Mehdi Fatan
3M-TRANSFORMER: A Multi-Stage Multi-Stream Multimodal Transformer for Embodied Turn-Taking Prediction
Nov 01, 2023Abstract:Predicting turn-taking in multiparty conversations has many practical applications in human-computer/robot interaction. However, the complexity of human communication makes it a challenging task. Recent advances have shown that synchronous multi-perspective egocentric data can significantly improve turn-taking prediction compared to asynchronous, single-perspective transcriptions. Building on this research, we propose a new multimodal transformer-based architecture for predicting turn-taking in embodied, synchronized multi-perspective data. Our experimental results on the recently introduced EgoCom dataset show a substantial performance improvement of up to 14.01% on average compared to existing baselines and alternative transformer-based approaches. The source code, and the pre-trained models of our 3M-Transformer will be available upon acceptance.
Survey on Reliable Deep Learning-Based Person Re-Identification Models: Are We There Yet?
Apr 30, 2020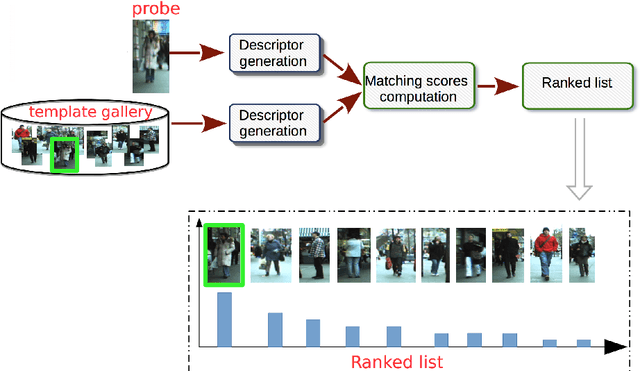
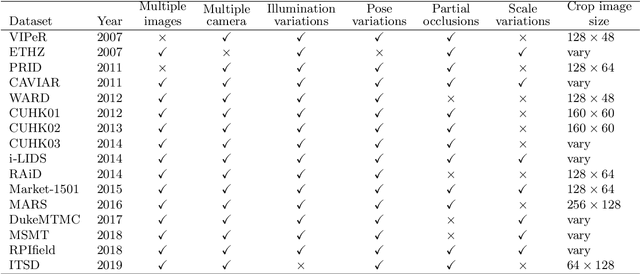
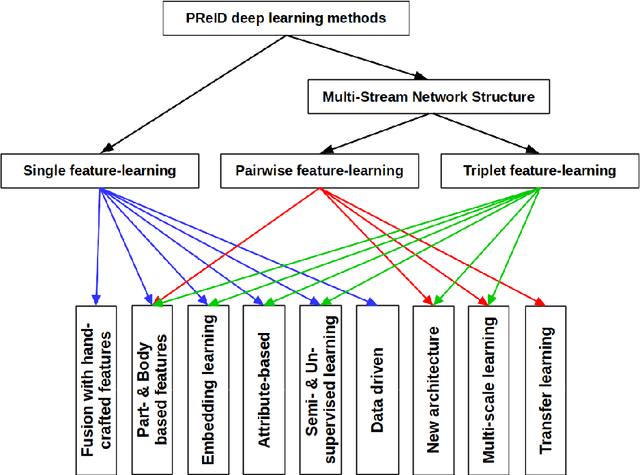
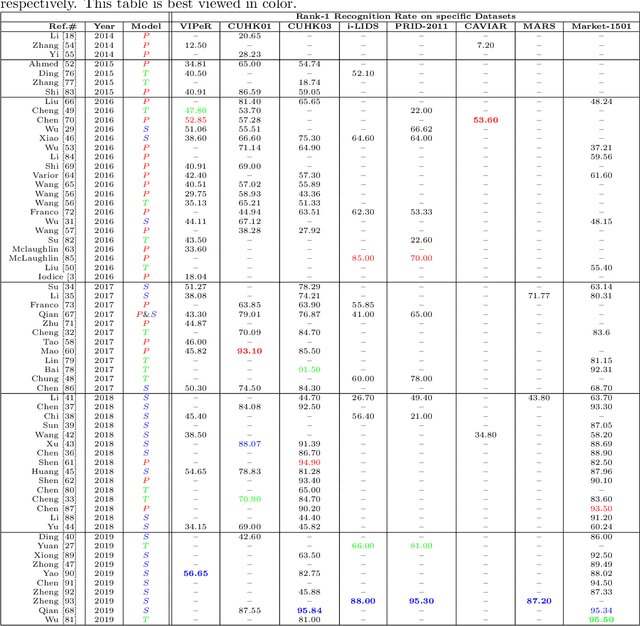
Abstract:Intelligent video-surveillance (IVS) is currently an active research field in computer vision and machine learning and provides useful tools for surveillance operators and forensic video investigators. Person re-identification (PReID) is one of the most critical problems in IVS, and it consists of recognizing whether or not an individual has already been observed over a camera in a network. Solutions to PReID have myriad applications including retrieval of video-sequences showing an individual of interest or even pedestrian tracking over multiple camera views. Different techniques have been proposed to increase the performance of PReID in the literature, and more recently researchers utilized deep neural networks (DNNs) given their compelling performance on similar vision problems and fast execution at test time. Given the importance and wide range of applications of re-identification solutions, our objective herein is to discuss the work carried out in the area and come up with a survey of state-of-the-art DNN models being used for this task. We present descriptions of each model along with their evaluation on a set of benchmark datasets. Finally, we show a detailed comparison among these models, which are followed by some discussions on their limitations that can work as guidelines for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge