Mei-Hsuan Wu
GRACE: Graph-Regularized Attentive Convolutional Entanglement with Laplacian Smoothing for Robust DeepFake Video Detection
Jun 28, 2024Abstract:As DeepFake video manipulation techniques escalate, posing profound threats, the urgent need to develop efficient detection strategies is underscored. However, one particular issue lies with facial images being mis-detected, often originating from degraded videos or adversarial attacks, leading to unexpected temporal artifacts that can undermine the efficacy of DeepFake video detection techniques. This paper introduces a novel method for robust DeepFake video detection, harnessing the power of the proposed Graph-Regularized Attentive Convolutional Entanglement (GRACE) based on the graph convolutional network with graph Laplacian to address the aforementioned challenges. First, conventional Convolution Neural Networks are deployed to perform spatiotemporal features for the entire video. Then, the spatial and temporal features are mutually entangled by constructing a graph with sparse constraint, enforcing essential features of valid face images in the noisy face sequences remaining, thus augmenting stability and performance for DeepFake video detection. Furthermore, the Graph Laplacian prior is proposed in the graph convolutional network to remove the noise pattern in the feature space to further improve the performance. Comprehensive experiments are conducted to illustrate that our proposed method delivers state-of-the-art performance in DeepFake video detection under noisy face sequences. The source code is available at https://github.com/ming053l/GRACE.
Visual Transformer with Statistical Test for COVID-19 Classification
Jul 12, 2021
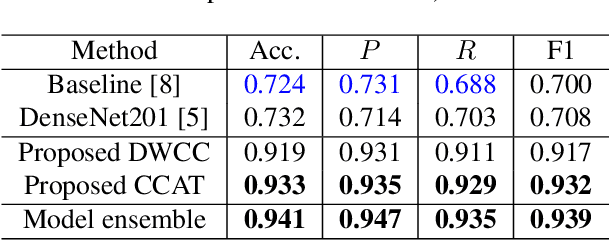


Abstract:With the massive damage in the world caused by Coronavirus Disease 2019 SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19), many related research topics have been proposed in the past two years. The Chest Computed Tomography (CT) scans are the most valuable materials to diagnose the COVID-19 symptoms. However, most schemes for COVID-19 classification of Chest CT scan is based on a single-slice level, implying that the most critical CT slice should be selected from the original CT scan volume manually. We simultaneously propose 2-D and 3-D models to predict the COVID-19 of CT scan to tickle this issue. In our 2-D model, we introduce the Deep Wilcoxon signed-rank test (DWCC) to determine the importance of each slice of a CT scan to overcome the issue mentioned previously. Furthermore, a Convolutional CT scan-Aware Transformer (CCAT) is proposed to discover the context of the slices fully. The frame-level feature is extracted from each CT slice based on any backbone network and followed by feeding the features to our within-slice-Transformer (WST) to discover the context information in the pixel dimension. The proposed Between-Slice-Transformer (BST) is used to aggregate the extracted spatial-context features of every CT slice. A simple classifier is then used to judge whether the Spatio-temporal features are COVID-19 or non-COVID-19. The extensive experiments demonstrated that the proposed CCAT and DWCC significantly outperform the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge