Mengjie Du
TELEVAL: A Dynamic Benchmark Designed for Spoken Language Models in Chinese Interactive Scenarios
Jul 24, 2025Abstract:Spoken language models (SLMs) have seen rapid progress in recent years, along with the development of numerous benchmarks for evaluating their performance. However, most existing benchmarks primarily focus on evaluating whether SLMs can perform complex tasks comparable to those tackled by large language models (LLMs), often failing to align with how users naturally interact in real-world conversational scenarios. In this paper, we propose TELEVAL, a dynamic benchmark specifically designed to evaluate SLMs' effectiveness as conversational agents in realistic Chinese interactive settings. TELEVAL defines three evaluation dimensions: Explicit Semantics, Paralinguistic and Implicit Semantics, and System Abilities. It adopts a dialogue format consistent with real-world usage and evaluates text and audio outputs separately. TELEVAL particularly focuses on the model's ability to extract implicit cues from user speech and respond appropriately without additional instructions. Our experiments demonstrate that despite recent progress, existing SLMs still have considerable room for improvement in natural conversational tasks. We hope that TELEVAL can serve as a user-centered evaluation framework that directly reflects the user experience and contributes to the development of more capable dialogue-oriented SLMs.
Speaker Contrastive Learning for Source Speaker Tracing
Sep 16, 2024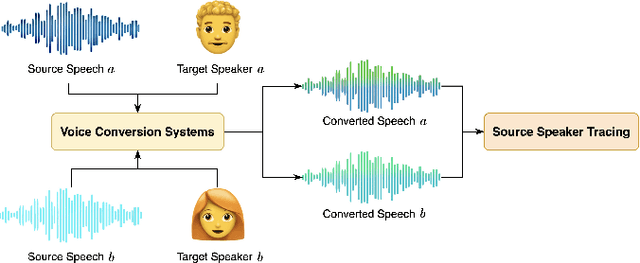
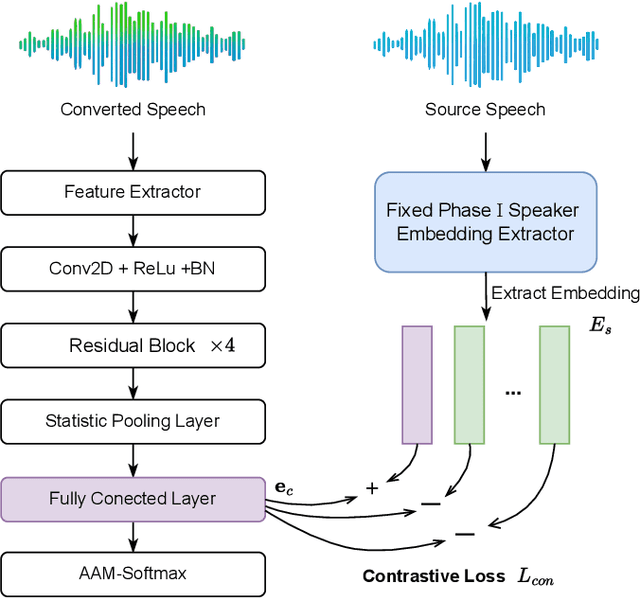

Abstract:As a form of biometric authentication technology, the security of speaker verification systems is of utmost importance. However, SV systems are inherently vulnerable to various types of attacks that can compromise their accuracy and reliability. One such attack is voice conversion, which modifies a persons speech to sound like another person by altering various vocal characteristics. This poses a significant threat to SV systems. To address this challenge, the Source Speaker Tracing Challenge in IEEE SLT2024 aims to identify the source speaker information in manipulated speech signals. Specifically, SSTC focuses on source speaker verification against voice conversion to determine whether two converted speech samples originate from the same source speaker. In this study, we propose a speaker contrastive learning-based approach for source speaker tracing to learn the latent source speaker information in converted speech. To learn a more source-speaker-related representation, we employ speaker contrastive loss during the training of the embedding extractor. This speaker contrastive loss helps identify the true source speaker embedding among several distractor speaker embeddings, enabling the embedding extractor to learn the potentially possessing source speaker information present in the converted speech. Experiments demonstrate that our proposed speaker contrastive learning system achieves the lowest EER of 16.788% on the challenge test set, securing first place in the challenge.
ChinaTelecom System Description to VoxCeleb Speaker Recognition Challenge 2023
Aug 16, 2023Abstract:This technical report describes ChinaTelecom system for Track 1 (closed) of the VoxCeleb2023 Speaker Recognition Challenge (VoxSRC 2023). Our system consists of several ResNet variants trained only on VoxCeleb2, which were fused for better performance later. Score calibration was also applied for each variant and the fused system. The final submission achieved minDCF of 0.1066 and EER of 1.980%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge