and algorithms frameworks with a focus on very recent approaches.
* 65 pages, 7 figures, 9 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge