Maximo Morales-Cespedes
Angle diversity receiver as a key enabler for reliable ORIS-based Visible Light Communication
May 15, 2025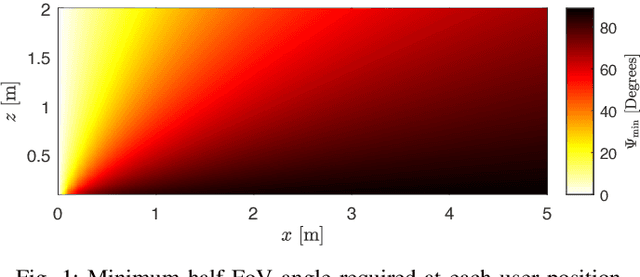
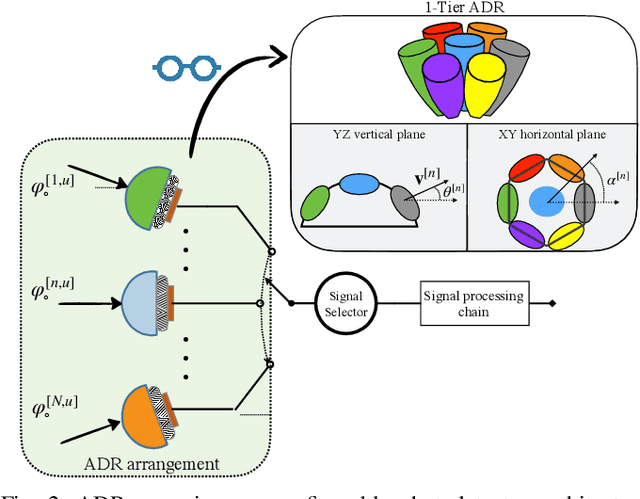
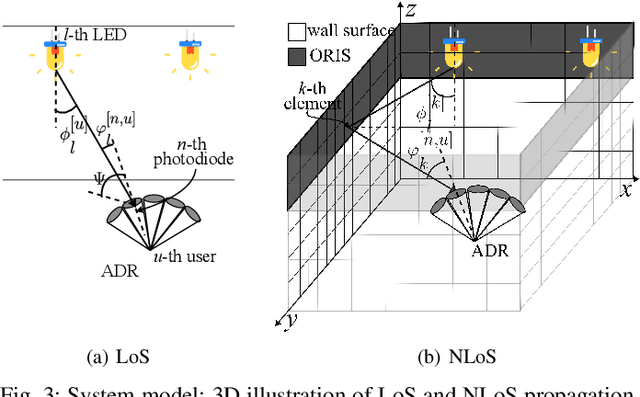
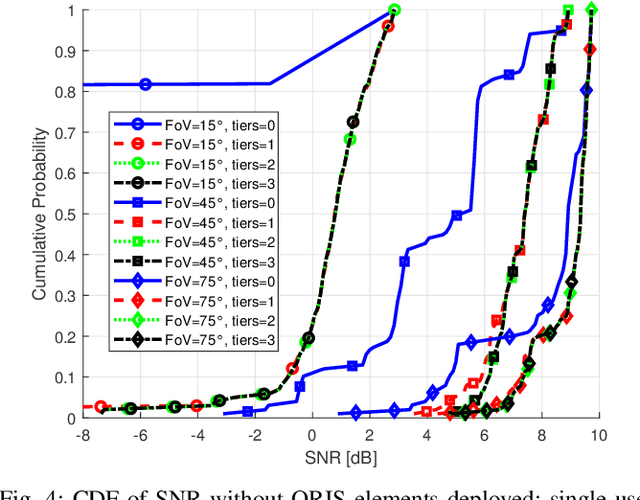
Abstract:Visible Light Communication (VLC) offers a promising solution to satisfy the increasing demand for wireless data. However, link blockages remain a significant challenge. This paper addresses this issue by investigating the combined use of angle diversity receivers (ADRs) and optical reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (ORISs) in multiuser VLC systems. We consider ORIS elements as small movable mirrors. We demonstrate the complementarity of ADR and ORIS in mitigating link blockages, as well as the advantages of using a larger number of ORIS elements due to the increased field-of-view (FoV) at the receiver enabled by the ADR. An optimization algorithm is proposed to maximize the minimum signal-to-noise power ratio (SNR) to deploy a fair communication network. Numerical results show that integrating ADR and ORIS significantly enhances VLC communication performance, achieving an SNR gain of up to 30 dB compared to a system without ORIS, and mitigating communication outages produced by link blockages or out-of-FoV received signals. We also prove that an ADR with a single tier of photodiodes is sufficient to complement ORIS-assisted VLC.
Resource Allocation in Laser-based Optical Wireless Cellular Networks
Nov 27, 2021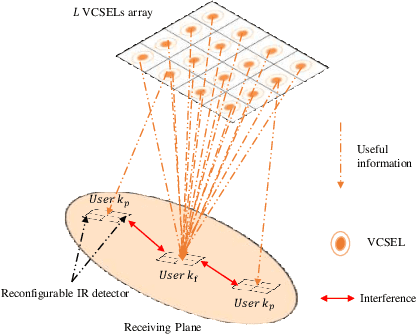
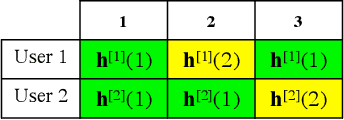
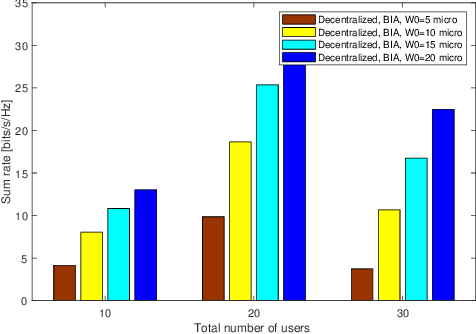
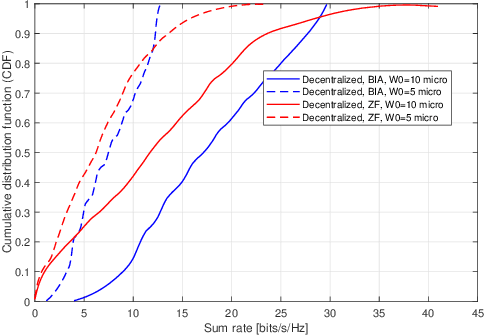
Abstract:Optical wireless communication provides data transmission at high speeds which can satisfy the increasing demands for connecting a massive number of devices to the Internet. In this paper, vertical-cavity surface-emitting(VCSEL) lasers are used as transmitters due to their high modulation speed and energy efficiency. However, a high number of VCSEL lasers is required to ensure coverage where each laser source illuminates a confined area. Therefore, multiple users are classified into different sets according to their connectivity. Given this point, a transmission scheme that uses blind interference alignment (BIA) is implemented to manage the interference in the laser-based network. In addition, an optimization problem is formulated to maximize the utility sum rate taking into consideration the classification of the users. To solve this problem, a decentralized algorithm is proposed where the main problem is divided into sub-problems, each can be solved independently avoiding complexity. The results demonstrate the optimality of the decentralized algorithm where a sub-optimal solution is provided. Finally, it is shown that BIA can provide high performance in laser-based networks compared with zero forcing (ZF) transmit precoding scheme.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge