Menghe Zhang
UniHands: Unifying Various Wild-Collected Keypoints for Personalized Hand Reconstruction
Nov 18, 2024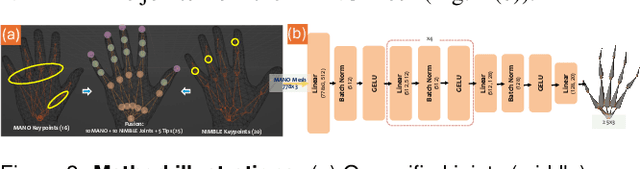
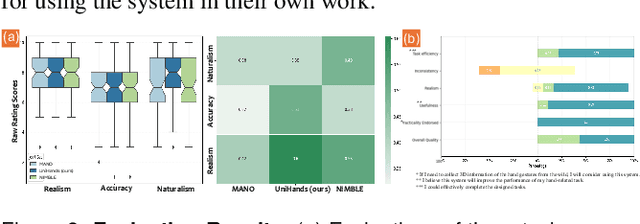
Abstract:Accurate hand motion capture and standardized 3D representation are essential for various hand-related tasks. Collecting keypoints-only data, while efficient and cost-effective, results in low-fidelity representations and lacks surface information. Furthermore, data inconsistencies across sources challenge their integration and use. We present UniHands, a novel method for creating standardized yet personalized hand models from wild-collected keypoints from diverse sources. Unlike existing neural implicit representation methods, UniHands uses the widely-adopted parametric models MANO and NIMBLE, providing a more scalable and versatile solution. It also derives unified hand joints from the meshes, which facilitates seamless integration into various hand-related tasks. Experiments on the FreiHAND and InterHand2.6M datasets demonstrate its ability to precisely reconstruct hand mesh vertices and keypoints, effectively capturing high-degree articulation motions. Empirical studies involving nine participants show a clear preference for our unified joints over existing configurations for accuracy and naturalism (p-value 0.016).
FaceAtlasAR: Atlas of Facial Acupuncture Points in Augmented Reality
Nov 29, 2021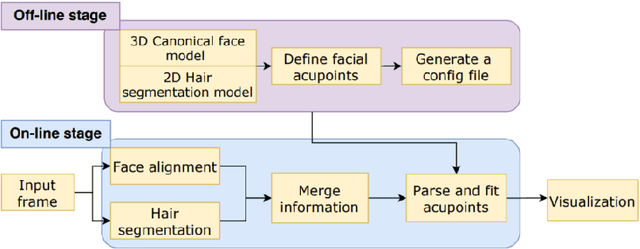
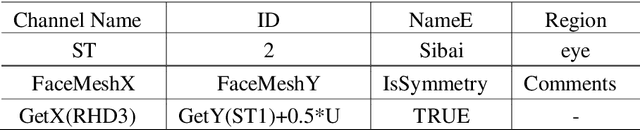
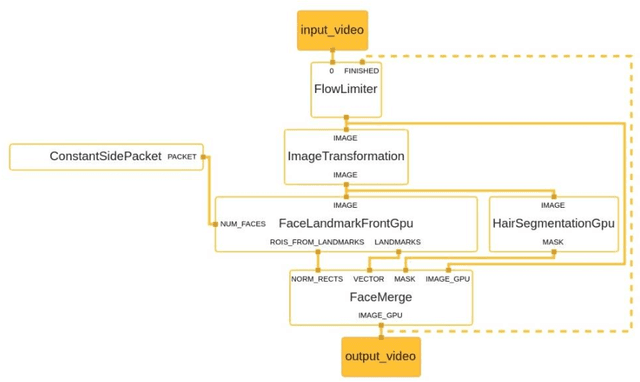

Abstract:Acupuncture is a technique in which practitioners stimulate specific points on the body. These points, called acupuncture points (or acupoints), anatomically define areas on the skin relative to some landmarks on the body. Traditional acupuncture treatment relies on experienced acupuncturists for precise positioning of acupoints. A novice typically finds it difficult because of the lack of visual cues. This project presents FaceAtlasAR, a prototype system that localizes and visualizes facial acupoints in an augmented reality (AR) context. The system aims to 1) localize facial acupoints and auricular zone map in an anatomical yet feasible way, 2) overlay the requested acupoints by category in AR, and 3) show auricular zone map on the ears. We adopt Mediapipe, a cross-platform machine learning framework, to build the pipeline that runs on desktop and Android phones. We perform experiments on different benchmarks, including "In-the-wild", AMI ear datasets, and our own annotated datasets. Results show the localization accuracy of 95% for facial acupoints, 99% / 97% ("In-the-wild" / AMI) for auricular zone map, and high robustness. With this system, users, even not professionals, can position the acupoints quickly for their self-acupressure treatments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge