Matthias Stierle
A Technique for Determining Relevance Scores of Process Activities using Graph-based Neural Networks
Aug 07, 2020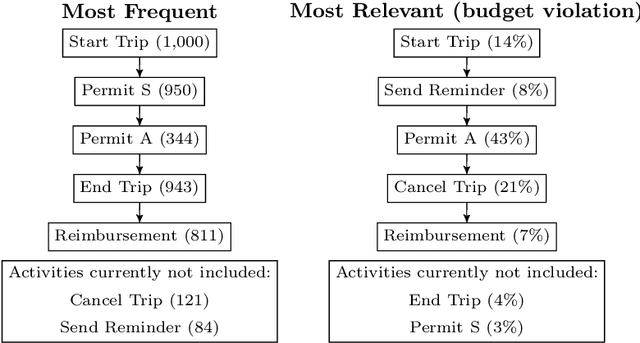
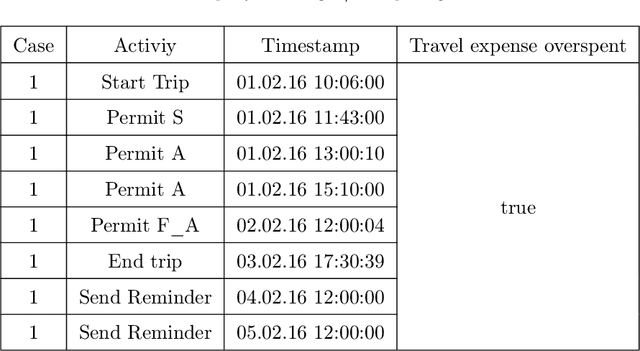
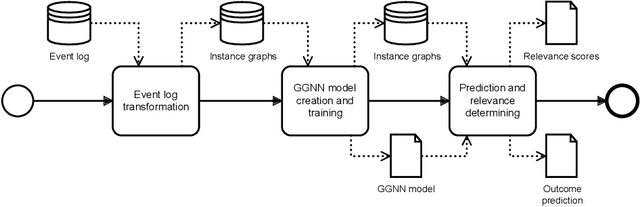
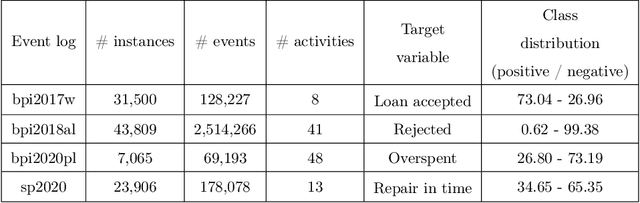
Abstract:Process models generated through process mining depict the as-is state of a process. Through annotations with metrics such as the frequency or duration of activities, these models provide generic information to the process analyst. To improve business processes with respect to performance measures, process analysts require further guidance from the process model. In this study, we design Graph Relevance Miner (GRM), a technique based on graph neural networks, to determine the relevance scores for process activities with respect to performance measures. Annotating process models with such relevance scores facilitates a problem-focused analysis of the business process, placing these problems at the centre of the analysis. We quantitatively evaluate the predictive quality of our technique using four datasets from different domains, to demonstrate the faithfulness of the relevance scores. Furthermore, we present the results of a case study, which highlight the utility of the technique for organisations. Our work has important implications both for research and business applications, because process model-based analyses feature shortcomings that need to be urgently addressed to realise successful process mining at an enterprise level.
Cause vs. Effect in Context-Sensitive Prediction of Business Process Instances
Jul 15, 2020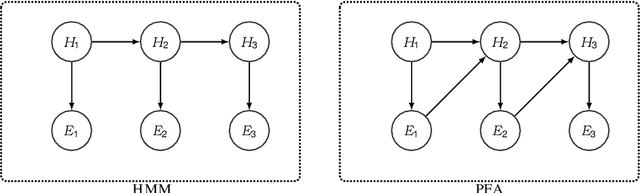
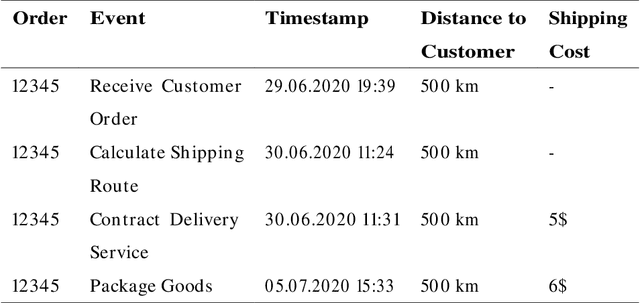
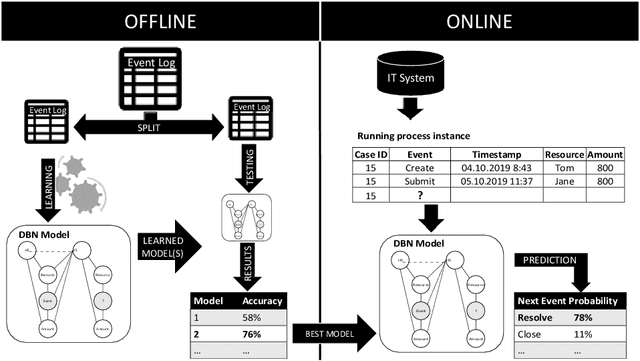
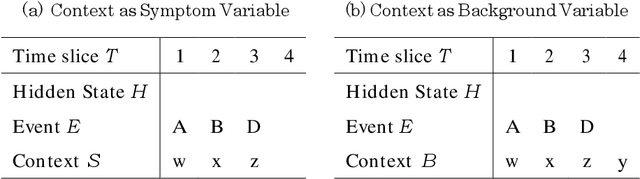
Abstract:Predicting undesirable events during the execution of a business process instance provides the process participants with an opportunity to intervene and keep the process aligned with its goals. Few approaches for tackling this challenge consider a multi-perspective view, where the flow perspective of the process is combined with its surrounding context. Given the many sources of data in today's world, context can vary widely and have various meanings. This paper addresses the issue of context being cause or effect of the next event and its impact on next event prediction. We leverage previous work on probabilistic models to develop a Dynamic Bayesian Network technique. Probabilistic models are considered comprehensible and they allow the end-user and his or her understanding of the domain to be involved in the prediction. Our technique models context attributes that have either a cause or effect relationship towards the event. We evaluate our technique with two real-life data sets and benchmark it with other techniques from the field of predictive process monitoring. The results show that our solution achieves superior prediction results if context information is correctly introduced into the model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge