Maya Ramanath
SARCH: Multimodal Search for Archaeological Archives
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we describe a multi-modal search system designed to search old archaeological books and reports. This corpus is digitally available as scanned PDFs, but varies widely in the quality of scans. Our pipeline, designed for multi-modal archaeological documents, extracts and indexes text, images (classified into maps, photos, layouts, and others), and tables. We evaluated different retrieval strategies, including keyword-based search, embedding-based models, and a hybrid approach that selects optimal results from both modalities. We report and analyze our preliminary results and discuss future work in this exciting vertical.
Tracking entities in technical procedures -- a new dataset and baselines
Apr 15, 2021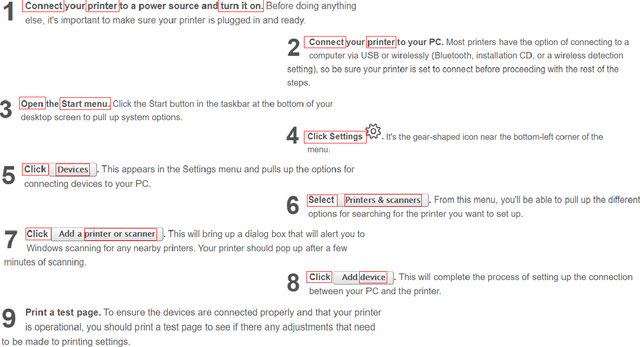

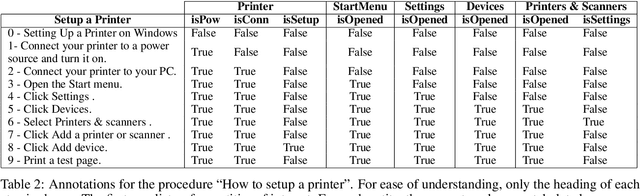
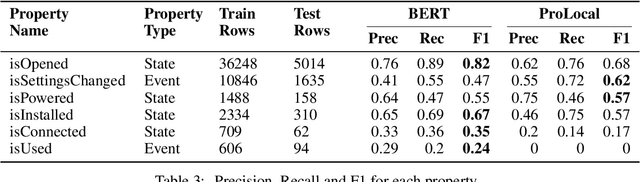
Abstract:We introduce TechTrack, a new dataset for tracking entities in technical procedures. The dataset, prepared by annotating open domain articles from WikiHow, consists of 1351 procedures, e.g., "How to connect a printer", identifies more than 1200 unique entities with an average of 4.7 entities per procedure. We evaluate the performance of state-of-the-art models on the entity-tracking task and find that they are well below the human annotation performance. We describe how TechTrack can be used to take forward the research on understanding procedures from temporal texts.
IterefinE: Iterative KG Refinement Embeddings using Symbolic Knowledge
Jun 03, 2020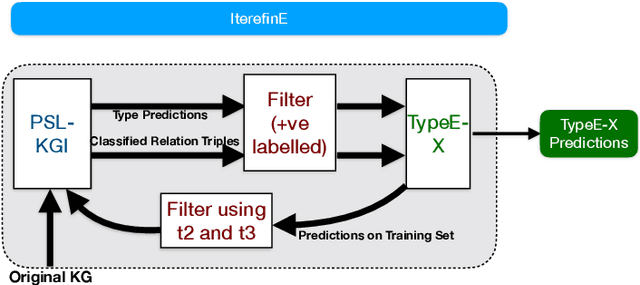
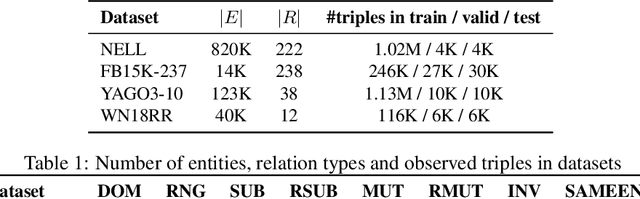
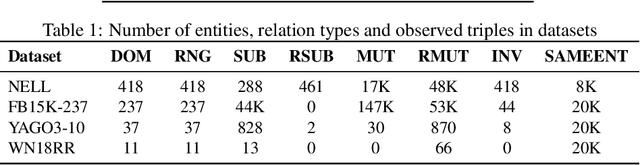
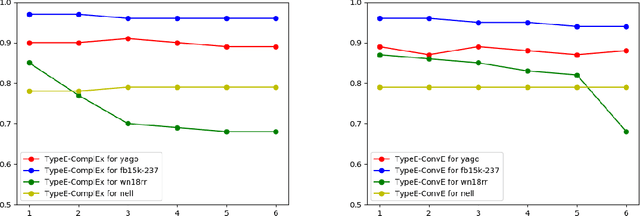
Abstract:Knowledge Graphs (KGs) extracted from text sources are often noisy and lead to poor performance in downstream application tasks such as KG-based question answering.While much of the recent activity is focused on addressing the sparsity of KGs by using embeddings for inferring new facts, the issue of cleaning up of noise in KGs through KG refinement task is not as actively studied. Most successful techniques for KG refinement make use of inference rules and reasoning over ontologies. Barring a few exceptions, embeddings do not make use of ontological information, and their performance in KG refinement task is not well understood. In this paper, we present a KG refinement framework called IterefinE which iteratively combines the two techniques - one which uses ontological information and inferences rules, PSL-KGI, and the KG embeddings such as ComplEx and ConvE which do not. As a result, IterefinE is able to exploit not only the ontological information to improve the quality of predictions, but also the power of KG embeddings which (implicitly) perform longer chains of reasoning. The IterefinE framework, operates in a co-training mode and results in explicit type-supervised embedding of the refined KG from PSL-KGI which we call as TypeE-X. Our experiments over a range of KG benchmarks show that the embeddings that we produce are able to reject noisy facts from KG and at the same time infer higher quality new facts resulting in up to 9% improvement of overall weighted F1 score
TeKnowbase: Towards Construction of a Knowledge-base of Technical Concepts
Dec 15, 2016


Abstract:In this paper, we describe the construction of TeKnowbase, a knowledge-base of technical concepts in computer science. Our main information sources are technical websites such as Webopedia and Techtarget as well as Wikipedia and online textbooks. We divide the knowledge-base construction problem into two parts -- the acquisition of entities and the extraction of relationships among these entities. Our knowledge-base consists of approximately 100,000 triples. We conducted an evaluation on a sample of triples and report an accuracy of a little over 90\%. We additionally conducted classification experiments on StackOverflow data with features from TeKnowbase and achieved improved classification accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge