Matthew Rodda
Camera-Pose Robust Crater Detection from Chang'e 5
Jun 07, 2024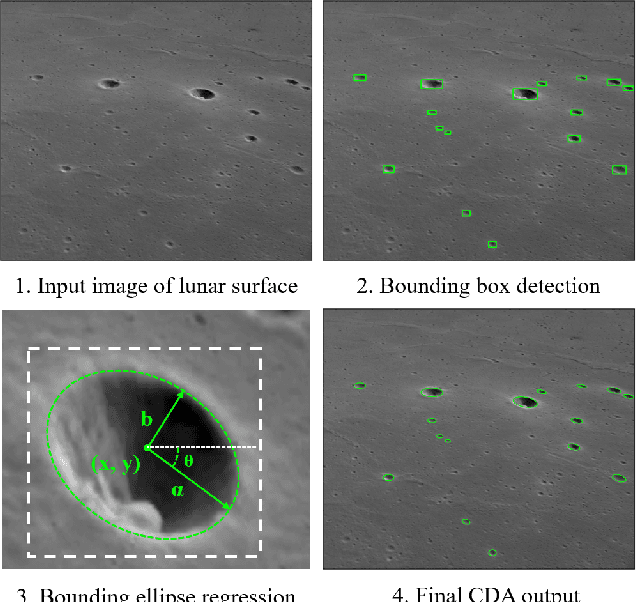


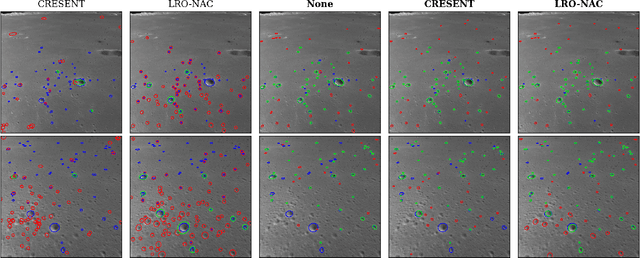
Abstract:As space missions aim to explore increasingly hazardous terrain, accurate and timely position estimates are required to ensure safe navigation. Vision-based navigation achieves this goal through correlating impact craters visible through onboard imagery with a known database to estimate a craft's pose. However, existing literature has not sufficiently evaluated crater-detection algorithm (CDA) performance from imagery containing off-nadir view angles. In this work, we evaluate the performance of Mask R-CNN for crater detection, comparing models pretrained on simulated data containing off-nadir view angles and to pretraining on real-lunar images. We demonstrate pretraining on real-lunar images is superior despite the lack of images containing off-nadir view angles, achieving detection performance of 63.1 F1-score and ellipse-regression performance of 0.701 intersection over union. This work provides the first quantitative analysis of performance of CDAs on images containing off-nadir view angles. Towards the development of increasingly robust CDAs, we additionally provide the first annotated CDA dataset with off-nadir view angles from the Chang'e 5 Landing Camera.
Board-to-Board: Evaluating Moonboard Grade Prediction Generalization
Nov 21, 2023



Abstract:Bouldering is a sport where athletes aim to climb up an obstacle using a set of defined holds called a route. Typically routes are assigned a grade to inform climbers of its difficulty and allow them to more easily track their progression. However, the variation in individual climbers technical and physical attributes and many nuances of an individual route make grading a difficult and often biased task. In this work, we apply classical and deep-learning modelling techniques to the 2016, 2017 and 2019 Moonboard datasets, achieving state of the art grade prediction performance with 0.87 MAE and 1.12 RMSE. We achieve this performance on a feature-set that does not require decomposing routes into individual moves, which is a method common in literature and introduces bias. We also demonstrate the generalization capability of this model between editions and introduce a novel vision-based method of grade prediction. While the generalization performance of these techniques is below human level performance currently, we propose these methods as a basis for future work. Such a tool could be implemented in pre-existing mobile applications and would allow climbers to better track their progress and assess new routes with reduced bias.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge