Md. Rakibul Islam
Jana
A Lightweight and Explainable Vision-Language Framework for Crop Disease Visual Question Answering
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Visual question answering for crop disease analysis requires accurate visual understanding and reliable language generation. This work presents a lightweight vision-language framework for crop and disease identification from leaf images. The proposed approach combines a Swin Transformer vision encoder with sequence-to-sequence language decoders. A two-stage training strategy is adopted to improve visual representation learning and cross-modal alignment. The model is evaluated on a large-scale crop disease dataset using classification and natural language generation metrics. Experimental results show high accuracy for both crop and disease identification. The framework also achieves strong performance on BLEU, ROUGE and BERTScore. Our proposed models outperform large-scale vision-language baselines while using significantly fewer parameters. Explainability is assessed using Grad-CAM and token-level attribution. Qualitative results demonstrate robust performance under diverse user-driven queries. These findings highlight the effectiveness of task-specific visual pretraining for crop disease visual question answering.
Detecting AI-Generated Paraphrases in Bengali: A Comparative Study of Zero-Shot and Fine-Tuned Transformers
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) can produce text that closely resembles human writing. This capability raises concerns about misuse, including disinformation and content manipulation. Detecting AI-generated text is essential to maintain authenticity and prevent malicious applications. Existing research has addressed detection in multiple languages, but the Bengali language remains largely unexplored. Bengali's rich vocabulary and complex structure make distinguishing human-written and AI-generated text particularly challenging. This study investigates five transformer-based models: XLMRoBERTa-Large, mDeBERTaV3-Base, BanglaBERT-Base, IndicBERT-Base and MultilingualBERT-Base. Zero-shot evaluation shows that all models perform near chance levels (around 50% accuracy) and highlight the need for task-specific fine-tuning. Fine-tuning significantly improves performance, with XLM-RoBERTa, mDeBERTa and MultilingualBERT achieving around 91% on both accuracy and F1-score. IndicBERT demonstrates comparatively weaker performance, indicating limited effectiveness in fine-tuning for this task. This work advances AI-generated text detection in Bengali and establishes a foundation for building robust systems to counter AI-generated content.
BeHGAN: Bengali Handwritten Word Generation from Plain Text Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Handwritten Text Recognition (HTR) is a well-established research area. In contrast, Handwritten Text Generation (HTG) is an emerging field with significant potential. This task is challenging due to the variation in individual handwriting styles. A large and diverse dataset is required to generate realistic handwritten text. However, such datasets are difficult to collect and are not readily available. Bengali is the fifth most spoken language in the world. While several studies exist for languages such as English and Arabic, Bengali handwritten text generation has received little attention. To address this gap, we propose a method for generating Bengali handwritten words. We developed and used a self-collected dataset of Bengali handwriting samples. The dataset includes contributions from approximately five hundred individuals across different ages and genders. All images were pre-processed to ensure consistency and quality. Our approach demonstrates the ability to produce diverse handwritten outputs from input plain text. We believe this work contributes to the advancement of Bengali handwriting generation and can support further research in this area.
FUSE: Unifying Spectral and Semantic Cues for Robust AI-Generated Image Detection
Dec 25, 2025



Abstract:The fast evolution of generative models has heightened the demand for reliable detection of AI-generated images. To tackle this challenge, we introduce FUSE, a hybrid system that combines spectral features extracted through Fast Fourier Transform with semantic features obtained from the CLIP's Vision encoder. The features are fused into a joint representation and trained progressively in two stages. Evaluations on GenImage, WildFake, DiTFake, GPT-ImgEval and Chameleon datasets demonstrate strong generalization across multiple generators. Our FUSE (Stage 1) model demonstrates state-of-the-art results on the Chameleon benchmark. It also attains 91.36% mean accuracy on the GenImage dataset, 88.71% accuracy across all tested generators, and a mean Average Precision of 94.96%. Stage 2 training further improves performance for most generators. Unlike existing methods, which often perform poorly on high-fidelity images in Chameleon, our approach maintains robustness across diverse generators. These findings highlight the benefits of integrating spectral and semantic features for generalized detection of images generated by AI.
Zero-Shot to Zero-Lies: Detecting Bengali Deepfake Audio through Transfer Learning
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:The rapid growth of speech synthesis and voice conversion systems has made deepfake audio a major security concern. Bengali deepfake detection remains largely unexplored. In this work, we study automatic detection of Bengali audio deepfakes using the BanglaFake dataset. We evaluate zeroshot inference with several pretrained models. These include Wav2Vec2-XLSR-53, Whisper, PANNsCNN14, WavLM and Audio Spectrogram Transformer. Zero-shot results show limited detection ability. The best model, Wav2Vec2-XLSR-53, achieves 53.80% accuracy, 56.60% AUC and 46.20% EER. We then f ine-tune multiple architectures for Bengali deepfake detection. These include Wav2Vec2-Base, LCNN, LCNN-Attention, ResNet18, ViT-B16 and CNN-BiLSTM. Fine-tuned models show strong performance gains. ResNet18 achieves the highest accuracy of 79.17%, F1 score of 79.12%, AUC of 84.37% and EER of 24.35%. Experimental results confirm that fine-tuning significantly improves performance over zero-shot inference. This study provides the first systematic benchmark of Bengali deepfake audio detection. It highlights the effectiveness of f ine-tuned deep learning models for this low-resource language.
Privacy-Preserving Chest X-ray Report Generation via Multimodal Federated Learning with ViT and GPT-2
May 27, 2025Abstract:The automated generation of radiology reports from chest X-ray images holds significant promise in enhancing diagnostic workflows while preserving patient privacy. Traditional centralized approaches often require sensitive data transfer, posing privacy concerns. To address this, the study proposes a Multimodal Federated Learning framework for chest X-ray report generation using the IU-Xray dataset. The system utilizes a Vision Transformer (ViT) as the encoder and GPT-2 as the report generator, enabling decentralized training without sharing raw data. Three Federated Learning (FL) aggregation strategies: FedAvg, Krum Aggregation and a novel Loss-aware Federated Averaging (L-FedAvg) were evaluated. Among these, Krum Aggregation demonstrated superior performance across lexical and semantic evaluation metrics such as ROUGE, BLEU, BERTScore and RaTEScore. The results show that FL can match or surpass centralized models in generating clinically relevant and semantically rich radiology reports. This lightweight and privacy-preserving framework paves the way for collaborative medical AI development without compromising data confidentiality.
Vision-Language Models for Automated Chest X-ray Interpretation: Leveraging ViT and GPT-2
Jan 21, 2025



Abstract:Radiology plays a pivotal role in modern medicine due to its non-invasive diagnostic capabilities. However, the manual generation of unstructured medical reports is time consuming and prone to errors. It creates a significant bottleneck in clinical workflows. Despite advancements in AI-generated radiology reports, challenges remain in achieving detailed and accurate report generation. In this study we have evaluated different combinations of multimodal models that integrate Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing to generate comprehensive radiology reports. We employed a pretrained Vision Transformer (ViT-B16) and a SWIN Transformer as the image encoders. The BART and GPT-2 models serve as the textual decoders. We used Chest X-ray images and reports from the IU-Xray dataset to evaluate the usability of the SWIN Transformer-BART, SWIN Transformer-GPT-2, ViT-B16-BART and ViT-B16-GPT-2 models for report generation. We aimed at finding the best combination among the models. The SWIN-BART model performs as the best-performing model among the four models achieving remarkable results in almost all the evaluation metrics like ROUGE, BLEU and BERTScore.
Preference-Guided Planning: An Active Elicitation Approach
Apr 19, 2018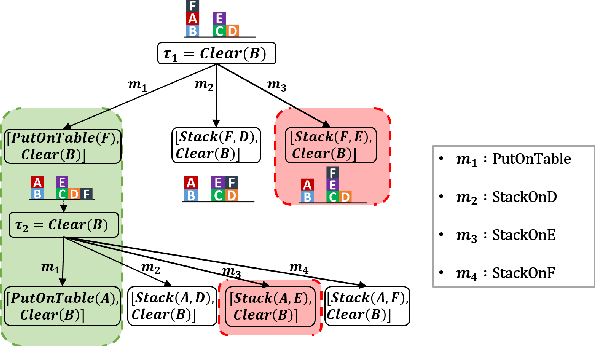
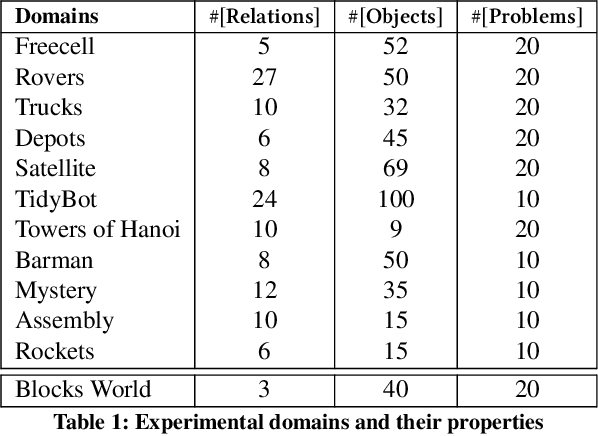

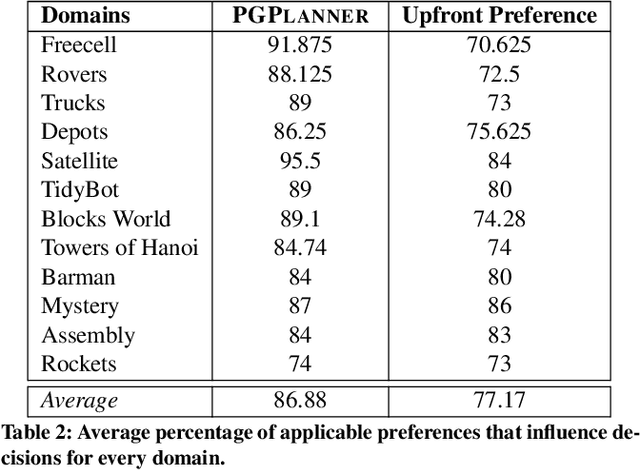
Abstract:Planning with preferences has been employed extensively to quickly generate high-quality plans. However, it may be difficult for the human expert to supply this information without knowledge of the reasoning employed by the planner and the distribution of planning problems. We consider the problem of actively eliciting preferences from a human expert during the planning process. Specifically, we study this problem in the context of the Hierarchical Task Network (HTN) planning framework as it allows easy interaction with the human. Our experimental results on several diverse planning domains show that the preferences gathered using the proposed approach improve the quality and speed of the planner, while reducing the burden on the human expert.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge