Maxim Romanov
Studying the History of the Arabic Language: Language Technology and a Large-Scale Historical Corpus
Sep 11, 2018



Abstract:Arabic is a widely-spoken language with a long and rich history, but existing corpora and language technology focus mostly on modern Arabic and its varieties. Therefore, studying the history of the language has so far been mostly limited to manual analyses on a small scale. In this work, we present a large-scale historical corpus of the written Arabic language, spanning 1400 years. We describe our efforts to clean and process this corpus using Arabic NLP tools, including the identification of reused text. We study the history of the Arabic language using a novel automatic periodization algorithm, as well as other techniques. Our findings confirm the established division of written Arabic into Modern Standard and Classical Arabic, and confirm other established periodizations, while suggesting that written Arabic may be divisible into still further periods of development.
Important New Developments in Arabographic Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
Mar 28, 2017



Abstract:The OpenITI team has achieved Optical Character Recognition (OCR) accuracy rates for classical Arabic-script texts in the high nineties. These numbers are based on our tests of seven different Arabic-script texts of varying quality and typefaces, totaling over 7,000 lines. These accuracy rates not only represent a distinct improvement over the actual accuracy rates of the various proprietary OCR options for classical Arabic-script texts, but, equally important, they are produced using an open-source OCR software, thus enabling us to make this Arabic-script OCR technology freely available to the broader Islamic, Persian, and Arabic Studies communities.
Shamela: A Large-Scale Historical Arabic Corpus
Dec 28, 2016
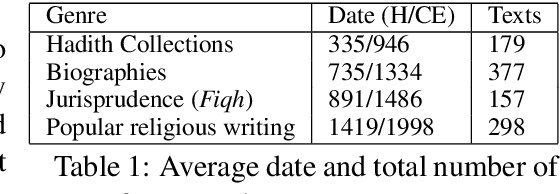


Abstract:Arabic is a widely-spoken language with a rich and long history spanning more than fourteen centuries. Yet existing Arabic corpora largely focus on the modern period or lack sufficient diachronic information. We develop a large-scale, historical corpus of Arabic of about 1 billion words from diverse periods of time. We clean this corpus, process it with a morphological analyzer, and enhance it by detecting parallel passages and automatically dating undated texts. We demonstrate its utility with selected case-studies in which we show its application to the digital humanities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge