Md. Saif Hassan Onim
Detection of Physiological Data Tampering Attacks with Quantum Machine Learning
Feb 09, 2025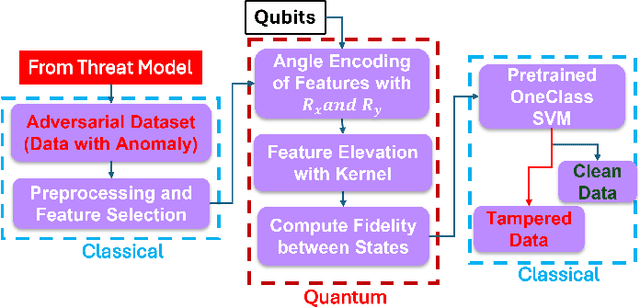
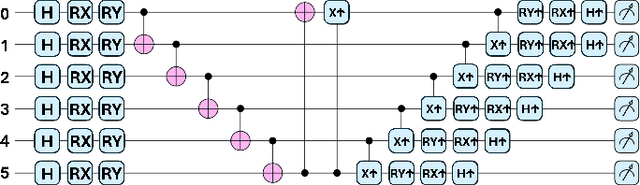
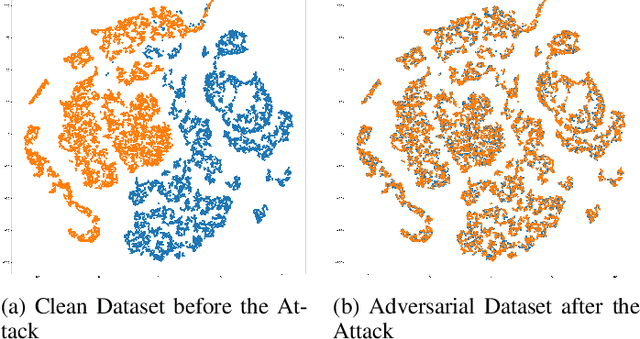
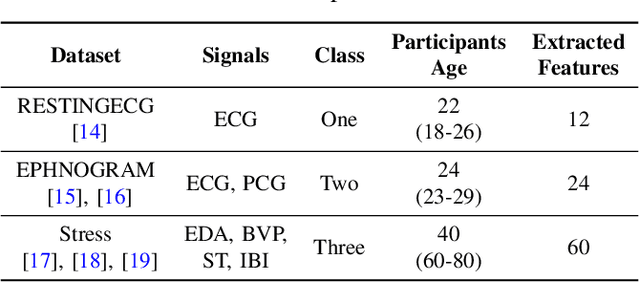
Abstract:The widespread use of cloud-based medical devices and wearable sensors has made physiological data susceptible to tampering. These attacks can compromise the reliability of healthcare systems which can be critical and life-threatening. Detection of such data tampering is of immediate need. Machine learning has been used to detect anomalies in datasets but the performance of Quantum Machine Learning (QML) is still yet to be evaluated for physiological sensor data. Thus, our study compares the effectiveness of QML for detecting physiological data tampering, focusing on two types of white-box attacks: data poisoning and adversarial perturbation. The results show that QML models are better at identifying label-flipping attacks, achieving accuracy rates of 75%-95% depending on the data and attack severity. This superior performance is due to the ability of quantum algorithms to handle complex and high-dimensional data. However, both QML and classical models struggle to detect more sophisticated adversarial perturbation attacks, which subtly alter data without changing its statistical properties. Although QML performed poorly against this attack with around 45%-65% accuracy, it still outperformed classical algorithms in some cases.
Anomaly Detection for Real-World Cyber-Physical Security using Quantum Hybrid Support Vector Machines
Sep 08, 2024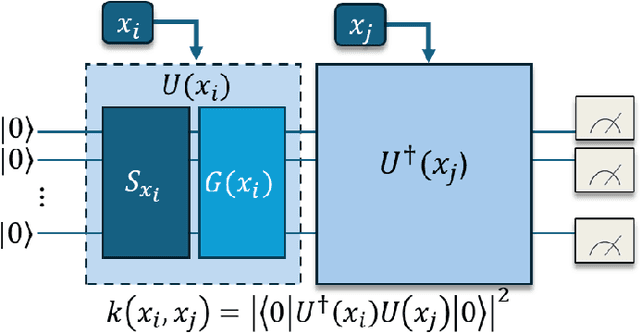
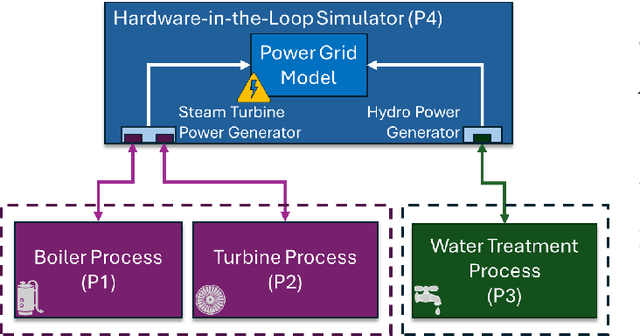
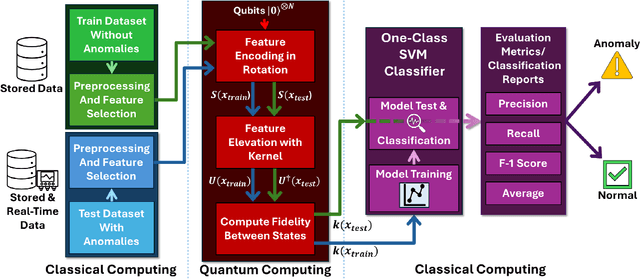
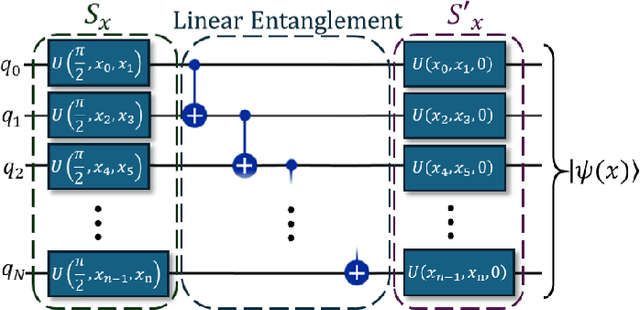
Abstract:Cyber-physical control systems are critical infrastructures designed around highly responsive feedback loops that are measured and manipulated by hundreds of sensors and controllers. Anomalous data, such as from cyber-attacks, greatly risk the safety of the infrastructure and human operators. With recent advances in the quantum computing paradigm, the application of quantum in anomaly detection can greatly improve identification of cyber-attacks in physical sensor data. In this paper, we explore the use of strong pre-processing methods and a quantum-hybrid Support Vector Machine (SVM) that takes advantage of fidelity in parameterized quantum circuits to efficiently and effectively flatten extremely high dimensional data. Our results show an F-1 Score of 0.86 and accuracy of 87% on the HAI CPS dataset using an 8-qubit, 16-feature quantum kernel, performing equally to existing work and 14% better than its classical counterpart.
A Transfer-Learning Based Ensemble Architecture for ECG Signal Classification
Jun 21, 2022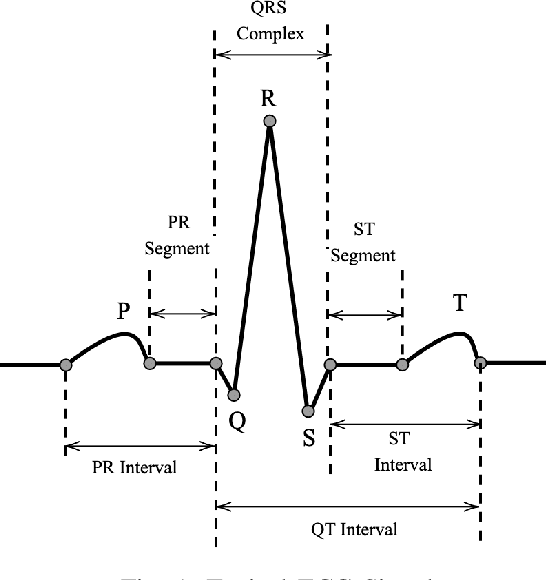
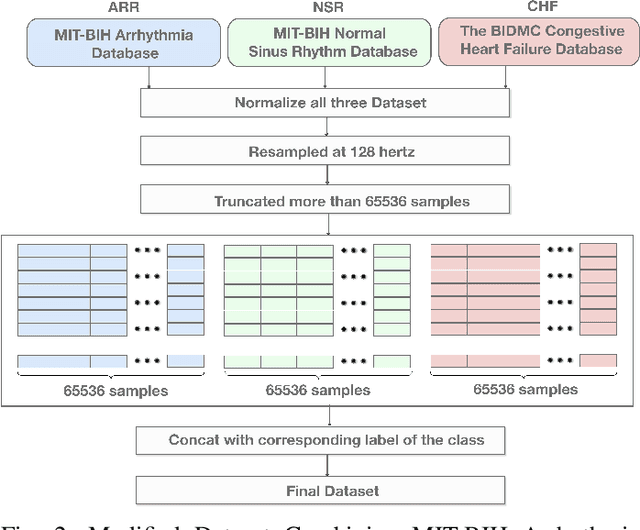
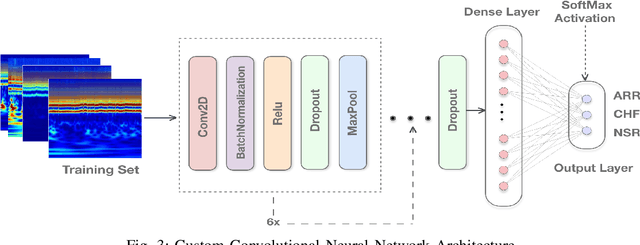
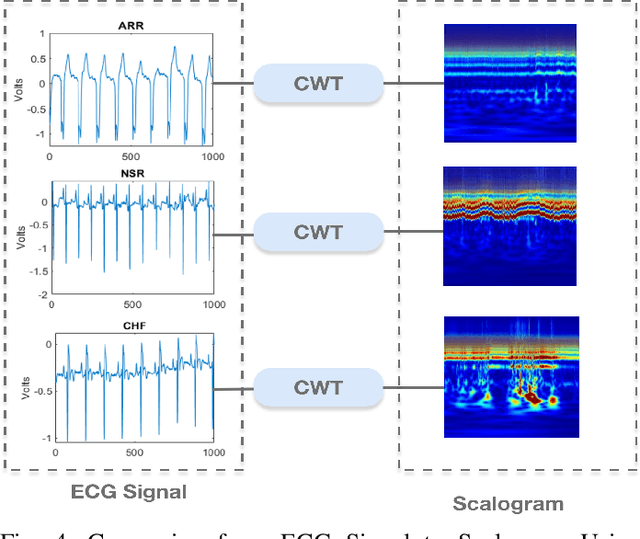
Abstract:Manual interpretation and classification of ECG signals lack both accuracy and reliability. These continuous time-series signals are more effective when represented as an image for CNN-based classification. A continuous Wavelet transform filter is used here to get corresponding images. In achieving the best result generic CNN architectures lack sufficient accuracy and also have a higher run-time. To address this issue, we propose an ensemble method of transfer learning-based models to classify ECG signals. In our work, two modified VGG-16 models and one InceptionResNetV2 model with added feature extracting layers and ImageNet weights are working as the backbone. After ensemble, we report an increase of 6.36% accuracy than previous MLP-based algorithms. After 5-fold cross-validation with the Physionet dataset, our model reaches an accuracy of 99.98%.
A Combined PCA-MLP Network for Early Breast Cancer Detection
Jun 18, 2022
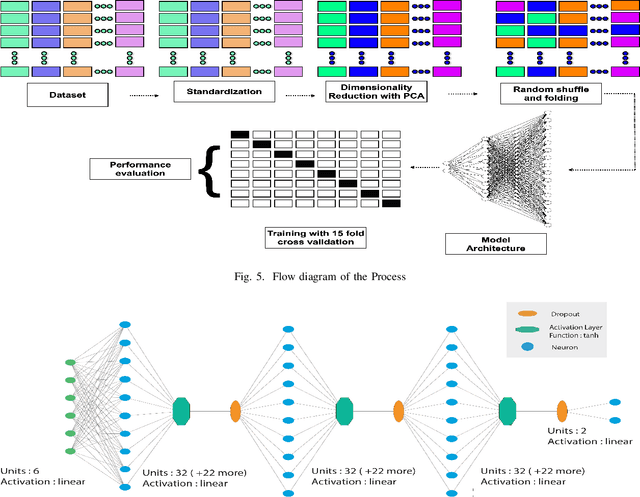
Abstract:Breast cancer is the second most responsible for all cancer types and has been the cause of numerous deaths over the years, especially among women. Any improvisation of the existing diagnosis system for the detection of cancer can contribute to minimizing the death ratio. Moreover, cancer detection at an early stage has recently been a prime research area in the scientific community to enhance the survival rate. Proper choice of machine learning tools can ensure early-stage prognosis with high accuracy. In this paper, we have studied different machine learning algorithms to detect whether a patient is likely to face breast cancer or not. Due to the implicit behavior of early-stage features, we have implemented a multilayer perception model with the integration of PCA and suggested it to be more viable than other detection algorithms. Our 4 layers MLP-PCA network has obtained the best accuracy of 100% with a mean of 90.48% accuracy on the BCCD dataset.
BLPnet: A new DNN model and Bengali OCR engine for Automatic License Plate Recognition
Feb 18, 2022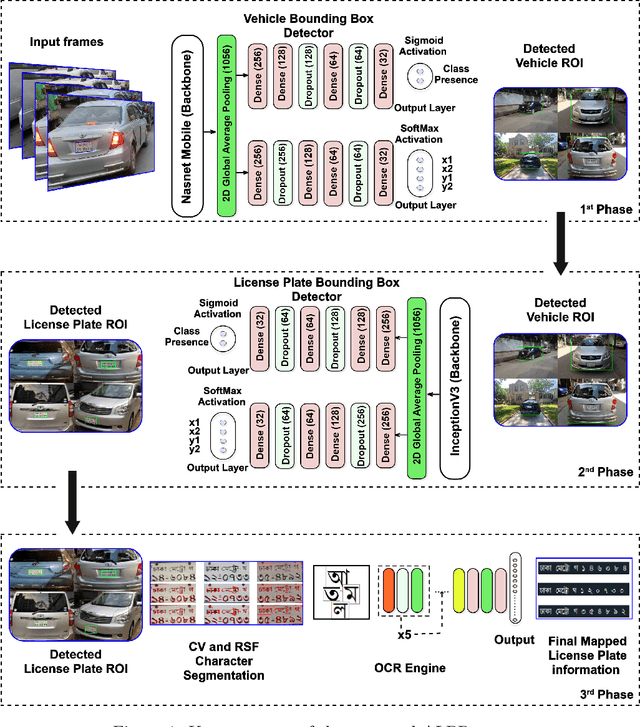
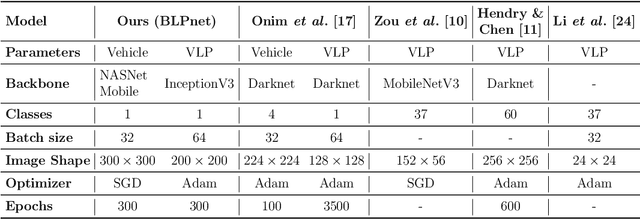
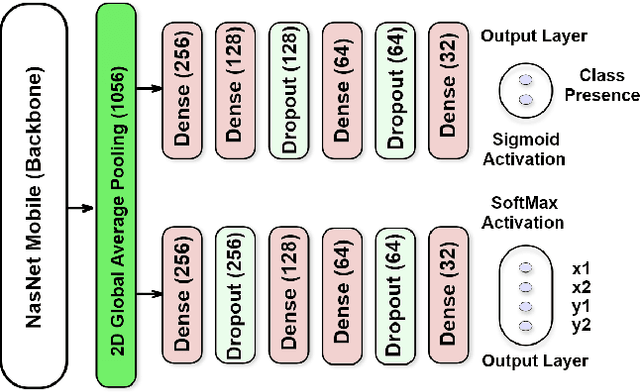
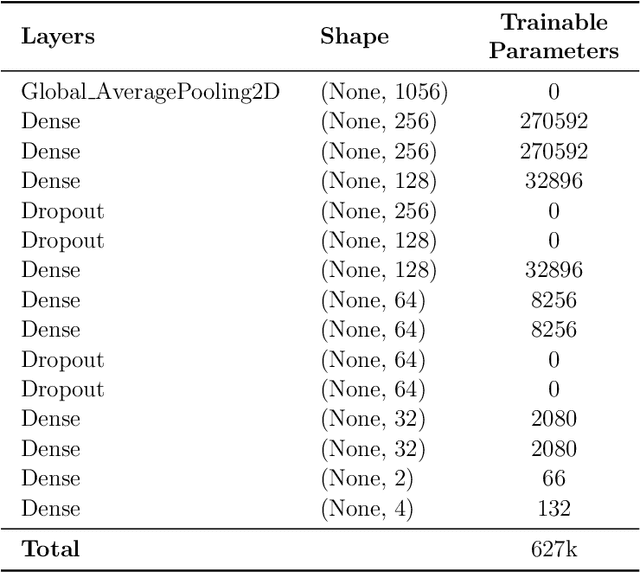
Abstract:The development of the Automatic License Plate Recognition (ALPR) system has received much attention for the English license plate. However, despite being the sixth largest population around the world, no significant progress can be tracked in the Bengali language countries or states for the ALPR system addressing their more alarming traffic management with inadequate road-safety measures. This paper reports a computationally efficient and reasonably accurate Automatic License Plate Recognition (ALPR) system for Bengali characters with a new end-to-end DNN model that we call Bengali License Plate Network(BLPnet). The cascaded architecture for detecting vehicle regions prior to vehicle license plate (VLP) in the model is proposed to eliminate false positives resulting in higher detection accuracy of VLP. Besides, a lower set of trainable parameters is considered for reducing the computational cost making the system faster and more compatible for a real-time application. With a Computational Neural Network (CNN)based new Bengali OCR engine and word-mapping process, the model is characters rotation invariant, and can readily extract, detect and output the complete license plate number of a vehicle. The model feeding with17 frames per second (fps) on real-time video footage can detect a vehicle with the Mean Squared Error (MSE) of 0.0152, and the mean license plate character recognition accuracy of 95%. While compared to the other models, an improvement of 5% and 20% were recorded for the BLPnetover the prominent YOLO-based ALPR model and the Tesseract model for the number-plate detection accuracy and time requirement, respectively.
Modelling Lips-State Detection Using CNN for Non-Verbal Communications
Dec 11, 2021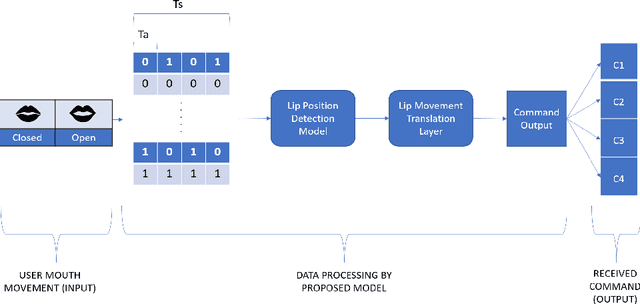
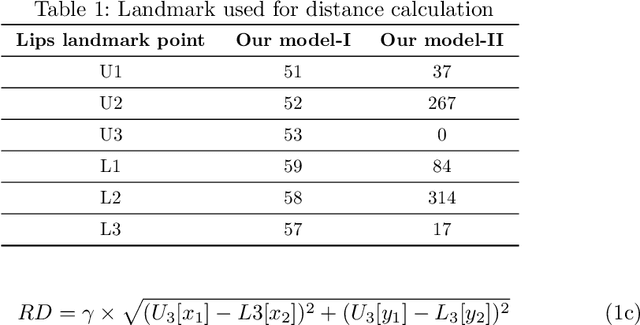
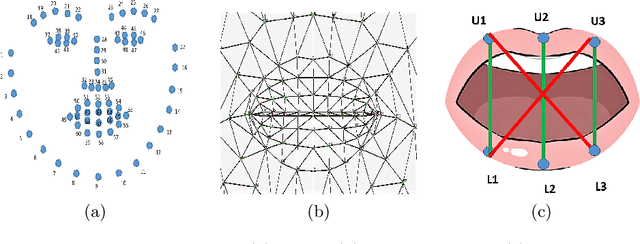
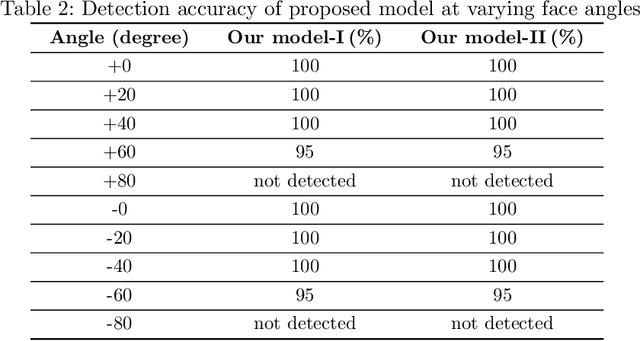
Abstract:Vision-based deep learning models can be promising for speech-and-hearing-impaired and secret communications. While such non-verbal communications are primarily investigated with hand-gestures and facial expressions, no research endeavour is tracked so far for the lips state (i.e., open/close)-based interpretation/translation system. In support of this development, this paper reports two new Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) models for lips state detection. Building upon two prominent lips landmark detectors, DLIB and MediaPipe, we simplify lips-state model with a set of six key landmarks, and use their distances for the lips state classification. Thereby, both the models are developed to count the opening and closing of lips and thus, they can classify a symbol with the total count. Varying frame-rates, lips-movements and face-angles are investigated to determine the effectiveness of the models. Our early experimental results demonstrate that the model with DLIB is relatively slower in terms of an average of 6 frames per second (FPS) and higher average detection accuracy of 95.25%. In contrast, the model with MediaPipe offers faster landmark detection capability with an average FPS of 20 and detection accuracy of 94.4%. Both models thus could effectively interpret the lips state for non-verbal semantics into a natural language.
LULC classification by semantic segmentation of satellite images using FastFCN
Dec 03, 2020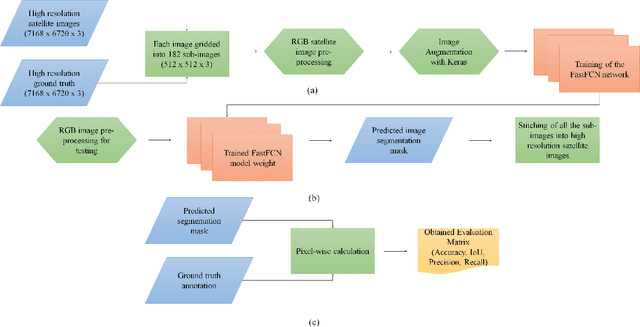
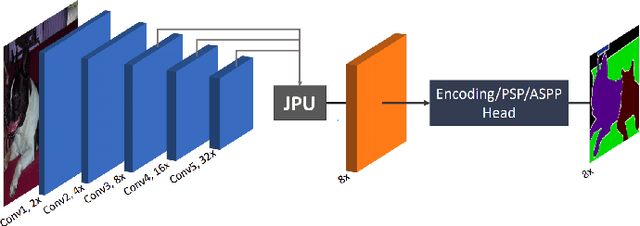
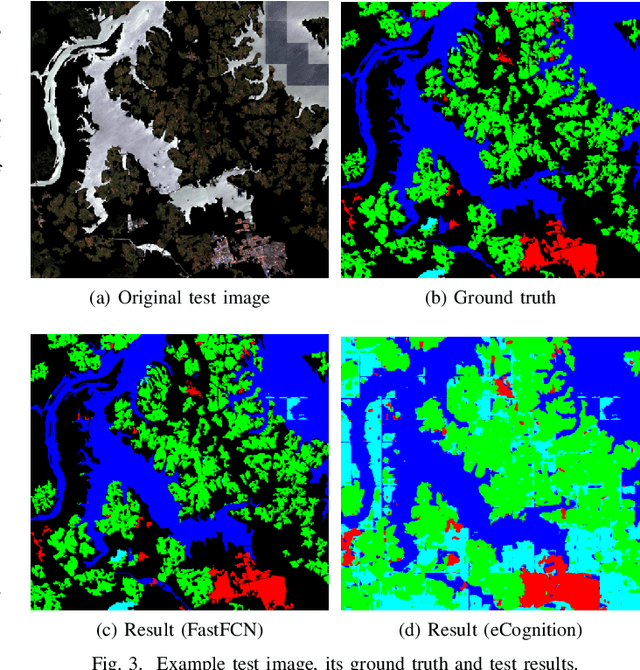
Abstract:This paper analyses how well a Fast Fully Convolutional Network (FastFCN) semantically segments satellite images and thus classifies Land Use/Land Cover(LULC) classes. Fast-FCN was used on Gaofen-2 Image Dataset (GID-2) to segment them in five different classes: BuiltUp, Meadow, Farmland, Water and Forest. The results showed better accuracy (0.93), precision (0.99), recall (0.98) and mean Intersection over Union (mIoU)(0.97) than other approaches like using FCN-8 or eCognition, a readily available software. We presented a comparison between the results. We propose FastFCN to be both faster and more accurate automated method than other existing methods for LULC classification.
Traffic Surveillance using Vehicle License Plate Detection and Recognition in Bangladesh
Dec 03, 2020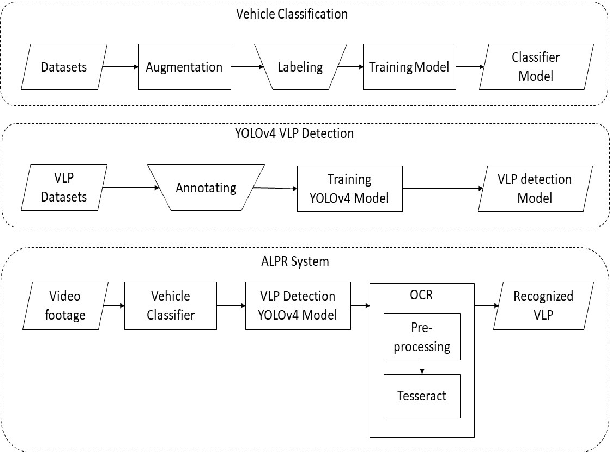


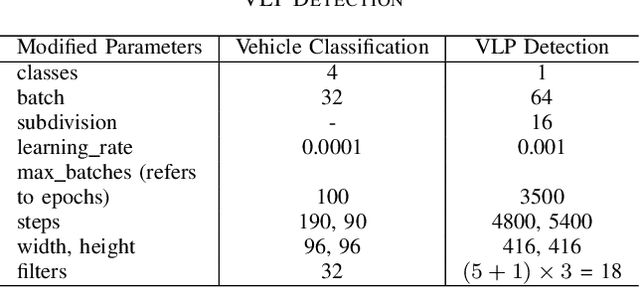
Abstract:Computer vision coupled with Deep Learning (DL) techniques bring out a substantial prospect in the field of traffic control, monitoring and law enforcing activities. This paper presents a YOLOv4 object detection model in which the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is trained and tuned for detecting the license plate of the vehicles of Bangladesh and recognizing characters using tesseract from the detected license plates. Here we also present a Graphical User Interface (GUI) based on Tkinter, a python package. The license plate detection model is trained with mean average precision (mAP) of 90.50% and performed in a single TESLA T4 GPU with an average of 14 frames per second (fps) on real time video footage.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge